
A state of lacking hair on the head is termed as baldness. Alopecia on the other hand, is a broader term, including several types of hair loss and hair thinning. Thus, baldness is a type of alopecia and its most common variant is scientifically known as androgenetic baldness or androgenic baldness or pattern baldness. Pattern baldness is the topic of interest of this article.
It affects men more commonly than women, accounting for more than 95% of cases in men. As per the American Hair loss Association estimate, about two-thirds of males would experience some form of hair loss by the age of 35 and approximately 85% of men will develop hair thinning by the age of 50. Although people consider baldness to be a male condition, women constitute nearly 40% of American hair loss sufferers. [1] However, the pattern of baldness varies with the gender.
Just like each cell of the human body, the hair too goes through a growth cycle, involving a cyclic process of dividing, resting and shedding. We all have about 1 lac hair on our head, with each hair being in different stage of hair growth cycle. Thus, it is normal to lose 50-100 hair per day. However, in pattern baldness, the size of follicles reduces in size, thus producing thinner, shorter and fragile hair, leading to a more than normal hair loss.
Although there are several causes of hair loss, including aging,hyperthyroidism, auto-immune conditions, etc., most researchers believe that genetics and imbalance in levels of androgen (male hormone, testosterone) are responsible for pattern baldness, in both males and females. This explains the occurrence of pattern baldness in females suffering from PCOS,which is marked by an elevated androgen level.
Although baldness is not a severe condition, it comes with loads of psychological burden, for people of all age and gender. But, baldness is a manageable condition in the initial stage. However, advanced stages may need more invasive treatment and offers a low remission rate.
Types

Based on the gender affected, pattern baldness can be of two types, each with a distinct pattern of appearance. These are described below.
1. Male Pattern Baldness: This variant of baldness is marked by a receding hairline, which usually begins in the temple or crown area of the scalp, thus forming a “M-shaped pattern” of hair loss. The hair loss from the front part of the head, is followed by loss of hair from the back of head. This leaves a band of hair, above the ear, often referred to as a “horse-shoe” appearance. This hair loss may progress over several years, leading to a complete baldness.
Pattern baldness in males is usually associated with certain medical conditions, such as obesit , diabetes prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension. According to a study published in the Indian Dermatology Online Journal, [2] males with androgenic alopecia are at an increased risk of developing Coronary Artery Disease
2. Female Pattern Baldness: In females, pattern baldness has an entirely different pattern of appearance, with no receding hairline. Unlike males, females do not lose hair from a particular area, progressing to another area. Instead, females usually lose hair from all over the head and experience a generalized thinning of hair. Although, the likelihood of females going bald is less, the hair thinning may be severely distressing.
In females, pattern baldness is usually seen associated with hormonal disorders, like PCOS.
Symptoms

The symptoms of pattern baldness are as follows.
Receding hairline: A characteristic M-shaped pattern of hair loss is one of the major presentation of baldness in men.
Thinning of hair: A gradual thinning of hair forms the chief symptom of baldness in females but may be seen in men too.
Other symptoms: Presence of acne along with weight gain and irregular periods, is seen in women suffering from PCOS.
Risk Factors
There are certain factors that increase the risk of developing pattern baldness. These are as follows.
1. Genetics: Heredity is the biggest risk factor, drastically increasing the risk of developing pattern baldness. If your parents, siblings or relatives are suffering from baldness, you have a very high chance of developing it too. A recent outbreak in this context suggests that, both maternal and paternal genetics play a role in androgenic alopecia. Genetics also determine the age and severity of baldness seen.
2. Age: As per a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the chances of developing androgenic alopecia increases with advancing age.[3]
3. Race: As per a study conducted in Turkey, published in Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia Journal, the prevalence and severity of Androgenic alopecia is lower in Caucasian men and women, as compared to Asian and Black individuals.[4]
4. Hormonal Imbalances: Any imbalance in androgen or male hormone, can cause the follicles to shrink, leading to baldness. This is especially true in genetically susceptible individuals. Females suffering from PCOS, pregnant women and post-menopausal women have elevated circulating androgens, which leads to female pattern baldness.
Do I have it?

