CBD or cannabidiol is one among many compounds extracted from the cannabis plant that are collectively, known as cannabinoids. CBD derived from either hemp or marijuana plant. Don’t get confuse between hemp and marijuana! They are two distinct species of cannabis plant that varies on the basis of the concentration of psychoactive components. There are two components present in the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa), viz., CBD and THC or delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol. The oil that contains CBD as an active ingredient is called as CBD oil. Uses of CBD oils varies with varying concentration levels. THC is psychoactive, i.e., it has mind-altering properties. On the other hand, CBD is a non-psychoactive component and known to bear several therapeutic properties.
What is CBD Oil:
CBD hemp oil or simply, CBD oil is an oil-based product obtained from high-CBD and low-THC hemp. As hemp doesn’t contain any psychoactive component, this hemp CBD oil has applications for a bevy of medicinal purposes. CBD oil never extracts from marijuana plant because it is saturated with THC, a highly psychoactive compound. Another reason, that CBD oil is extracted from hemp and not marijuana, because, marijuana is still illegal in most of the countries except in several U.S. states. Whereas, hemp is legal in most countries and produced for industrial purposes and medicinal uses.

Nevertheless, you must be careful while buying a CBD hemp oil product. If the product contains 10 ml of CBD hemp oil and the CBD concentration is 8%, then the product actually contains 0.8 ml of pure CBD. A number of brands for the same product are available in the market. So, how to select the right product? Ideally, you should go for a product that has been advised to you by your expert. Further, you can a product that is certified by a reputed laboratory.
General Benefits of CBD Oil:
- Relives pain and inflammation.
- Reduces symptoms anxiety and sometimes, effective in patients of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD).
- In the treatment of breast cancer; CBD oil is known to restrict the growth of cancer cells lines.
- CBD oil is found be effective in the treatment of Type 1 diabetes.
- Patients of epilepsy – a neurological disorder – when treated with CBD, showed improvement, as reported by a group of researchers.
- Also, used in the treatment of acne.

How CBD Works Inside a Human Body:
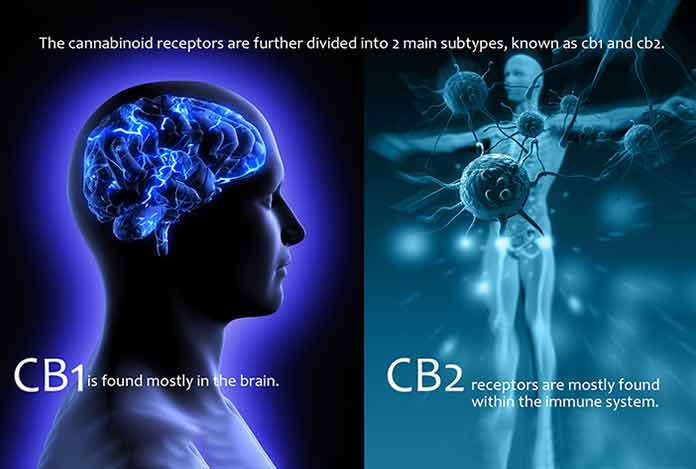
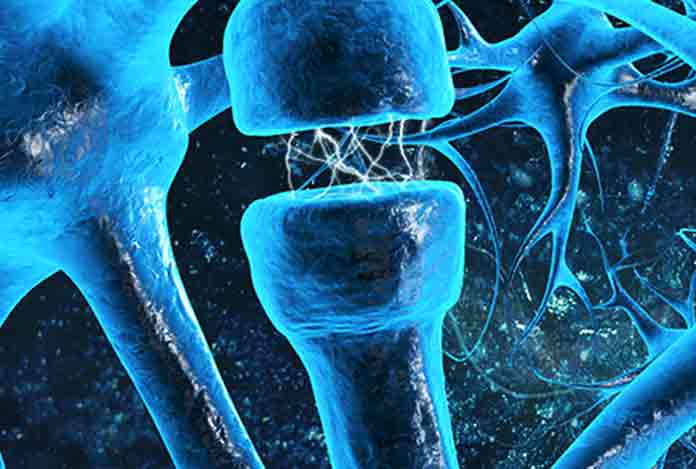
In general, human body is capable to produce cannabinoids (CBDs) whenever required. They are called endocannabinoids – a lipid-based neurotransmitters that bind with cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoid-receptor proteins. There are two types of cannabinoid receptors (CBD) present in the human body, mostly in the brain. These receptors are broadly classified into two categories, viz., CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors are majorly present in the brain and some in liver, kidney as well as lungs. CB2 receptors are part of the immune system. CB1 works for psychoactive cannabis components and stimulates the production and release of neurotransmitters. CB1 receptors of the brain controls behavioral coordination, such as thought, memory, mood, emotions, pain, comfort, appetite and so forth.
Whereas, CB2 regulates pain sensation and affects the immune functions. Study suggests, CB2 could impact programmed cell death. It also has effects on inflammation and pain.
Furthermore, new researches have pointed out that CBD doesn’t impact any of the receptors. Instead of direct interaction with the receptors, CBD stimulates the body to use its very own endocannabinoids. While CBD has low affinity for CB1 and CB2, it usually activates some ion channels and non-cannabinoid receptors. It functions across a couple of receptor-independent channels; for e.g., it delays the process of the reuptake of neurotransmitters (like adenosine and anandamide) and sometimes, inhibits or boosts the binding process of several G-coupled protein receptors.
Inside a human body, CBD majorly works as a reuptake inhibitor and allosteric modulator.
- Reuptake Inhibitor: According to a research, CBD acts as an anandamide (neurotransmitter) reuptake and breakdown inhibitor, and thus, elevates levels of endocannabinoid – the body’s very own CBD-like molecule – in the synapse of the brain. This activity is responsible for neuroprotective effects of CBD against seizures; in addition to several other health benefits. On the other hand, its anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory effects can be attributed to its ability to inhibit adenosine reuptake. By delaying the adenosine (neuromodulator) reuptake process, CBD increases the its level inside the brain. Incidentally, adenosine in brain controls the activity of adenosine receptors that are important for myocardial and cardiovascular functions.
- Allosteric Receptor Modulator: This implies that by altering the shape of a receptor, CBD can inhibit or boost receptor transmission. As reported in a study, CBD functions as a allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptor, i.e., it engages with GABA-A receptor to enhance its binding affinity for its agonist, gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) – an inhibitory neurotransmitter. CBD boosts the natural soothing effect of GABA by changing the shape of GABA-A receptors; thus, helps reduce anxiety.
Another research claimed CBD to be a CB1 receptor’s negative allosteric modulator. Unlike THC, CBD doesn’t attach with CB1, but alters its shape and reduces its capacity to attach with THC. For this reason, CBD-dominant products don’t allow people to feel “high” as in the case of THC-rich products.

