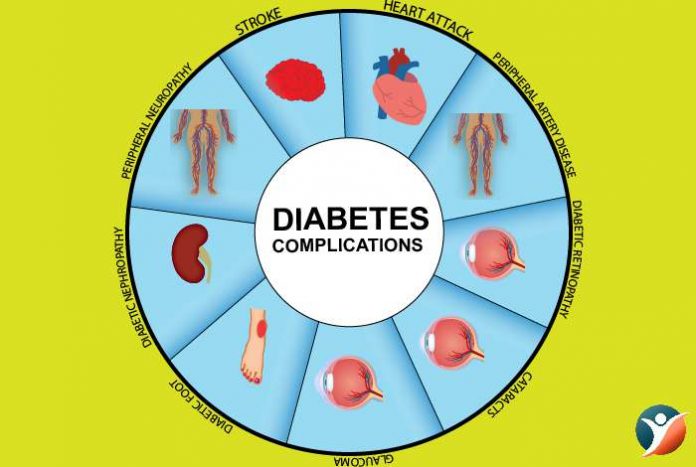
Diabetes can be managed considerably if it is detected early, but when left untreated it can cause severe complications. These diabetes complications are less severe in people with properly controlled blood sugar levels.
With diabetes, if you do not work hard to keep your blood glucose levels in control, you will have to be ready to face many short-term and long-term complications. But watching the food that you eat, bringing about necessary changes in your lifestyle, exercising and taking medications, these complications can be prevented.
And although you may be having long-term and serious complications after getting diagnosed with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels will prevent worsening of complications.
With type 2 diabetes it may be possible that you have already developed some complications when you are diagnosed for the first time. This is because type 2 diabetes develops gradually and it may go unnoticed or you may not realize that you have diabetes for a considerably long period of time. With time, high blood glucose can cause a lot of damage. Let’s take a look at some of the complications which may arise as a result of diabetes.
Table of Contents
- Skin Complications
- Eye Complications
- Cardiovascular Complications
- Nerve Damage
- Kidney Damage
- Foot Damage
- Diabetic Blisters
- Hearing Impairment
- Mental Health Disorders
- Diabetic Coma
- Hypertension
- Oral Health
- Pregnancy Complications
Skin Complications
Diabetes can affect each and every part of our body including the skin. These issues are in fact an indication that a person has diabetes. Fortunately, most skin conditions can be treated if detected early. Many of these skin conditions can be present in people who are not diabetic but these are more common in diabetics are:
Fungal infections,
Bacterial infections
Itching
Some skin conditions that happens only to diabetics are:
- Dermopathy,
- Diabetic blisters,
- Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum,
- Eruptive xanthomatosis
Common bacterial infections in diabetics
Some of the common bacterial infections that occur in people with diabetes are [1] :
- Styes (Infection in eyelid glands)
- Folliculitis (Infection of hair follicles)
- Boils
- Carbuncles (skin infection and the tissue underneath also get infected)
- Infection near the nails
There are many organisms that can cause infections but the most common one is Staphylococcus bacteria, also known as staph
Treatment:
Till sometime back bacterial infections were life-threatening particularly for people with diabetes. Today the chances of death are very minimal due to better techniques for controlling blood sugar and better antibiotics.
Take good care of your skin and maintain hygiene.
In case you get an infection make sure to visit a doctor who will prescribe proper antibiotics for curing the infection.
Fungal Infections in Diabetics
Fungal infections in diabetics are caused by Candida albicans. This can cause rashes which are itchy and blisters and scales can also form.
Some of the common fungal infections are:
- Athlete’s foot,
- Jock itch,
- Ringworm,
- Vaginal yeast infection.
Treatment:
Fungal infections need warm and moist environment to thrive. So, they are found under the breast, between fingers and toes, around the nails, mouth corners, armpit, groin etc. The best way to keep yourself away from fungal infections is by keeping yourself as dry as possible. Maintaining a proper hygiene is also a must.
Speak to your doctor if you are suspecting an infection. The doctor is going to prescribe some antifungal medicines.
Itching
There’s a thing called localized itching which is common in diabetics. It results from yeast infection, poor circulation, dry skin. When the cause is poor circulation, itching generally happens in the lower part of the leg.
