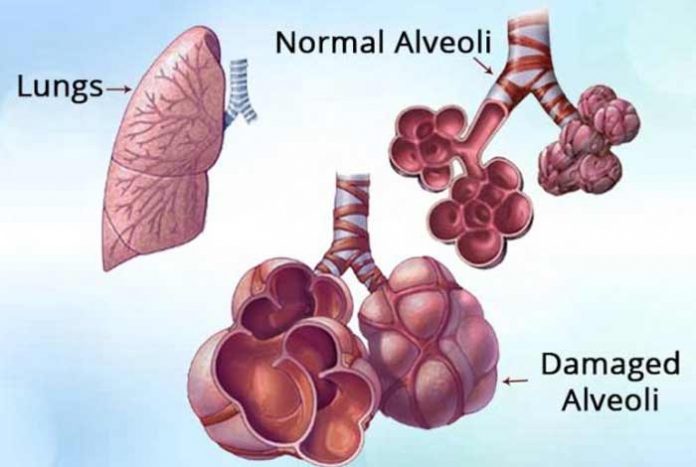
Overview and Facts
When a person inhales air, it travels through the trachea into the lungs, through two large bronchial tubes. These tubes divide into several smaller branches known as bronchioles, inside the lungs. These bronchioles end in the clusters of air sacs known as alveoli. These alveoli have significantly thin walls full of blood capillaries. The oxygen from the inhaled air is passed to the bloodstream through these blood capillaries. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide is exhaled out as metabolism’s waste product. Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder or COPD. It occurs when the alveoli or air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged. These damaged air sacs or alveoli lose their normal elasticity and cause difficulties in breathing. The narrowed bronchioles and inelastic alveoli do not allow air to fully expel out during exhaling. With the air already trapped inside the alveoli, there is no room for fresh oxygen-rich air to enter. This causes breathing difficulties as the oxygen reaching the bloodstream is very less. Emphysema causes rupture of alveoli, decreased surface area for gaseous exchange and a reduced number of alveoli in the lungs.
General symptoms of emphysema are wheezing, shortness of breath, frequent respiratory infections, fatigue, reduced appetite and weight loss. These symptoms can range from mild, moderate to being severe. It is most common among the people who smoke but several cases are also due to a rare genetic condition. Treatment can slow down the progression of emphysema and also reduces the associated symptoms. The lung tissue damage due to emphysema is permanent and cannot be reversed with treatment. If left untreated, it can cause several complications such as a collapsed lung, heart problems and large empty spaces in the lungs (bullae). Emphysema can also co-occur along with other respiratory conditions like chronic bronchitis.
In 2016, around 1.5 percent or 3.5 million people were diagnosed with emphysema in the U.S. The number of deaths due to emphysema reached around 3 in every 100,000 people. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), smoking and second-hand smoking are the leading causes of emphysema.
Types and Symptoms of Emphysema
Types of Emphysema:
There are three types of emphysema based upon the area of the lungs it is affecting. The types of emphysema are:
- Paraseptal Emphysema: It affects the paraseptal area of the lungs.
- Centrilobular Emphysema: It affects the upper lobes of the lungs and is most common among the smokers.
- Panlobular Emphysema: It affects both paraseptal and centrilobular areas of the lungs.
Symptoms of Emphysema:
The two main initial symptoms of emphysema are:
- Chronic cough
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea
These symptoms are present only during or after a physical activity. As the disease progresses, the symptoms appear even during rest.
In the moderate to severe stage of emphysema, the symptoms also include:
- Excess mucus production
- Frequent lung infections
- Wheezing or noisy breathing
- Chest tightness
- Reduced appetite
- Weight loss
- Slight barrel-shaped chest
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Stress and anxiety
- Restlessness, forgetfulness, confusion, slurred speech, or irritability
- Blue-tinged fingernail bed and lips or cyanosis
- Sleep disorders or insomnia
- Morning headaches due to breathing difficulties at night