If you are losing few hairs daily (around 100 hairs per day), you need not be anxious as it is the normal rate of shedding hair. If you are not having proper nutrition and are losing hair, you are probably suffering from anemia and vitamin deficiency. Being on certain medications, like those for bipolar disorder, arthritis, epilepsy and even excess of vitamin A can increase your hair loss. But, these are not suggestive of androgenic alopecia and can be easily reversed by terminating the trigger factor.
However, if you have a genetic history of baldness, and your hairline is receding or hair is thinning, you definitely are suffering from androgenic baldness. Presence of genetic and hormonal factors are necessary to label a baldness as “androgenic baldness”.
If you are a male with baldness running in family, and you are losing hair from sides of the head, you have entered the initial stages of male pattern baldness. If you have already lost the hair from the sides and front part of your head and are losing hair from the vertex or top of head, you have reached an advanced stage, which may eventually lead to baldness.
If you are a female with a positive family history, and have been experiencing generalized thinning of hair, you are developing female pattern baldness. Also, if you have developed acne, gained weight, is experiencing increased body hair, irregular periods and has developed thin hair on scalp, you have an increased androgen level and is suffering from androgenic baldness. If you are pregnant or have reached menopause, and you are losing more than normal hair, you are suffering from androgenic baldness.
Causes
Although the pattern of baldness varies with the gender, the mechanism involved remains the same. A research paper published in the American Journal of Human Genetics, suggests that genetics and hormonal influence are the leading factors, that disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and mark the onset of androgenic baldness.[5]
Normal Hair Growth Cycle
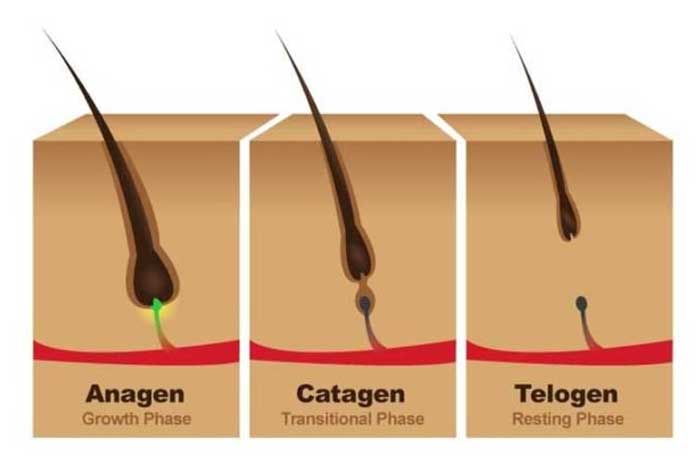 As per a research paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, our hair normally goes through a growing phase (anagen phase), a regression phase (catagen phase) and a resting phase (telogen phase), eventually leading to shedding of hair. Length of the hair is determined by the duration of the anagen phase. The anagen phase is longest, lasting for around 2 to 7 years, as compared to catagen phase (10 days) and telogen phase (3 months).
As per a research paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, our hair normally goes through a growing phase (anagen phase), a regression phase (catagen phase) and a resting phase (telogen phase), eventually leading to shedding of hair. Length of the hair is determined by the duration of the anagen phase. The anagen phase is longest, lasting for around 2 to 7 years, as compared to catagen phase (10 days) and telogen phase (3 months).
While some hair follicles are resting in the telogen phase, some are growing in the anagen phase. Thus, the process of hair growth and shedding occurs in a cyclic manner. However, any disruption in this process can lead to baldness.[6]
How Do Androgens and Genetics Cause Pattern Baldness?