Treatment:
For treating itching, take care of your bathing patterns.
Use soap that is mild.
Use a moisturizer.
Diabetes-Related Skin Conditions
Acanthosis Nigricans:
It is a condition in which brown areas appear on neck sides, groin and armpits. At times they can also be present on hands, knees and elbows. This condition usually hits people who are overweight.
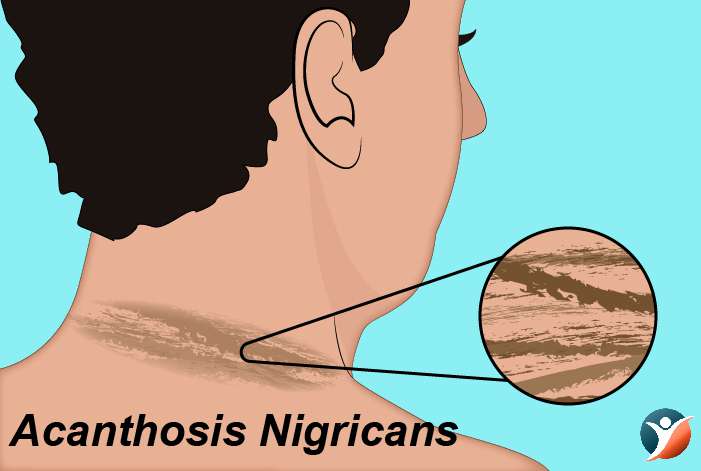
Treatment: There are some creams that can better the spots.
Diabetic Dermopathy:
Diabetes can bring about changes in the small blood vessels which can lead to skin issues known as diabetic dermopathy. It shows itself as scaly, brown patches. These may be mistaken for age spots. This is seen on the front of the legs. The effect may not be the same on both the legs.
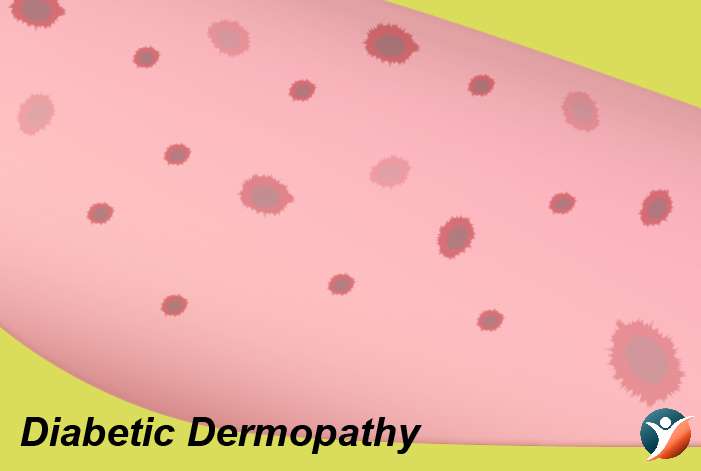
Treatment: If there is no itching or hurting in the patches it doesn’t need treatment. It is not a very dangerous condition.
Necrobiosis Lipoidica Diabeticorum (NLD):
This is another condition that may be caused due to changes in blood vessels. The spots in NLD are similar to diabetic dermopathy but they are few, large and deep. It starts as a dull and red scar, then becomes shiny in which the blood vessels are easier to see. Sometimes it can be painful and itchy. The condition is rare and generally older women get it.
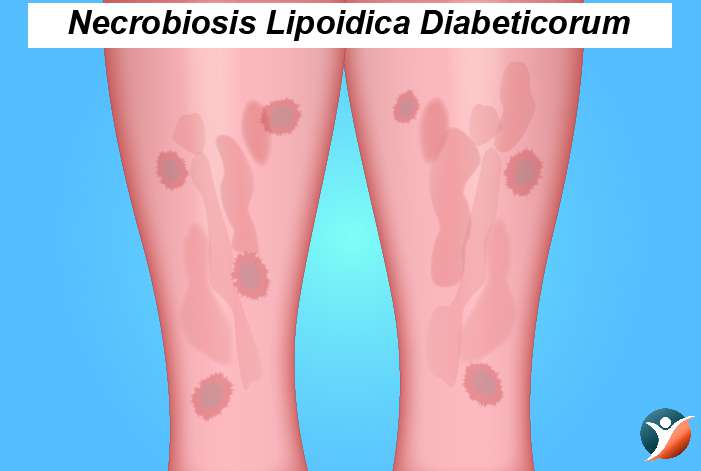
Treatment: Treatment may not be necessary when the sores have not cracked but you should see a doctor if they crack.