Risk Factors of Emphysema
The risk factors of emphysema include:
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is a significant risk factor for emphysema. The more cigarette packs and more years a person smokes, the greater is the risk of developing emphysema. Marijuana smokers, pipe smokers, e-cigarette smokers and cigar smokers are also at an increased risk. People who are regularly exposed to second-hand smoke (passive smoking) are equally at risk of developing emphysema.
- Occupational Exposure to Chemical Fumes and Dust: A long-term exposure to chemical fumes, vapors and other particulate matter at workplace can leave lungs inflamed, damaged and swelled. This increases the risk of developing emphysema and several other respiratory conditions.
- People with Asthma Who Smoke: People who already are suffering from asthma, a chronic and inflammatory lung condition, and smoke increase their risk of developing emphysema in future.
- Exposure to Fumes of Burning Fuel: People who are regularly exposed to burning fuel during heating or cooking in poor ventilated homes, mostly women, are at an increased risk of developing emphysema.
- Age: Emphysema generally develops with age, so a person between 40 and 60 years might notice the symptoms.
- Gender: Men are at increased risk of developing emphysema because they tend to smoke more than women.
- Genetics: The rare genetic disorder alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a risk factor of emphysema. This deficiency increases the risk of developing emphysema and other respiratory disorders. Certain other genetic factors might make smokers more prone to develop emphysema.
- Low Body Weight: Several studies have revealed that having a low body weight might lead to emphysema. Further research is required to confirm this risk factor.

Do I have Emphysema?
If you experience:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea) which occurs more often or has become worse
- Excess mucus build-up
- More and frequent coughing or wheezing
These symptoms might indicate emphysema or several other conditions such as obstruction of the lung airways, bronchiectasis, asthma, bronchiolitis, chronic bronchitis, COPD, interstitial lung diseases, coronary artery disease (CAD), pulmonary edema, or pulmonary embolism. You must visit a doctor immediately to diagnose the condition which is causing these symptoms. Only a doctor can properly diagnose emphysema through several diagnostic tests and initiate the treatment accordingly.

Causes and Prevention of Emphysema
Causes of Emphysema:
- Smoking: Smoking is one of the leading causes of emphysema. Emphysema is more common in smokers or a person having a long history of smoking. The toxic and harmful chemicals present in smoke can inflame and damage the lining of lung airways. Cessation of smoking can prevent worsening of emphysema symptoms. Also, being regularly exposed to passive smoke can lead to development of emphysema.
- Dust and Chemical Fumes Exposure at Workplace: Exposure to certain types of industrial chemicals, dust and fumes at work might lead to development of emphysema.
- Genetics: Around 1 person in 100 has a rare genetic condition, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), which makes them more susceptible to the lung damage. Alpha-1 antitrypsin helps in protecting lungs and its deficiency causes progressive lung damage including emphysema. People who have this deficiency and who also regularly also smoke can develop emphysema.

Prevention of Emphysema:
The preventive measures for emphysema are:
- Cessation of Smoking: Developing emphysema is linked to smoking and second- hand smoking. It can, however, prevented by quitting smoking. If a person is a heavy smoker who wants to quit and has failed quite many times, he/she must keep trying to quit smoking. If necessary, a smoker can also join a smoking cessation program to quit smoking.
- Avoid Chemical Fumes and Dust Exposure at Workplace: A person who is constantly exposed to vapors, dust and chemical fumes at workplace must take necessary measures to prevent the exposure. Use of respiratory protective equipment can help in preventing exposure to harmful chemical fumes, vapors and particulate matter.

