Overview and statistical facts:
Pancreatic cancer is the ninth most common cancer in women and the fourth leading cause of cancer death in men and women. Cancer is uncontrolled or abnormal growth of the cells in the body, that causes lumps or tissue masses known as tumours. The cells of malignant(cancerous) tumours have the ability to move from one place to another in the body and creating new cancers. This process is called metastasis. It is this property of metastasizing that makes cancers so deadly.
In 2017, there were about 53,670 cases reported of Pancreatic cancer in U.S. About 43,090 people are estimated to die of this cancer in 2017. The average lifetime risk is 1.5% which means 1 in every 65 people might have it. It spreads silently to the nearby organs without being diagnosed in the earlier stages making it one of the deadliest cancers. Pancreatic cancer is often difficult to diagnose due to the dearth of specific screening tests that can easily and reliably find early-stage pancreatic cancer in people who have no symptoms. This cancer is often not found until later stages when the cancer can no longer be removed with surgery and has spread from the pancreas to other parts of the body.
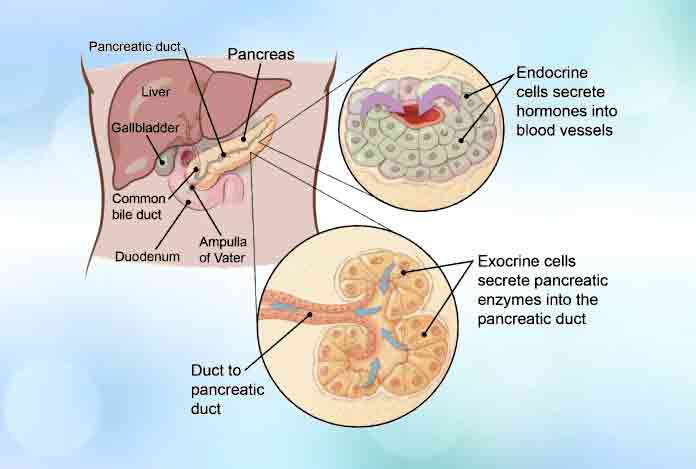
The pancreas is a pear-shaped gland located in the abdomen between the stomach and the spine. It has two parts.
- The exocrine part is responsible for making enzymes that are released into the small intestine to help the body digest and break down food, particularly fats.
- The endocrine part of the pancreas is made up of cells lumped together in different locations within this part of the pancreas, called islets of Langerhans. These cells make different hormones like as glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide (PP), and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). This part of pancreas is also responsible for synthesizing Insulin, which as well all know, is the substance that helps control the amount of sugar in the. blood in our body.
Types and symptoms:
There are several types of pancreatic cancer, depending on whether the cancer began in the exocrine or endocrine component
Exocrine pancreatic cancer- The exocrine part of pancreases makes digestive substances. Exocrine pancreatic cancer is by far the most common type of pancreatic cancer. The exocrine part of pancreases forms the 95% of the pancreas so most of the pancreatic cancers are exocrine and are due to pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Less common types of exocrine tumours are squamous cell carcinoma, adeno squamous carcinoma, giant cell carcinoma, acinar cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma
Endocrine pancreatic cancer- the endocrine part of pancreas produces hormones. Cancerous cells arising from this part of pancreas are called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (PNETs)or islet cell tumour. They are much less common than exocrine tumors, making up about 1% of pancreatic cancers. PNETs can be functioning or nonfunctioning in nature. A functioning tumor makes hormones while as nonfunctioning tumor does not make hormones. Functioning neuroendocrine tumors are named based on the hormone the cancerous cells normally make. These include:
- Insulinoma
- Glucagonoma
- Gastrinoma
- Somatostatinoma
- VIPomas
- PPomas
Symptoms of pancreatic cancer:
The symptoms of this cancer are not usually detected unless it has already reached an advanced stage but the following are the ones:
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Painful swelling of an arm or leg due to a blood clot
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in the upper part of the abdomen that advances further to the back
Jaundice - Dark urine or light stool
- Vomiting, itching or sense of nausea
- Bloating or swelling in the belly
Risk factors:
Some of the risk factors of the pancreatic cancer are:
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Workplace exposure to certain cancer inducing chemicals
- Obesity
- Family history of the same
- Older age as most of the cases are after age of 65
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Hepatitis B infection.
- Race/ethnicity
- Gender
- Obesity, diet, and alcohol
Inherited genetic syndromes such as hereditary ovarian and breast cancer syndrome, lynch syndrome Peutz- Jegher’s syndrome, familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome and Von hippel -lindau syndrome might lead to pancreatic cancer in future.