Allergic Reactions:
These may happen as a response to taking some diabetes medicine or insulin. Consult a doctor if you see abrasions, rashes or bumps where you inject insulin.

Treatment: If you suspect an allergic reaction, you must see a doctor as he would prescribe a suitable antiallergic medicine.
Diabetic Blisters:
These can occur on the back side of hands, fingers, toes, forearms or sometimes legs. These sores resemble blisters and occur in people with diabetic neuropathy. They do not pain and heal on their own without leaving scars.
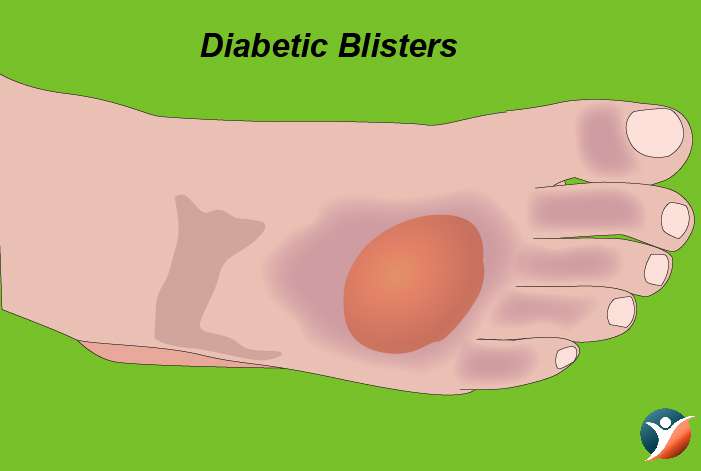
Treatment: The treatment is to bring blood sugar levels in control and these blisters disappear.
Eruptive Xanthomatosis:
It is also a common condition in diabetes. In this condition, yellow pea like enlargements are seen. It happens mostly on the back of the hands, buttocks, feet. This is seen in young men having type 1 diabetes.
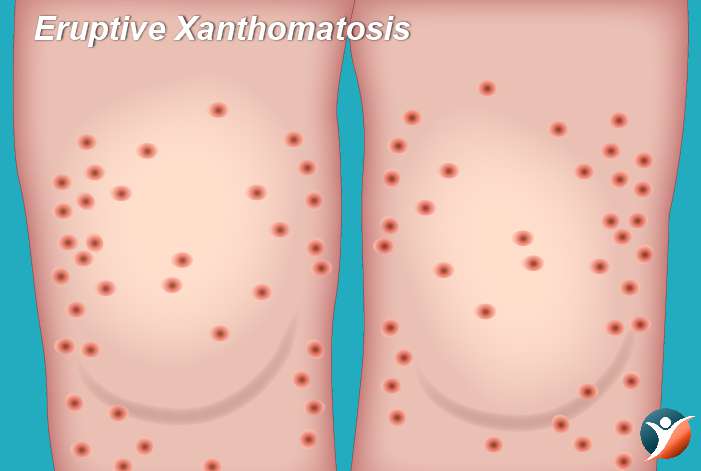
Treatment: By controlling the blood sugar, these may be managed.
Digital Sclerosis:
At times diabetics develop a waxy, tight skin on the back of their hands and forehead. The joints in the fingers become thick and movement may become difficult. Stiffness may also be observed in elbows, knees and ankles.
