Have you been experiencing a burning sensation in the chest or neck area, especially after meals? This is nothing but, what is commonly referred to as “heartburn”. It signifies a digestive condition, known as “Gastroesophageal Reflux” (GER). As the name implies, GER is marked by reflux or backflow of contents of stomach into the food pipe (medically known as esophagus). Apprantly GERD is a mild condition, which occasionally occurs in a large number of people.
According to an estimate by American College of Gastroenterology, GER is a common condition with more than 60 million Americans experiencing it at least once in a month. [1]
However, if you have been experiencing this reflux of stomach acid more than twice a week for few weeks, you are suffering from a much severe and life-long condition, known as Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Statistics by National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases suggest that almost 20% of the U.S. population are suffering from GERD. [2]
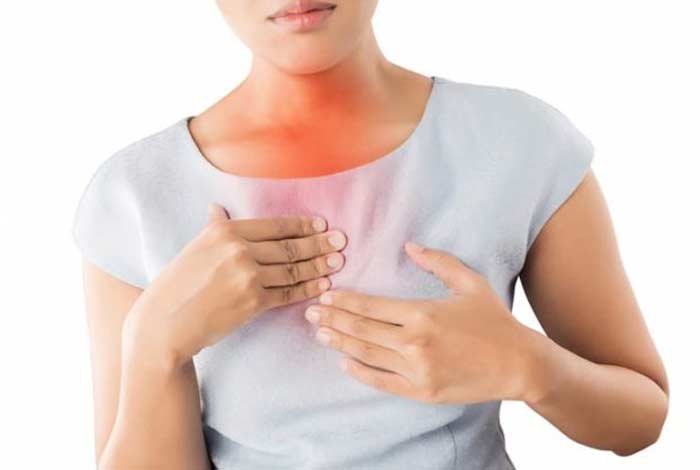
Understanding the normal anatomy is crucial to understand the abnormality seen in GERD. Esophagus, commonly known as food pipe, is a muscular tube which connects mouth to the stomach. Normally esophagus is separated from the stomach by a circular ring of muscle, known as lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Consider this LES to be a one-way valve, which only opens when we swallow food, thus allowing the food to enter the stomach. Following the entry of food in the stomach, LES closes and prevents the backflow of stomach content into the esophagus.
Experiencing the acid reflux once in a while is normal and indicates a transient defect in LES. However, in GERD, this sphincter becomes permanently weak with an inability to close properly or tightly, thus causing a persistent chronic reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. The acidic content of stomach touches the lining of esophagus and possibly even the throat and mouth, producing heartburn and other distressing symptoms. This weakness of LES has a strong association with conditions like obesity, smoking, alcoholism, aging, unhealthy dietary habits, etc.
Although it is not a fatal condition, it is a life-long condition which severely deteriorates a person’s quality of life. However, it can be effectively managed through medications and lifestyle changes. If left untreated, it can cause some serious complications, which may require surgery for its correction.
Types of GERD
Although GERD usually produces some classic features, there are certain variants of GERD with some atypical features. These variants are described below.
1. Non-erosive Reflux Disease (NERD)
Patients with NERD experience similar symptoms, as are experienced by GERD affected people. But, unlike GERD, NERD patients on examination do not demonstrate esophageal erosions, i.e., no breach in the lining of esophagus is seen.
2. Extra-esophageal Reflux (EER)
GERD typically involves esophagus. However, in some cases, the acid reflux may affect other organs, such as larynx (voice box), pharynx (commonly called throat), lungs and even heart. Involvement of organs, other than esophagus, is referred to as Extra-esophageal reflux (EER). EER produces some atypical symptoms, which are described below.
- Laryngitis, i.e., swelling of voice box, leading to chronic cough, voice disturbances and hoarseness of voice
- Recurrent pneumonia
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
- Chest pain
- Abnormal heart rate or rhythm
- Sleep apnea, i.e., difficulty in breathing while asleep
- Erosion of teeth due to acid reflux
3. Silent Reflux
This type of reflux does not produce any symptom. This is known as “Silent killer” as the person may not seek medical help due to the absence of symtoms, causing the disease to progress to a severe stage. This unrecognized chronic acid reflux can lead to serious changes in esophaugus, like barrett’s esophagus (changes in the lining of esophagus) and even esophageal cancer
Symptoms of GERD
Various symptoms of GERD are as follows.