Diagnosis and Tests for Emphysema
There are several diagnostic tests conducted by the doctor to confirm emphysema. These include:
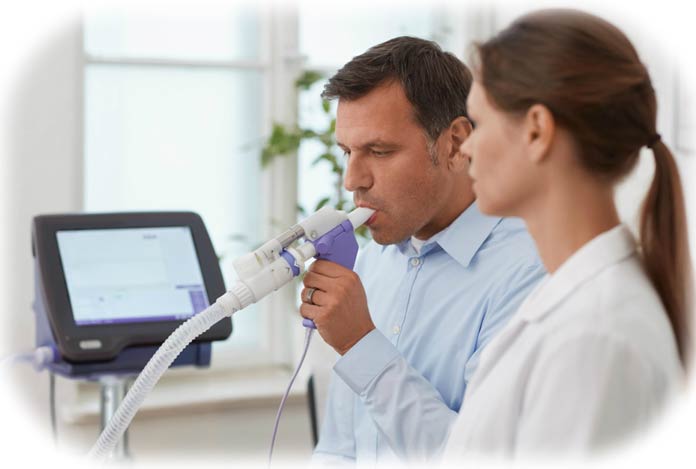
- Pulmonary Function Tests: These tests measure the amount of air a person can inhale or exhale and if the lungs are providing sufficient amount of oxygen to the blood. Spirometry, a pulmonary function test, is most common to diagnose emphysema. During spirometry, a person is asked to blow air into a small device known as spirometer. The machine measures how fast a person can blow out air and how much air the lungs can hold. Spirometer is effective in detecting emphysema even before the actual symptoms surface. This is often used to check the progression of the disease and the effect of treatment on respiration. Other lung function tests help in the measurement of pulse oximetry, diffusing capacity and lung volumes.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can show emphysema and damage to the lung tissues effectively. An X-ray can also rule out any other lung condition or even a heart failure.
- CT Scan: A CT scan can help in detecting emphysema and whether a person can be benefited by a surgery.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: This analysis test involves a blood test to measure how well the lungs are bringing oxygen to the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide from it.
- Laboratory Tests: These tests do not help in detecting emphysema, but they help in finding the underlying cause of symptoms. For example, laboratory tests to identify rare genetic condition such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) Analysis: There is a possibility of an underlying heart disease or condition which might be causing emphysema symptoms. These are ruled out by an electrocardiography (ECG or EKG).

Treatment and Care for Emphysema
Treatment of Emphysema:
The treatment of emphysema involves medication and therapies for people with mild to moderate emphysema. But people with severe emphysema might require undergoing a surgery. The treatment options available for emphysema are:
1. Medications: The doctor might prescribe several medications to control the symptoms of emphysema. These medications are:
- Bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles around the lung airways and usually come in form of inhalers. Bronchodilators help in relieving the shortness of breath and coughing, thereby easing the breathing process. Depending upon the severity of emphysema, a person might require a short-acting bronchodilator before any physical activity or a long-acting bronchodilator every day. A person with severe emphysema might require both. albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin), metaproterenol (Alupent), levalbuterol (Xopenex) and ipratropium (Atrovent) are various bronchodilators which can be prescribed.
- Inhaled steroids: Inhaling corticosteroid medications can help in reducing inflammation in the lung airways and also prevents worsening of emphysema symptoms. Side-effects of inhaled steroids include oral infections, hoarseness and bruising. Fluticasone and Budesonide are examples of inhaled steroids.
- Combination inhalers: Few inhalers have a combination of inhaled steroids and bronchodilators. Fluticasone and salmeterol (Advair) and budesonide and formoterol (Symbicort) are the examples of combination inhalers.
- Antibiotics: According to a recent study, antibiotics helps in preventing worsening of symptoms associated with emphysema. Azithromycin might help in preventing worsening of emphysema symptoms.
2. Lung therapies: Doctors often use these additional lung therapies in patients with moderate to severe emphysema. These therapies are:
- Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen is required when there isn’t adequate oxygen in a person’s blood. There are several devices which provide extra amount of oxygen to a person suffering with emphysema. It includes small, lightweight and portable devices that provide extra required oxygen.
- Nutrition therapy: This involves advice on nutrition for people suffering with emphysema. In initial stages of emphysema, a person is asked to lose weight but during advanced stages, it is advised to gain weight.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation program: These pulmonary rehabilitation programs include education, exercise training, counseling and nutrition advice. A variety of specialists create a custom program to meet all the needs of a patient. These pulmonary rehabilitation programs can improve the quality of life and help the patient to actively participate in daily activities.
3. Surgery: People with severe emphysema who are not helped by medications and therapies, opt for surgery. The surgery options for these people are:
- Lung volume reduction surgery: In this surgery, a surgeon removes damaged lung tissues from the upper part of lungs. This extra space helps diaphragm to work more efficiently. The healthier lung tissues expand in that increased space. This surgery can expand lifespan and improve quality of life.
- Lung transplant: Certain people with emphysema who meet the set criteria for lung transplant undergo this surgery. It helps them in leading an active life with no or reduced breathing problems. However, they can take life-long immune suppressing medications to prevent organ rejection. One or both the lungs can be transplanted.
- Bullectomy: In certain cases of emphysema, there is formation of large air spaces known as bullae in the lungs. These bullae can become larger and might start causing difficulties in breathing. A bulla can be as large as half the size of a lung. In a bullectomy surgery, the doctor removes bullae from the lungs to improve the airflow.

