
Diabetes ketoacidosis is a serious, life threatening complication of diabetes that is commonly seen in people with type I diabetes but not unheard in type II diabetes patients. It is a complex metabolic disorder which is characterized by several distinct symptoms. This serious condition occurs when there is excessive production of ketones when the blood glucose remains high for a long period of time. Although it can become life threatening, it takes a lot of time to become serious. It is possible to treat it and prevent it too.
This condition arises when the body is unable to produce enough insulin. Pancreas secrete the hormone insulin which plays an important role in getting glucose absorbed by the cells for producing energy. In the absence of insulin, cells cannot use glucose for producing energy and therefore, they turn to the next energy source i.e. fat, for keeping the cells alive. When the body burns fat for producing energy, it leads to production of acids called ketones in the body. If this process continues for a long time, it leads to build up of ketones in the body which can change the chemical balance of your body. A whack in chemical balance throws the entire body out of balance.
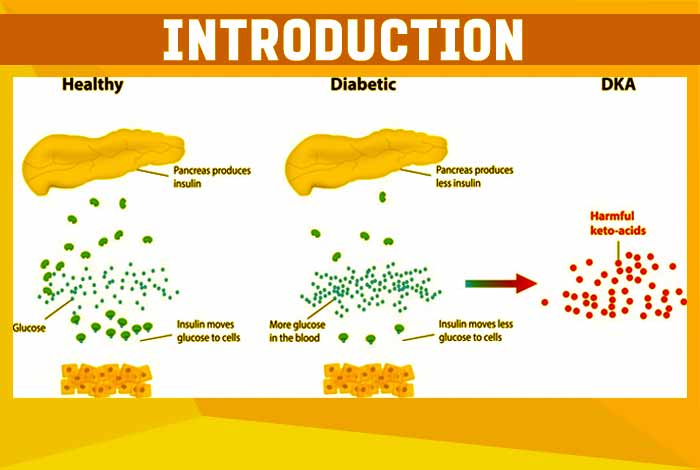
People who have type I diabetes are at a high risk of developing ketoacidosis as their bodies cannot produce insulin. The level of ketones in the body can increase in type I diabetics if they miss their meals, are stressed or have an insulin reaction.
Sometimes ketoacidosis can occur in people with type II diabetes as well. If you have type II diabetes, there is a possibility of acquiring a condition with similar symptoms, called hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) which can lead to severe dehydration.[1]
If you have diabetes, it is important to learn about the warning signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis so that you can seek emergency medical help in time.
Table of Content
- Causes of Diabetics Ketacidosis
- Illness
- Problem with insulin therapy
- Other reasons of diabetes ketacidosis
- Symptoms of Diabetes Ketoacidosis
- Treatment of Diabetes Ketacidosis
- Fluid replacement
- Electrolyte replacement
- Insulin therapy
- Final Word
Causes of Diabetes Ketoacidosis

Sugar is the main energy source for the cells body. Insulin acts as a catalyst that helps sugar to get absorbed by the cells for production of energy.
When there isn’t enough insulin being produced in the body, the cells are unable to use sugar properly for producing energy. This signals release of hormones in the body that break down another energy source in the body, fat. This leads to production of acids known as ketones which continue to build up in the body. Eventually, ketones get spilled in the urine.[2]
Some of the factors that can trigger diabetic ketoacidosis are:
Illness
An infection or other illness can lead to production of higher amounts of hormones like adrenaline or cortisol in the body. These hormones counter the action of insulin and sometimes trigger diabetes ketoacidosis episode. Urinary tract infection and pneumonia are such diseases.
Problem with insulin therapy
If you miss an insulin dose or if an inadequate dose of insulin is taken, it can leave your body with very little amount of insulin which can trigger an episode of diabetes ketoacidosis.
Other reasons of diabetes ketoacidosis
Some of the other reasons which can lead to diabetes ketoacidosis are:
-
- Physical or emotional trauma
- Heart attack
- Drug, especially cocaine abuse
- Alcohol abuse
- Certain medications like diuretics and corticosteroids
Symptoms of Diabetes Ketoacidosis
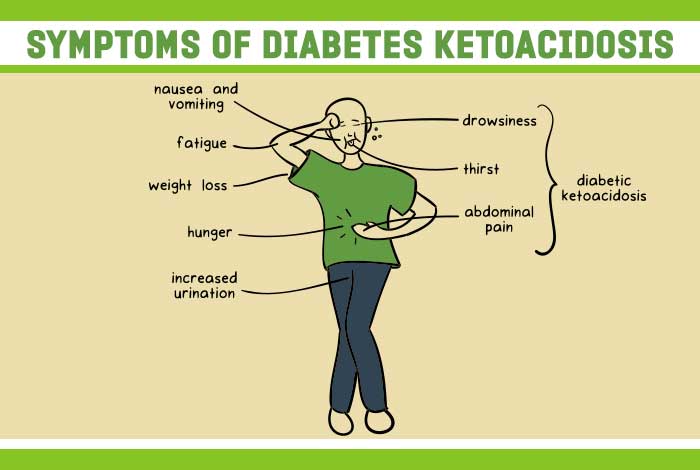
The signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis develop quickly and sometimes even within 24 hours.[3] Therefore, you need to look out for these indications and take emergency steps:
- Excessive thirst
- Nausea
- Frequent urination
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Fruity breath
- Confusion
You can also detect some of the more specific signs of diabetic ketoacidosis through home urine and blood testing kits:
-
- High blood sugar level (hyperglycemia)
- High ketone levels in your urine
Treatment of Diabetes Ketoacidosis

If you are diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis, you will be admitted in hospital and treatment will be focused on saving your life. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis involves:
Fluid replacement
You will be given a lot of fluids — either by mouth or intravenously- until your body is rehydrated. The administered fluid will help in replenishing fluids that is lost through excessive urination and will also help in diluting the glucose build up in your blood.
Electrolyte replacement
Electrolytes like sodium, chloride, and potassium are found in your blood that are charged minerals. When there is deficiency of insulin in the body, the level of these electrolytes can decrease which can cause a number of problems. Therefore, these minerals will be replenished in the body intravenously in order to keep your vital organs like heart, liver and nerves functioning properly.
Insulin therapy
Diabetic ketoacidosis can be reversed by insulin. Along with fluids and electrolytes, you will be given insulin therapy — usually through intravenously. It will be stopped when your blood glucose level reaches nearly 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) and it is no longer acidic. After that, you can continue with subcutaneous administration of insulin.
Final Word
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an emergency condition that can affect people with diabetes. But, if they are careful and keep their blood glucose level in check, they can avoid it and lead a healthy and fuller life. However, as a precaution, family, friends and colleagues of people with diabetes should be made aware of the symptoms of diabetes ketoacidosis so that they can take emergent steps when the situation arises