Heartburn
This is the most common symptom of GERD, which occurs due to the reflux of stomach acid. This most commonly occurs after meals and worsens on lying down or bending over. It is usually described as a burning sensation in the chest or neck area. It may start high up in the abdomen and extend to the back or neck.
Chest pain or discomfort
Sometimes, the patient may experience severe sharp chest pain, which may mimic angina attack. However, individual experiencing such pain must seek emergency medical help to rule out angina.
Sour taste in the mouth
This occurs due to reflux of stomach acid extending all the way up to the mouth, producing the sour taste of stomach acid.
Chronic dry cough
A long-lasting nagging dry cough, which is worse during night may be suggestive of GERD. The exact reason how GERD produces or triggers cough is not clear.
Asthma
The reflux acid on entering airways may irritate the airway lining and can cause or trigger an asthma attack. Also, asthma itself and drugs used for asthma can aggravate GERD.
Other Symptoms
Other than the typical symptoms described above, certain other symptoms may also be seen, which are described below.
- Bad breath
- Tooth decay and erosion
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Feels like a lump is in the throat
- Difficulty or pain in swallowing
- Earaches
- Sudden increase in salivation
Risk Factors of GERD

Occasional reflux of stomach acid is very common, especially after having large meals, immediately lying down after meals or due to specific food items. However, persistent chronic acid reflux is less common and can affect people of all ages and genders. Sometimes, the exact reason of GERD is unknown.
However, certain factors increase the risk of developing GERD. These are mentioned below.
Obesity
When a person is obese, the abdomen is distended or the abdominal pressure is more than normal. Thus, the LES may not function properly, leading to GERD.
Pregnancy
It is another condition marked by distended abdomen, hence putting pregnant women at a higher risk of developing GERD.
Sliding Hiatal Hernia
A muscular structure, known as diaphragm separates the chest cavity from abdominal cavity. Esophagus connects to stomach by passing through a small opening in the diaphragm, known as hiatus. When the hiatus enlarges, a small part of stomach herniates or bulges upwards into the chest cavity. This condition is known as sliding type of hiatal hernia. This causes changes in pressure of LES and puts a person at a greater risk of developing GERD.
Scleroderma
It is an autoimmune connective tissue disorder, wherein body provokes the immune system to produce more collagen. This collagen gets deposited in skin and internal organs, making them hard. Normally, the muscular movement of esophagus (medically known as peristalsis) along with optimal function of LES propels the food in stomach and prevent acid reflux. However, in scleroderma, the muscles of esophagus and LES may not function adequately, thus increasing the chance of developing GERD.
Other than the above listed conditions, certain factors trigger the reflux of stomach acid. These are described below.
- Smoking
- Excess consumption of coffee or alcohol
- Having large meals
- Eating meals close to bedtime
- Certain food items, especially fatty or fried foods, chocolates, peppermint, etc.
- Specific medications, such as aspirin, calcium channel blockers, sedatives, antihistamines, anti-asthma drugs, etc.
Do I have GERD?

If you have been experiencing heartburn, more than twice a week for several weeks, you are most likely suffering from GERD. Occasional acid reflux is not a bothersome issue and is not indicative of GERD.
If you are obese, smoker or consume excess alcohol, you are at a very high risk of developing GERD. If you are fond of eating fried fatty foods or chocolates, you may develop GERD in the long-run. If you are pregnant, you definitely have a high chance of developing GERD.
If you do not experience heartburn but develop respiratory infections quite frequently, or have developed hoarseness of voice or a chronic cough, you may want to get yourself tested for EER and silent GERD.
If you are on medicines for conditions, like hypertension , depression , asthma, allergy, etc., you may be experiencing heartburn frequently and may have developed GERD.
A notable point here is that, heartburn may mimic an angina attack. Hence, a doctor’s consultation must be sought.