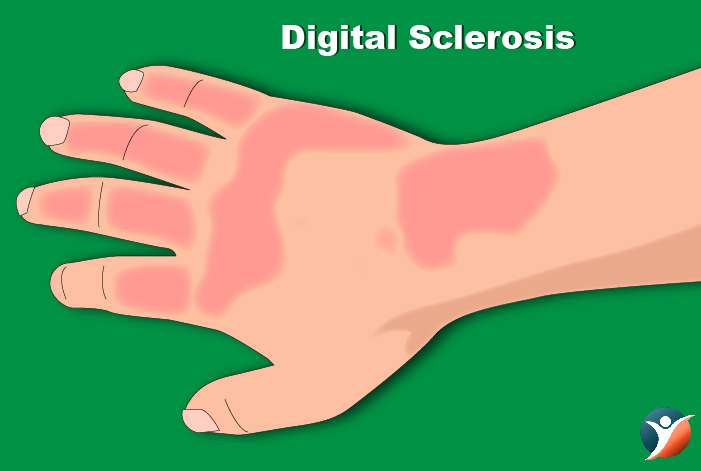
Treatment: Treatment is to bring blood sugar levels in control.
Disseminated Granuloma Annulare:
In this, the person gets sharply defined rings on the skin. These rashes occur on ears and fingers. They are skin-colored, brown or red.
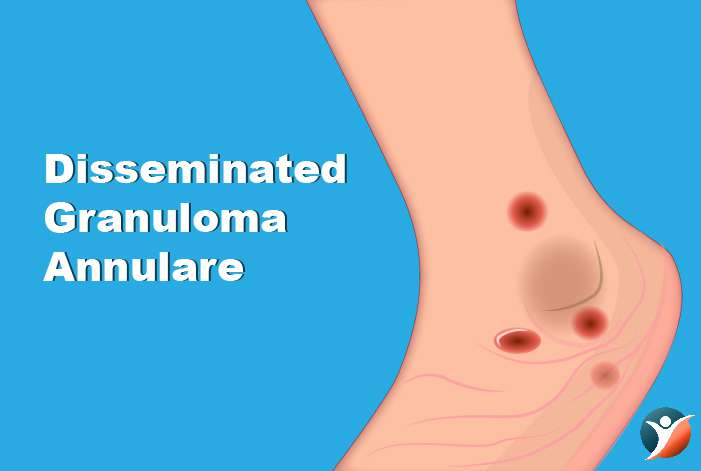
Treatment: If you see these rashes, you must consult a doctor.
Eye Complications
It is known that diabetes can cause problems for the eyes and may lead to blindness. Diabetics have a greater likelihood of having blindness [2]. Generally, people having diabetes do not have very complex eye disorders.
Glaucoma:
The chances of diabetics having glaucoma are 40% more than the normal counterpart. If someone has had diabetes for quite a long time, the chances of having glaucoma rise. With age, there is a greater risk. Glaucoma is believed to occur when pressure mounts in the eye. In majority of the cases, it slows down the drainage of the aqueous humor causing it to build up in the anterior chamber. The pressure damages the blood vessel that carry blood to the optic nerve and retina. This results in loss of vision.
Treatment: There are many treatment modalities like reducing the pressure in the eyes or opting for surgery.
Cataracts:
The chances of diabetics having cataracts are 60% more than non-diabetics. People having diabetes get cataracts at quite a young age and it progresses at a fast rate. In cataracts, the light gets blocked and there is clouding of the lens.
Treatment: For dealing with cataracts, wear sunglasses or anti-glare glasses. In cataracts that deter the vision, doctors tend to remove the lens. In diabetics, retinopathy may worsen after removal of lens.
Retinopathy:
Diabetic retinopathy is an all in one term for referring to the disorders of the retina which are caused by diabetes. There are two types of diabetic retinopathy: Non-proliferative and proliferative.
Non-Proliferative Retinopathy:
In this condition capillaries in the back of the eye form pouches. It can be mild, moderate and severe.
Macular Edema:
Vision loss is not caused at this stage. But the capillaries may lose their ability to control the flow of substance between the retina and the blood. Fluid may leak into the macula which may cause blurring or complete loss of vision.
Proliferative Retinopathy:
This is a more serious form in which the blood vessels get damaged. New blood vessels start forming. But these are weak causing leakage of blood and blocking of vision. The retina may get distorted resulting in a condition known as retinal detachment.
Treatment: Keeping blood glucose levels is the only treatment for this condition.
