Research has revealed that having healthy gut microbes can help reduce the risk of heart disease in a mouse. A study published in the European Heart Journal shows that this could be true for humans, too.
The risk factors for heart disease are high blood cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and smoking. However, these factors are not sufficient to predict heart disease in women, in younger people, and in a few ethnic groups.
Inflammation and Heart Disease
The risk developing a heart attack or stroke is determined by measuring the hardening of arteries. This arterial stiffness isn’t very closely associated with high cholestInflammation and Heart Diseaseerol levels or smoking, but it is closely linked to inflammation. Also, inflammation is the body’s reaction to injury, but if it is too high, it can lead to several diseases, such as eczema and arthritis.
Studies have found that more the intensity of inflammation, the higher is risk of developing heart diseases and atherosclerosis. Several clinical studies have revealed that inflammation is one of the key factors that leads to the development of heart diseases and hardening of arteries.
In a study, a group of people were given a drug to reduce inflammation. It was found that the medication helped bring down the number of heart attacks in people who had a heart attack. It also reduced the risk of cancer.
But the question arises how can people reduce inflammation without taking fancy drugs? It has been seen that besides avoiding obesity and quitting smoking, maintaining healthy gut bacteria can also be helpful in reducing inflammation.
How Healthy Gut Microbes Help Prevent Heart Disease?
Our gut microbes play an important role in preventing many diseases caused due to inflammation, like diabetes, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It has been found that all these diseases are associated with a lack of good gut bacteria.
In the current study, it was observed that the women who reported hardening of arteries had less microbial diversity in the gut, and the women having healthier arteries had more good gut microbes.
Also, certain substances produced by healthy microbes were also found at higher levels in blood of people having healthier arteries. One of these substances is indoleproprionic acid, which helps in lowering the risk of diabetes. Gut bacteria produce more indoleproprionic acid if a person consumes more fiber.
It was found that in 10 percent of cases of inflammation, arterial hardening was explained by gut microbes and the substances produced by microbes. Cholesterol levels, diabetes, smoking, and obesity explained less than two percent of the risk of heart diseases. This finding was found very exciting as unlike genetic risks, the gut microbes and the substances produced by them can be changed.
Diet Is the Key to Maintaining Healthy Gut Microbes
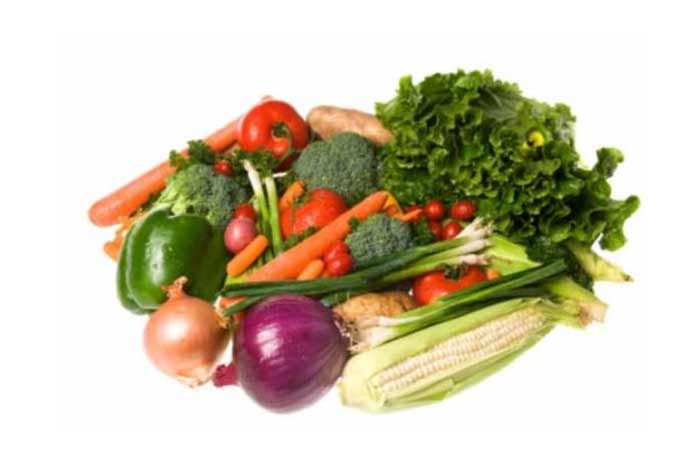

We can increase gut microbial diversity by consuming good bacteria. This can be done by eating probiotic supplements or foods, or by undergoing a fecal transplant. A study found this method helpful in diabetes. Scientists studied gut microbes from diabetics and healthy individuals. The result of the study was evaluated a few weeks later and it was found that there was some improvement in the health of the diabetics. Not only this, the gut microbes also showed some changes.
Another way to increase good gut microbe is to change our diet. The good gut bacteria grow better when we consume a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fish oil) or in dietary fiber, which can be found in fruits and vegetables. You can also eat foods such as whole meal bread, oats, nuts, beans, and dark chocolate.