Causes of GERD
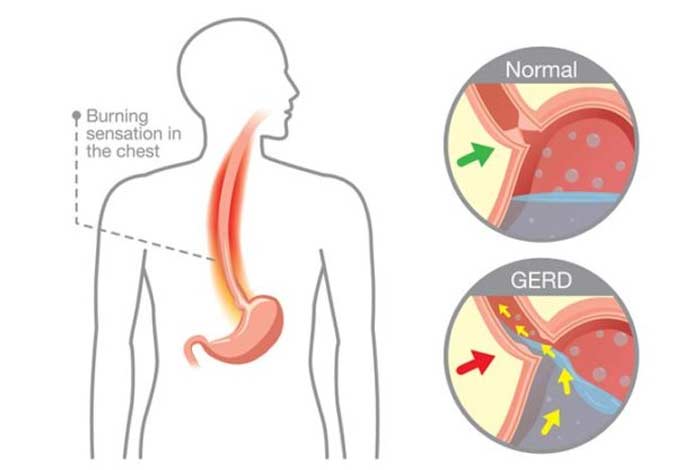
Optimal strength and functioning of lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is necessary to keep the stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus and other organs.
When the LES loses its strength or relaxes when not required, the stomach contents including acid, food and gastric juice, refluxes into the esophagus and may also enter lungs, throat, voice box and mouth.
Occasional reflux is not suggestive of a disease. However, frequent reflux of acid can cause severe injury and inflammation of the lining of esophagus and other organs. People belonging to high-risk category of developing GERD can develop it in the long run if the trigger factor is not controlled.
Prevention of GERD

GERD is preventable in most cases. If you feel heartburn even once a month, or you are at a high risk of developing GERD, you must take appropriate measures to prevent the onset of GERD. These measures are described below.
1. Avoid culprit foods and beverages
As already stated, certain foods and beverages can trigger GERD. These include:
- Chocolate
- Fatty fried food
- Peppermint
- Coffee
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Tomato products
Avoiding these foods and beverages can significantly reduce your risk of developing GERD.
2. Lose weight
Being obese or overweight drastically increases your risk of developing GERD. Exercise and consume a balanced diet to lose weight and reach a healthy BMI.
3. Abstain from smoking and alcohol
It is a well-proven fact that smoking and alcohol consumption increases your risk of developing GERD. Hence, completely refrain from smoking and alcohol.
4. Eat smaller meals
Large portion size can cause abdomen to bloat, thus causing improper functioning of LES. Therefore, eat smaller meals to reduce the reflux of stomach acid.
5. Get yourself checked
If you have been experiencing any abdominal distress, heartburn, chest pain, chronic cough, voice disturbances, etc, talk to your doctor about it. Early recognition of the trigger factor may help you in preventing GERD.
Diagnosis of GERD
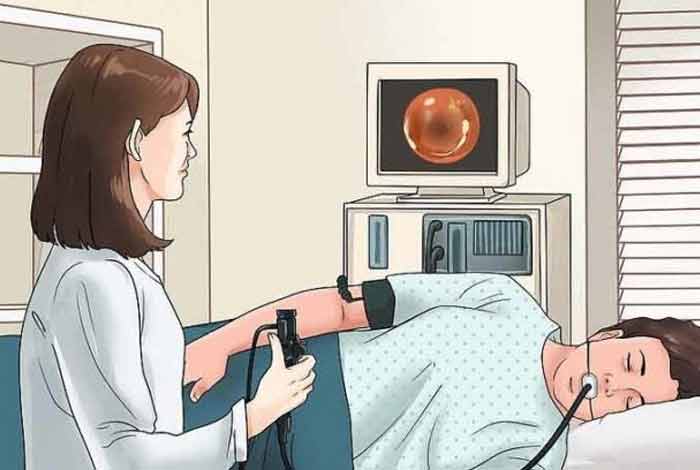
You must not try to diagnose GERD on your own as some of its symptoms, like chest pain could be an indicator of a serious health issue. Hence, seek medical help. Various methods of diagnosis of GERD are as follows.
1. History and Physical Exam
Your doctor may ask you to describe your symptoms and seek information about when and how are they aggravated. Your doctor will ask you if you are suffering from some medical condition or you are on some medication. You may also be asked to enlist the foods you eat and when do you experience symptoms. Once a thorough history is sought, your doctor will examine your general health and may also examine your abdomen to check for any abnormality or distension.
2. Ambulatory acid (pH) probe test
This test determines the amount of acid released in the stomach in 24 hours. A long thin tube, called catheter is placed in your stomach, through your nose and esophagus. This catheter or probe is attached to a device placed on a waist or shoulder strap. Through this device, doctor assesses the amount of acid refluxed in your esophagus.