Do i have Pancreatic cancer?
If symptoms like diabetes, persistent weight loss, obesity, bowel obstruction, jaundice, and unexplained abdominal pain are present in a person, there might be a chance of pancreatic cancer. An abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen, called ascites, may be a sign of cancer. If all these symptoms are constant and occur for a consistent period of time along with a persistent abdominal pain it may be time to go see a doctor for a detailed diagnosis.
Causes and prevention:
1. Causes:
The causes of the pancreatic cancer are briefed below:
- Pancreatic cancer initiates when one of its cell sustains damage to its DNA content which leads to the abnormal or uncontrolled growth and division of the cell. This cell then goes on to create a tumour which can then travel elsewhere in the body through the lymphatic system or blood.
- Pancreatic cancer can be caused by the genetic mutations in the DNA or turning off or deletion of the tumour suppressor genes.
- There are innate gene mutations that pass from parents to the offspring resulting in development of cancer whereas there are several rare inherited syndromes that can make a person more predisposed to develop pancreatic cancer.
- Acquired gene mutations can be caused due to extended exposure with the cancer-causing chemicals or carcinogens but often what is the real cause behind this type of gene mutations is not yet known. When enough mutations occur, the cells become malignant and a tumour begins to grow.

Prevention of pancreatic cancer:
One can reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer by adopting a healthy life style.
- Quit smoke- Smoking is the most crucial risk factor linked with the cancer. Help from people, communities and rehabs can help you avoid smoking if you have been smoking.
- Maintain a healthy weight and have balanced diet- a healthy weight and balanced diet with proper nutrients intake can help in reducing the risk of the pancreatic cancer.
- Limit alcohol use: limiting the alcohol intake can considerably reduce your risk of the cancer.
- Reduce the workplace exposure of chemicals: reducing the exposure of cancer causing chemicals can reduce the risk of being threatened by the pancreatic cancer.

Diagnosis and tests:
Doctor make the diagnosis of pancreatic tumours by going through the following steps and tests:
- Medical history and physical exam: The doctor will ask about the detailed history of your symptoms, risk factors and the family presence of the cancer. A physical exam of the stomach would help him feel the presence of some swelling or bloating that might indicate the cancer. The doctor will then surely recommend several other tests to make sure that its cancer.
- Blood tests: the blood tests done for exocrine pancreatic cancer include liver function tests and other blood tests. Blood test for endocrine pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (NETs) are testing blood for high levels of glucose chromogranin A (CgA), and C- peptide. Serotonin is checked in the blood for carcinoid tumours.
- Imaging tests: there are several imaging tests that can be performed to detect the cancer and its extent. Some of these are computed tomography scan (CT), ultrasound, cholangiopancreatography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS), Positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
- Biopsy: Biopsy is the sure shot way of confirming the pancreatic cancer by taking a piece of the tumour and viewing it under the advanced microscope. Biopsies can be done in different manners including percutaneous biopsy, laparoscopy, surgical biopsy and endoscopic biopsy.
Treatment and care:
Treatment for the pancreatic cancer depends on the stage, location of the cancer cells, and also on the overall health and preferences of the patient. The treatment may include chemotherapy, surgery, radiation, or the combination of these.
1. Surgery- operations that are done for the pancreatic cancer involves surgery in pancreatic head, or pancreatic tail, whole pancreas or the surrounding vessels around the cancerous cells.
2. Chemotherapy- this method uses drugs to treat cancer. These drugs can be injected into a vein or can also be taken orally. Either you can be prescribed one drug or can be more than one drug. This may also be combined with radiation therapy to reduce or shrink the size of the cancer. Often chemoradiation can be used when the cancer has far spread beyond the pancreas. Chemoradiation can also be used after the treatment to prevent cancer relapse.
3. Radiation therapy- this therapy uses the high radiation beams such as the X rays for treatment of the cancer. This can be used simultaneously with the chemotherapy if the cancer can’t be treated by surgery. The X rays are often used externally focussing on the part that has cancer and also can be used during operation.
Care during the pancreatic cancer:
Supportive (palliative) care is specialized care that is provided to the terminally ill patients to reduce the pain and the symptoms of the lethal diseases like cancer. There are several doctors and special teams of medical experts that provide the extra support required to the patients and work in close association with the patient and their families.
Treatment to help one cope up with devastation and distress caused by this disease involves various alternative therapies that keep up the hopes of a cancer patient. The families, friends and the close ones of the patient can provide loving care and support a cancer patient needs to recover and stay sane during this lethal disease.
OTC and Self-management methods:
Being a type of cancer, pancreatic cancer does not have any OTC available. Nevertheless, the symptoms and the pain associated with the cancer can be lessened or reduced by the medications such as opioids and non-steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), but it is advisable to only use these drugs if prescribed by the doctor.
- One can manage the disease by being optimistic and involving oneself in music and other recreational activities like meditation, exercising and doing what one likes.
- Having a balanced and full of nutrition diet.
- Regular check-ups and follow ups with the doctor.
- Being self-motivational.
- Learning what you need to learn about cancer.
- Assembling a support system, finding someone to talk with and express your feelings.
- Connecting with other people with pancreatic cancer or any other type of cancer.
- Interacting with the survivors of cancer.

Natural ways to cure:
Natural ways to cure pancreatic cancer includes:
- Consider recreational options like art therapy, massaging, excercise, music therapy, meditation, relaxation exercises, spirituality and meditation.
- Eat foods that contain healthy fats, avoid excess sugar and salt
- Be as active as possible.
- Drink plenty of fluids and water to avoid dehydration.

Health tip by expert:
It is advised that the person should discuss the family history with the doctor in advance. Knowing the family history helps in better prognosis of pancreatic cancer.