Care during Emphysema:
- Learn certain breathing techniques to breath effectively throughout the day. A doctor or a certified therapist can teach breathing techniques to a person suffering from emphysema.
- Practice controlled coughing, using a humidifier at home and drinking plenty of water helps in eliminating mucus from the airways.
- Use an air humidifier at homes to keep the surrounding air moist. This relieves pain due to frequent coughing and wheezing.
- Being regular in exercise as it can improve overall health and strengthen the respiratory muscles. A doctor or therapist can advise suitable exercises for a person suffering from emphysema.Be sure to quit smoking and also completely avoid second hand smoke to prevent worsening of symptoms or flare up.
- Get a flu vaccination annually to help in prevention of respiratory infections. Consult a doctor for pneumococcal vaccination once in every five years.
- See a doctor regularly to monitor lung functions and effect of treatment. This would help in preventing flare up.
- Take the medications on time and as prescribed by the doctor.
- Avoid other lung irritants and pollutants such as fumes, chemical vapors, dust, pollen, particulate matter from construction sites and strong smells.
- Use of cough suppressants is not advised as coughing helps in eliminating excess cough.
- Maintain a healthy weight. An overweight person with emphysema must shed the excess weight during the early stages. However, if the stage is advanced, the patient is asked to gain some weight.
- Avoid being in cold air as it can trigger shortness of breath in emphysema patients.
- Get the daily adequate nutrition by consuming a well-balanced diet.
- Try sleeping around seven hours a day. It helps the body in recovering.
- Learn as much as possible about emphysema to understand this lung condition better.