3. Esophageal Manometry
Optimal motility or movement of esophageal muscles while swallowing is necessary to prevent the backflow of stomach acid. By inserting a catheter in the esophagus, doctor analyzes the movement of esophageal muscles.
4. X-ray
Patient is asked to swallow a chalky liquid, called barium. It stains the lining of esophagus, stomach and upper part of intestine. Following this, an X-ray is taken and these organs are then examined.
5. Endoscopy
A thin, flexible tube with light and camera is inserted down the throat into the esophagus and stomach. This does not indicate the amount of acid being refluxed, but helps in ruling out esophagitis (swelling of esophageal lining) or any other complication. It may also be used to perform biopsy, which involves removing a small amount of tissue from the esophagus and then sending it for laboratory examination.
Treatment of GERD
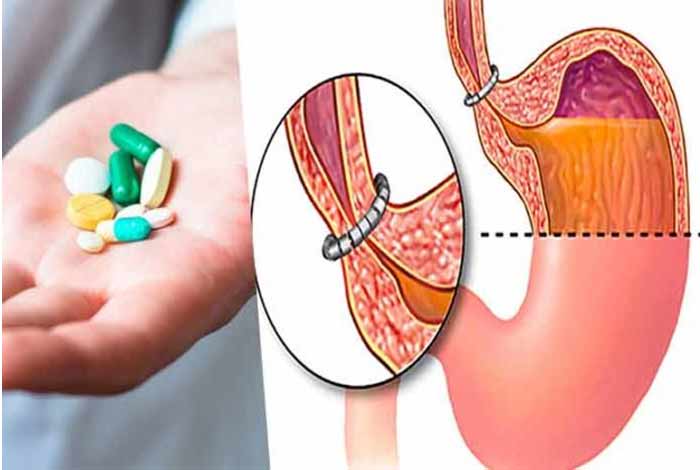
Once your symptoms and diagnostic tests confirm the presence of GERD, your doctor may offer certain treatment methods. These are listed below.
1. Lifestyle modifications
A faulty lifestyle plays an important role in developing GERD. Hence, certain lifestyle changes can keep the acid reflux in control. Having smaller meals, and maintaining a gap of 2-3 hours between your last meal and bedtime can prevent the stomach acid from refluxing. Maintain a healthy BMI and avoid trigger factors like spicy food, smoking, etc. to prevent the acid reflux.
2. Medications
Along with the lifestyle changes, some medications can also relieve the symptoms of GERD. The drugs for GERD are as follows.
- Antacids, such as magnesium hydroxide, aluminium hydroxide, etc. are given to neutralize the stomach acid
- Proton Pump Inhibitors, like pantoprazole, rabeprazole, etc. are strong acid blockers, which give adequate time for esophagus to heal
- H2 blockers, like cimetidine, famotidine, etc. reduces the production of acid
- Skeletal muscle relaxant like baclofen may also be used to reduce the frequency of opening of lower esophageal sphincter
3. Surgery
Although GERD can be controlled through medications, surgery may be advised to people not responding to medications or who prefer to avoid long-term use of these medications. Various surgical options for GERD are as follows.
- Fundoplication: This procedure involves wrapping the upper part of stomach around the lower esophageal sphincter. It is a minimally invasive procedure.
- LINX device: This involves placing a ring of magnetic beads at the junction of esophagus and stomach. The magnetic attraction of the beads is strong enough to prevent the reflux of stomach acid and weak enough to allow easy passage of food to the stomach.
Care

GERD can cause some distressing symptoms, affecting the daily life of an individual. Most people neglect the condition, thinking it to be a mild indigestion. However, if you or your close one has been experiencing the symptoms, twice a week for few weeks, GERD must be suspected.
Encourage your family, friend or peer, dealing with such symptoms, to seek medical help. If the patient is overweight, or has an unhealthy lifestyle, motivate him/her to reach a healthy BMI. Encourage them to seek appropriate treatment.