Androgen (i.e., testosterone), which is present in both males (in higher amount) and females (in minimal amount), gets converted to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by an enzyme, called 5-alpha reductase.
In genetically susceptible individuals, the gene AR undergoes variation that leads to baldness because of the following processes.
Increase in DHT and Androgen receptor: People with genetically altered AR gene demonstrate an increase in the 5-alpha reductase activity, which in turn increases the production of DHT. Also, these individuals have more androgen receptors on their hair follicle. DHT binds to androgen receptor on hair follicles and causes follicular miniaturization, i.e., reduction in size of follicles, which over a prolonged period of time leads to baldness.[7]
Increased sensitivity to DHT: Individuals with an inherited AR gene, have a hypersensitive androgen receptor on the hair follicles. This increased sensitivity to DHT further accelerates the follicular miniaturization and causes baldness.
Alteration in hair growth cycle: A research paper published in the British Medical Journal, suggests that besides follicular miniaturization, disruption of hair growth cycle also leads to androgenic baldness. It says that in balding scalp, the length of anagen phase keeps reducing, thus producing shorter hair with each cycle, eventually leading to growth of extremely short hair that does not even reach the skin of scalp. It also suggests that with the reduction in duration of anagen phase, the telogen phase also prolongs. Since the telogen hair are loosely attached to the hair follicle, they eventually shed. Also, the duration of time period between the telogen and anagen phase becomes longer, which in turn is responsible for scanty hair visible on the scalp. [8]
Inheritance pattern of AR gene
This is a well-established fact that AR gene is located on the X chromosome. However, whether the gene is inherited from paternal or maternal gene is a matter of controversy. Most researchers suggest that both maternal and paternal genes play a role in transmission of this gene.
Conditions with Increased Androgen
 There are several conditions that increase the androgen levels. These are as follows.
There are several conditions that increase the androgen levels. These are as follows.
1. Stress: It is well-known that stress augments the level of testosterone in both males and females. Hence, leading a stressful life can cause pattern baldness.
2. Pregnancy and Menopause: These conditions are characterized by fluctuations in levels of estrogen as well as testosterone. Therefore, it is not uncommon to see pattern baldness in pregnant and post-menopausal women.
3. Ovarian cyst: Conditions, like PCOS, marked by presence of several cysts in ovaries, feature an increase in testosterone level, thus leading to baldness.
4. High androgen index Birth Control Pills: Some birth control pills, with a high androgen index, can also lead to pattern baldness.
Prevention

Owing to its genetic predisposition, pattern baldness may seem inevitable. However, it must be noted that elevated androgens are essential to make the genes express themselves and cause baldness. Hence, some measures can be taken to prevent the emergence of high androgen levels. These are as follows.
1. Manage stress levels: Since stress can significantly contribute to development of pattern baldness by increasing androgen levels, managing stress can prove beneficial in preventing the onset of pattern baldness. Walking and other forms of exercise can help alleviate stress.
2. Eat healthy diet: A healthy balanced diet can prevent the onset of elevated androgens and hence, protect you from hair loss.
Diagnosis
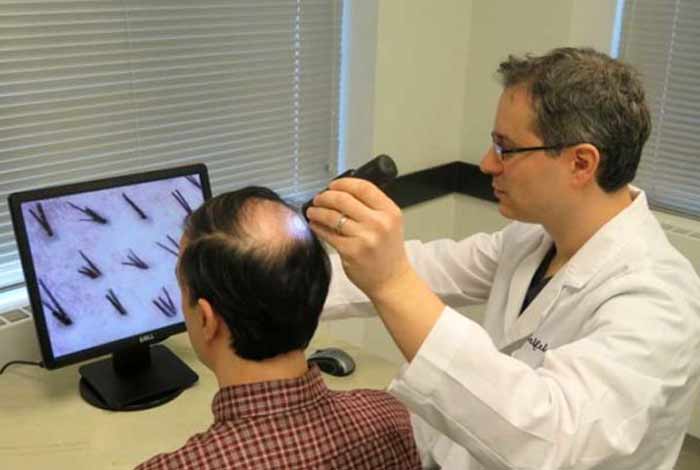
Dermatologists make diagnosis of the pattern baldness by keeping in mind following features.
1. Detailed history: A detailed history helps the specialist in ruling out other causes of baldness, such as fungal infection, etc. Doctor will also ask you about the presence of similar condition in your family, i.e., both maternal and paternal relatives. Information will be sought regarding your general well-being, such as presence of any disease or if you are on some medication. All this information helps the specialist in reaching a provisional diagnosis, which can then be confirmed through definitive tests.
2. Diagnostic tests: Once a thorough history has been recorded, doctor may run some diagnostic tests to establish a final diagnosis of pattern baldness. These tests are as follows.
- Blood test: Blood tests are done to get information about the patient’s hemoglobin levels (to rule out anemia), androgen levels (to rule out PCOS in females), thyroid hormone levels (to rule out thyroid disorders), etc. in order to reach to a conclusion.
- Pull test: In this test, your doctor may gently pull tufts of hair along the scalp to determine the pattern and severity of your hair loss.
- Dermoscopy: In this procedure, the hair follicles are examined microscopically. The presence of follicular miniaturization (shrunken hair follicles) is suggestive of pattern baldness.
- Scalp biopsy: This procedure involves removing a small section of scalp tissue to be examined under a microscope. This is usually used as a last resort, when no other test facilitates a diagnosis.
Based on the above findings, the severity of pattern baldness can be assessed through various grading systems, most common being Norwood’s (in males) and Ludwig’s (in females) grading systems.[9]
Treatment
Various treatment methods used to treat baldness are listed below.
1. Medications
Since androgens are the primary cause of hair loss in pattern baldness, certain drugs can be given by your doctor, which can block the effects of androgens and promote hair re-growth. The drugs for male pattern baldness may differ from drugs for female pattern baldness. The most commonly used drugs are as follows.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, including finasteride and Dutasteride
- Androgen-independent hair growth stimulator, like minoxidil
- Androgen receptor inhibitor, like spironolactone and cyproterone acetate
- Antihistamine, which acts as anti-androgenetic agent, like cimetidine
- Oral contraceptives, including desogestrel, ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate
2. Low-level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
A research study, published in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, laser light stimulates the hair follicles, thus causing hair re-growth. LLLT is a non-surgical procedure involving exposure of scalp to a laser beam with the aid of laser devices, such as laser combs.[10]
3. Surgery
Based on the chances of hair re-growth, your doctor may suggest surgery to reverse your baldness. Various surgical options are as follows.
- Hair Transplantation: This procedure involves taking hair follicles from hair-rich baldness-resistant area of scalp, like back of the head (donor area) to the bald area of scalp (recipient area). The donor site will grow the hair back and the recipient site will have live follicles now, thus covering the bald area.
- Scalp Reduction Surgery: This is an alternative to hair transplant surgery. This procedure involves reduction of the bald area of scalp by bringing together the hair-bearing areas of the scalp.
- Hair Cloning: This is a recent method of reversing baldness. This involves extracting existing hair follicles and multiplying them in a lab. This is followed by inserting the multiplied follicles in the bald area of scalp.
4. Wigs and Hairpieces
In people who have lost all the hair of head or who have a very low chance of hair re-growth, wigs and hairpieces can be used to give a natural-looking appearance to the head.
Care
Pattern baldness can be a distressing situation to cope with. Family, friends and peer should understand that people facing the hardships of baldness do not need to be looked down upon. Instead, give them emotional and mental support to seek medical help. If someone’s baldness has compromised his/her confidence and self-esteem, tell them to opt for treatment through medications or surgeries or even wigs.
In case of females, pattern baldness comes with even more dreadful psychological implications. Encourage such females to approach a doctor as pattern baldness is usually a sign of hormonal imbalance, which can have other medical complications, like diabetes.
OTC
Cimetidine and Minoxidil are available over-the-counter in various countries for treatment of pattern baldness.
Self-Management Methods Available