Other Roles of CBD:
- Serotonin Receptors: CBD directly activates 5-HT1A (hydroxytryptamine) serotonin receptor, which is known for its anti-anxiety effects. This G-coupled protein receptor also has impact on other biological and neurological processes like addiction, anxiety, appetite, sense of pain, sleep, and nausea.

- Vanilloid Receptors: CBD interacts with TRPV1 (transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V Type 1) or vanilloid receptors that are associated with sense of pain, inflammation and body temperature.
- GPR55-Orphan receptor: This CBD acts as an antagonist by deactivating or restricting the G protein-coupled receptor, known as GPR55, which is known to regulate blood pressure and bone density. Hyperactivity of this receptor is associated with osteoporosis.
- PPARs Nuclear Receptors: The anti-cancer effect of CBD can be attributed to its ability to activate PPARs (peroxisome proliferator activated receptors) that are positioned on the surface of the nucleus inside cells. Activation of PPARs-gamma receptors is said to prevent cancer cell proliferation and known to be responsible for tumor regression in lung cancer. This activity also deteriorates amyloid-beta plaque – a molecule responsible for Alzheimer’s disease.
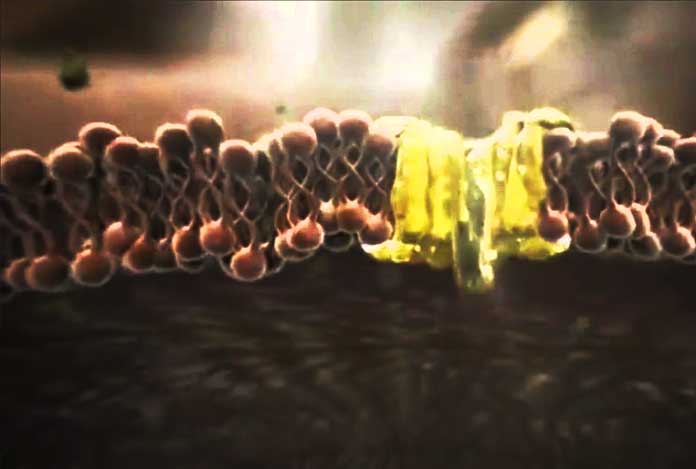
Source: projectcbd.org