OTC and Self-Management Methods Available for Emphysema
OTC Medications for Emphysema:
Several non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including aspirin, naproxen, and ibuprofen are common OTC medications which relieve pain and also reduce fever associated with emphysema. They are also used in cases of cold, allergies and sinus pressure. Acetaminophen is also an easily available OTC that relieves pain due to emphysema. Certain other supplements that are available over-the-counter for emphysema include amino acids, coenzyme Q 10, and antioxidant vitamins (Vitamin C and E).
Self-Management Methods for Emphysema:
- Lungs get weakened due to the damaged and decreased alveoli. Avoid everything that might damage the lungs or worsen the symptoms associated with emphysema.
- Quit smoking and also avoid passive smoking. If a person wants to quit smoking, he/she can also join a smoking or tobacco cessation program.
- Exercising each day helps in keeping the mind and body healthy. A doctor or therapist can advise how much exercise is sufficient for a person with emphysema.
- Avoid air pollutants, pollen, dust particles, particulate matter and strong pungent smells. Use respiratory masks at workplace to avoid chemicals vapors and fumes. Avoid being near or around construction sites.
- Always consume a well-balanced diet that has high nutritional value. Strictly avoid packaged and highly processed foods that are deficient in essential nutrients.
- Limit salt intake to a minimum amount each day to prevent strained breathing.
- Maintain a healthy weight to prevent further difficulties in breathing.
- Increase intake of nutritious foods such as dairy, protein, fruits, grains, and vegetables.
- Consume around 8-10 glasses of water daily. Among other fluids, include only noncaffeinated drinks and juices.
- It is crucial to manage other chronic diseases like heart diseases and diabetes if these conditions co-occur along with emphysema.
- Keep homes dust and clutter free to prevent exposure to dust.
- Join a local support group nearby or online. This provides much needed inspiration and motivation to cope up with emphysema.
- Reduce anxiety and stress through meditation and yoga.
- Avoid crowded places such as local markets as they can increase risk of other respiratory infections.
- Take the medications and inhalers only as prescribed by the doctor.
- Cover mouth and nose with a soft scarf while getting out in cold, dust or fog. It helps in preventing worsening of emphysema symptoms.
- Wear loose clothes especially around chest and waist area. They ease the breathing and provide comfort. Collars and ties must be avoided.
- Implement several breathing techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed lip breathing which help in breathing effectively. A doctor or therapist can teach these breathing exercises to an emphysema patient.
- Do most of the household chores while sitting.
- Sleep around seven hours a day to help body get appropriate rest.
- Avoid respiratory infections by regularly washing hands and getting vaccinated annually.
- Practice huff and deep coughing methods to expel excess mucus due to moderate or severe emphysema.
Natural Ways to Cure Emphysema
Fortunately, there are several ways to cure emphysema naturally. These natural ways include:
- Garlic: It can help in thinning of mucus. Coughing can thereby eliminate mucus. A naturperson with emphysema must consume two to three garlic cloves in the morning on an empty stomach. Regular consumption of garlic helps in reducing symptoms associated with emphysema. Garlic juice can also be consumed by mixing it in vegetable juice.
- Rose haw or rose hip tea: Rose haw or rose hips are the fruits of the rose plant. Consuming rose hips tea daily helps in eliminating excess mucus and promotes the healing process.
- Eucalyptus oil: This is very effective in improving lung function and overall health of an emphysema patient. Cineole is the main chemical constituent of eucalyptus oil. It helps in reducing lung airways inflammation and shortness of breath. A person with emphysema can use eucalyptus oil in an air humidifier or a diffuser and breath in that air. It can also be topically applied over chest regularly. Eucalyptus can also be consumed by boiling its leaves into water and making herbal tea.
- Lemon: Lemon juice is effective in curing emphysema. Its juice can be consumed multiple times a day, before or between meals. Lemon helps in providing elasticity to the alveoli and reduces inflammation owing to its anti-inflammatory properties. It is also a rich source of Vitamin C. Do not add salt in its juice, however honey or sugar can be added.
- Astragalus: It is a Chinese herb which supports the healing process of the lungs and reduces excess mucus build-up. It must be consumed daily to help in eliminating the excess mucus during emphysema.
- Aniseed: Aniseed has expectorant properties that help in reducing the inflammation of alveoli caused by emphysema. Add brown sugar to around 10-15 drops of aniseed juice. Consume two teaspoons of this mixture two times a day to cure emphysema naturally.
- Amaranth: It is a green leafy herb which is highly effective in curing several lung conditions including emphysema. A person can consume amaranth’s fresh juice along with honey or sugar, multiple times a day. This juice also helps in balancing blood’s biochemical balance.
- Anti-emphysema diet- With the initiation of treatment, a person with emphysema must consume fruit juices only for the first two days. It can be followed by consuming fruits such as pear, papaya, pineapple, peach, etc. Fresh vegetables should be consumed raw rather than boiling them. Include whole grains, goat’s milk, nuts, curd and buttermilk to the daily diet. Salt intake must be minimum because sodium in it causes inflammation in the bronchial passages. Water and fluids must be consumed throughout the day. Smoking and alcohol consumption must be completely avoided.
- Acupuncture: It is an ancient Chinese technique which involves inserting fine needles into the skin at special points known as meridians. Acupuncture helps in easing the breathing process which is hampered by emphysema. A person with emphysema must only visit a licensed practitioner for acupuncture sessions. It is also effective in other lung conditions including COPD.
- Ivy leaf: Its extract can be used to cure emphysema naturally. Ivy leaf can be consumed by drying several ivy leaves and grinding them to form a powder. This powder can be consumed several times a day to repair damaged lung tissues.
- Horsetail: It is an effective herbal remedy to cure the alveoli damage caused by emphysema. Add a few drops of horsetail extract to one-fourth cup of water and consume this few times daily. Horsetail helps in repairing lung tissues and eliminating excess mucus from the bronchial tubes.
- Breathing techniques: A person with emphysema is advised to practice various breathing techniques. Most commonly practiced breathing techniques include diaphragm and pursed lip breathing. A therapist or doctor can teach these breathing techniques to an emphysema patient.
- Mullein: It is also known as Verbascum thapsus. A person suffering with emphysema, can consume its tea by boiling a few leaves of mullein in water. It must be consumed around three to four times a day to cure emphysema.

Health Tip by Expert
It is advised to quit smoking and completely avoid second-hand smoke, as soon as a person is diagnosed with emphysema. If unable to quit smoking, a person with emphysema can join a tobacco cessation program. Consuming a healthy diet, exercising each day and maintaining a healthy weight will help in managing the symptoms associated with emphysema.