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes:
People having diabetes have a greater likelihood of cardiac disease and they die younger. Further cardiovascular complications are primary cause of mortality and morbidity in patients with diabetes. Hyperglycemia is the long-lasting inflammation that drives cardiac complications like coronary heart disease. Further diabetes also affects the myocardial function leading to diabetic cardiomyopathy and heart failure. So, diabetes ups the risk of cardiovascular issues like coronary artery disease along with chest pain, angina, stroke, heart attack, narrowing of arteries or atherosclerosis [3] .
Treatment: Managing diabetes effectively and leading a healthy lifestyle can prevent cardiovascular treatment in diabetics.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy):
Excess sugar can damage the walls of the vessels which nourish the nerves particularly legs. This leads to sensations like tingling, burning, pain, numbness which starts at the toes and then moves upwards [4]. Damage to nerves related to digestion can lead to issues with nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea. In men, erectile dysfunction may occur.
Treatment: Keeping blood glucose levels near normal can delay neuropathy due to diabetes.
Kidney Damage:
The kidneys have so many clusters of tiny blood vessels which filter waste from the blood. Diabetes can damage this filtering system. Severe damage can cause kidney failure [5] and irreversible end-stage kidney disease which may need transplant of kidney.
Treatment: Leading a healthy lifestyle and keeping a tract of your diabetes and associated conditions like high blood pressure can really help in preventing kidney complications.
Foot Damage:
In diabetics, poor blood flow to the feet or nerve damage increase the chances of foot complications [6] . If not treated, the blisters and cuts may develop which may not heal properly. These infections may lead to amputation of foot, leg or toe.

Treatment: Diabetics need to take care of their feet a lot by regularly massaging and wearing soft and comfortable footwear.
Hearing Impairment
Studies [7] show that hearing loss is two times more common in diabetics than those who do not have diabetes. Researchers conducted a study in 2008 which examined the link between hearing ability of adults in the age range of 20-69 and diabetes. It was concluded that diabetes causes hearing loss by damaging blood vessels and nerves.
Treatment: Managing diabetes and use of hearing aids are required.
Mental Health Disorders
Diagnosis of diabetes can lead to anger, denial, depression and fear [8] . This is a serious issue. Also, type 2 diabetes may up the chances of having dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. If the blood sugar cannot be controlled, there is more risk. Depression is also common in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It affects the management of the condition.
Treatment: A positive attitude towards life and support from friends and family are very important for keeping these disorders at bay.
Diabetic Coma
It is basically unconsciousness which is serious. Dangerously high blood sugar known as hyperglycemia or excessively low blood sugar known as hypoglycemia can cause a diabetic coma. Diabetic coma does not mean that you are dead but it means you cannot respond to sounds, sights or other stimulation. You are not able to remain awake. If not treated, diabetic coma can cause brain damage and eventually death.
Treatment: It is a very dangerous condition where a patient needs to be immediately taken to hospital where Intravenous fluids are administered.
High Blood Pressure or Hypertension:
Around 66% of the people with diabetes have high blood pressure and take prescription medicines to reduce their blood pressure. So, having diabetes means greater chances of hypertension.
Treatment: Managing your hypertension by dietary modification and use of blood pressure lowering drugs is very important.
Oral Health:
The chances of inflammation of the tissue which surrounds the teeth (periodontitis) are higher in people with poor glucose control. Loss of tooth is caused by periodontitis and also ups the chances of having cardiovascular disease.

Treatment: Managing periodontitis is important in diabetics as good oral hygiene and controlling blood glucose levels can prevent loss of teeth.
Pregnancy Complications:
High blood glucose can affect the fetus’ development. So careful monitoring is needed before and during pregnancy for decreasing the risks [8] . While the woman is pregnant, high blood glucose during this time can cause weight gain and increase the size of the fetus to more than normal. This will cause problems while delivering increasing the chances of injury to mother and child and hypoglycemia in child after it is born. Children who get exposed to high glucose levels while they are still in the womb of the mother have greater chances of developing type 2 diabetes when they grow up.

The development of complications of diabetes depends on the length of the time you have had the condition and also on how you’ve been managing the condition.
But when blood glucose is tightly under control, complications can be prevented or delayed. Get yourself monitored regularly by your diabetes care team. Some monitoring checks can be carried out at each visit like HbA1c, blood pressure, cholesterol and some can be done annually like eyes, kidney and foot review.