OTC for GERD

Certain mild antacids, proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor blockers are available as over-the-counter medications. However, stronger medications would require a prescription by a health care professional. Also, research has shown that dietary supplements with trypophan, melatonin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folic acid can relieve the symptoms of GERD. [3]
Self-Management Methods Available for GERD
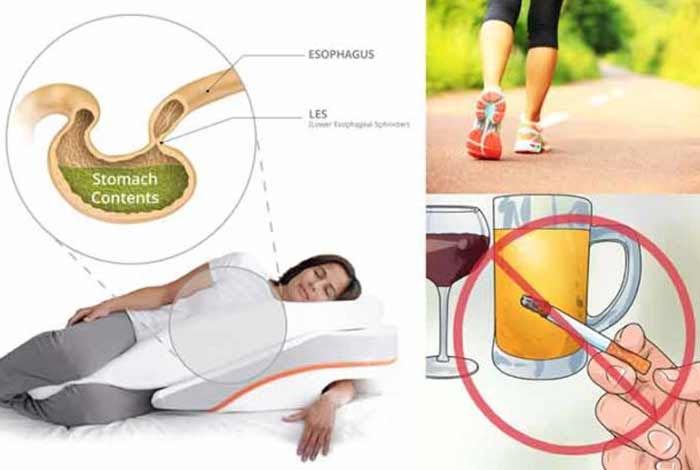
Symptoms of GERD can be relieved through several self-management methods, which are described below.
1. Reduce weight
Being overweight puts excess pressure on abdomen, increasing the chances of stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Thus, reducing and maintaining a healthy weight can play a great role in managing symptoms of GERD.
2. Maintain a food diary
Write down the foods you eat and try to locate the trigger food causing acid reflux. Completely refrain from foods that could provoke the reflux of stomach acid, including fatty fried food, chocolate, garlic, tomato juice, mint, onion, etc.
3. Limit alcohol intake and smoking
Smoking and alcohol have a strong association with GERD. Hence, limit your alcohol intake and avoid smoking.
4. Sleep with your head elevated
Acid reflux usually occurs while a person is lying down or asleep. This is so because in this position, the stomach contents do not face resistance of gravity and the contents can easily flow back into the esophagus. Thus, patients usually experience heartburn in the morning. Hence, it is advised that such people should sleep with their head elevated by 6 inches, either by elevating the head side of the bed or with the help of books or blocks.
5. Do not lie down immediately after eating
Lying down immediately after eating can aggravate the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, which in long run can lead to GERD. Hence, maintain a gap of at least 2 to 3 hours between your last meal and your bedtime.
6. Reduce your portion sizes
over-eating is one of the important cause of acid reflux. Hence, reducing your portion sizes may help you with the occasional reflux and can definitely prevent it from progressing to GERD.
7. Avoid tight-fitting clothes
Clothes that fit tight around the waist or abdomen can put pressure on the stomach and lower esophageal sphincter, thus increasing the chances of acid reflux. Therefore, avoid such clothing.
Natural Ways to Cure GERD

Although most patients with GERD may require medical intervention, some natural ways to manage GERD can prove beneficial. These are as follows.
1. Baking soda
Baking soda contains sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes stomach acid. Thus, it can play a great role in relieving the symptoms of GERD. Mix 1tbsp of baking soda with 8 ounces of water. Drink the mixture several times a day, but not exceeding 7 doses a day. Research has shown that excess consumption of this mixture can cause water to retain in body, leading to some serious side-effects, like heart complications, liver diseases, etc. [4]
2. Chewing gum
Research has shown that chewing sugar-free gum for about 30 minutes after a meal can reduce the acid reflux from stomach. It has been seen that chewing a gum after meals increases the release of saliva in the mouth. This saliva when swallowed can wash off the acid being refluxed in the food pipe. [5]
3. Have more fruits
Fruits, like bananas, apple, watermelon and cantaloupe have been shown to neutralize stomach acid and provide relief in GERD. Avoid acidic fruits like oranges, pineapple and grapefruit.
4. Herbal remedies
Certain herbs, like chamomile and licorice are known to benefit people suffering from GERD. However, they can cause some side-effects if taken in an inappropriate dose. Therefore, a doctor’s consultation is necessary before taking these remedies.
5. Progressive Relaxation Technique
This technique is known to relieve anxiety and stress, which can aggravate GERD. This technique involves progressively contracting and relaxing different group of muscles of the body.
Health Tip by Experts
It can be unsettling to bear the burning sensation of acid reflux throughout the day. But, with little steps to a healthy lifestyle, you can conquer your distress and lead a disease-free life.