Bilberry – Uses, Interactions, Side Effects and Dosage

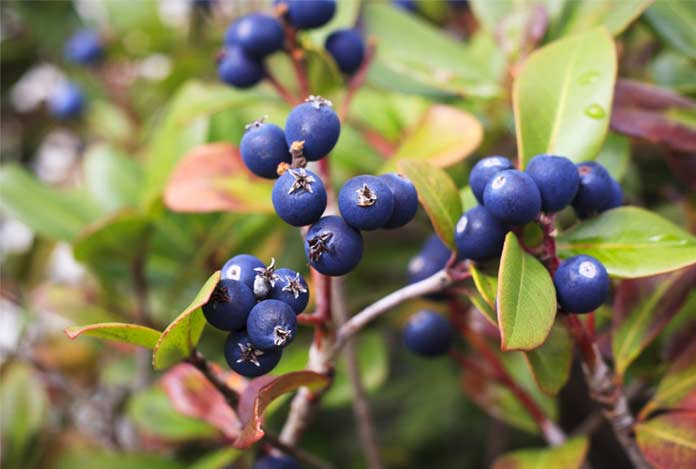
Bilberry is botanically related to the cranberry and blueberry. It has leathery leaves. The name of this shrub is obtained from a Danish term ‘bollebar’ which means dark berry as the fruit is dark colored. Bilberries are used for making pies and jams and are also used for treating conditions like diarrhea and varicose veins.
Dr. Andrew Weil says that the roots of the plant can be used as a gargle to treat mouth sores and sore throat. The leaves are used for treating minor urinary tract infections. The health benefits of bilberry can be attributed to the presence of antioxidants known as anthocyanosides.
Uses
Available both as leaves and fruits, it is used for treating many disorders including diarrhea, vision issues, varicose veins, menstrual cramps, and other circulatory conditions in which there is insufficient blood flow. These extracts can be used for treating venous insufficiency.
Dr. Weil says that bilberry is used in treatment of atherosclerosis. Studies say that anthocyanosides present in bilberry can improve the strength of the blood vessels, boost circulation and inhibit oxidation of bad cholesterol.
Bilberry is used in treatment of fatigue, diabetes , hemorrhoids, kidney disease, skin infection, gout and urinary tract infection. Let’s see how bilberry helps in these health conditions:
- Diabetes: Bilberry leaves have been used for a long time in controlling levels of blood sugar in people having diabetes. All types of berries can be used in lowering down the blood sugar levels. Research says bilberries are helpful in managing blood sugar levels when consumed with oatmeal.
- Vision Issues: Anthocyanosides in bilberries help in protecting the retina and so this is the very reason why bilberry is used in the treatment of retinal damage or retinopathy. Bilberry also protects against macular degeneration, cataracts, and glaucoma.
- Diarrhea: Bilberry helps in controlling diarrhea as it reduces intestinal inflammation.
Availability
Bilberry leaves and fruits can be used for making tea. These can also be used in making extracts. Bilberry capsules and extracts contain about 25% anthocyanins.
Herb-Drug Interactions
If you take bilberry in addition to the medicines you are taking for diabetes, it may result in excessive reduction of blood sugar levels. So, you must monitor your blood sugar. The anthocyanides present in blueberries affect the clotting of blood. So, if you are on blood thinning medicines, you should avoid bilberries for minimizing the bleeding risk.
Some Other Safety Concerns
These are safe if consumed as food at recommended dosages. It is considered safe for short-term use. Side effects associated with the long-term use of bilberry are not known yet. If large amount of bilberry extract is used, it can cause side effects like weight loss, muscle spasms and also death. It is not known whether bilberry is safe in case of pregnancy and breast-feeding. It is advised to avoid its usage during these times. Bilberry affects the levels of blood glucose which interferes with control of blood sugar during and after surgery, so you must stop taking bilberry before surgery. While purchasing, buy standardized bilberry with specific flavonoid content.
Dosage
For treating vision problems, 25 to 50 mg of bilberry extract is enough. Effects can be observed in the first four hours and gradually wean off during the course of the day. For other things, take 80-120 mg two times a day standardized bilberry extract. For diarrhea, crush 5-10 g of bilberries in a cup of cold water. Boil it and then strain. Use this remedy within four days. For circulatory issues, take about 80-480 mg of the extract in capsule form.
In children age 2 or above having diarrhea, crushed bilberries can be used for treatment but only under medical supervision.
Dr. Weil recommends bilberry extract for treating eye strain. Bilberry extract contains antioxidants that helps reduce bruising by stabilizing collagen , increasing the levels of intracellular Vitamin C and improving the strength of capillaries.