Pattern baldness usually requires medical intervention. However, some self-management methods can complement the beneficial effects of medical therapy. These measures aim at reducing damage to hair and are described below.
1. Protect your hair from heat and chemical: Exposure of scalp to heat or chemical treatment can make the hair brittle, worsening loss of hair. Hence, such treatments should be avoided.
2. Avoid improper handling of hair: Handling the hair gently is a must to prevent hair loss. Compulsive twisting, braiding or pulling of hair can extensively damage the hair shaft, leading to hair loss.
3. Reduce alcohol and caffeine intake: Alcoholism has a strong association with hair loss. Similarly, excessive caffeine consumption can also lead to baldness. Hence, cut down your alcohol and caffeine intake.
Natural Ways to Cure

Although conventional medicine is indispensable to treat pattern baldness, natural remedies are pacing up too in this direction. Various natural ways to treat pattern baldness are as follows.
1. Organic Foods: Chemically processed food can severely disrupt hormonal balance. Hence, opt for organic foods, which are chemical-free.
2. Omega-3 fatty acids: Research has shown that food rich in omega-3 fatty acids not just have anti-inflammatory property, but also aids in maintaining the health of hair. Wild-caught salmon fish is an extremely rich source of omega-3 fatty acids.
3. Green tea: There is no denying the fact that green tea is enriched with anti-oxidants, which blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, hence proving beneficial in pattern baldness.
4. Bone broth: With high amounts of protein, amino acids and collagen, bone broth helps in hair growth and reduces hair loss.
5. Avoid refined sugar: Sugar has been shown to disrupt optimal hormonal levels. Moreover, females with PCOS have a high risk of developing diabetes. Hence, cutting down sugar intake can arrest the hair loss.
Health Tip by Experts
Pattern baldness is unavoidable in most cases. But, unfortunately our society defines beauty by the number of hair on head. If this condition has encroached you, do not feel disheartened. Manage your stress levels and aim for a healthy and happy life.



