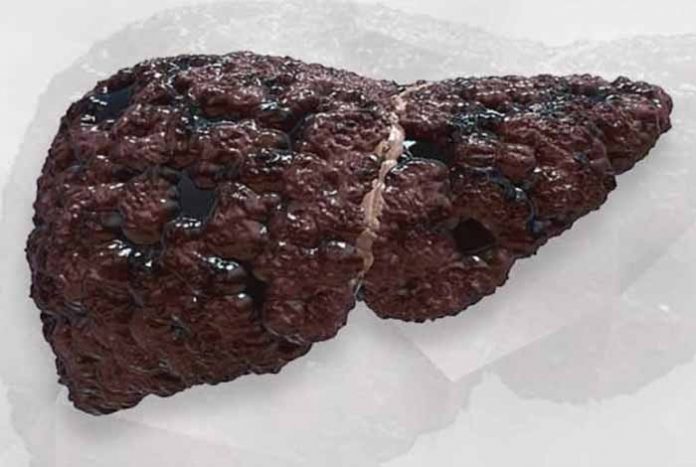

Overview and Facts
Liver is one of the most vital organs of the body. It performs numerous functions like detoxification of metabolites, protein synthesis and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. It is the only organ in the body, which can regenerate itself.
When there is an injury to the liver, its tissue tries to repair itself. During long-term illness or continuous injury, regeneration of liver tissues is incomplete and scar tissues start to develop. This buildup of scarred tissues in the organ leads to liver cirrhosis. These scarred tissues are unable to perform functions of normal tissue. According to the American Liver Foundation, liver cirrhosis is a life-threatening, irreversible disease.
Liver continues to function almost properly in the early stages of cirrhosis. Gradually, the scar tissue replaces healthy tissue, making the organ lumpy and hard, leading to liver failure.
A small percentage of people having liver cirrhosis develop liver cancer.
Liver cirrhosis is considered to be the 7th leading cause of death in the U.S. and the 3rd most-common cause for deaths of adults in the age group of 45-60 years. Men have 50% more chances of developing liver cirrhosis than women. It affects more than half malnourished chronic alcoholics in the world. In the U.S., it is estimated to kill approximately 31,000 people annually.
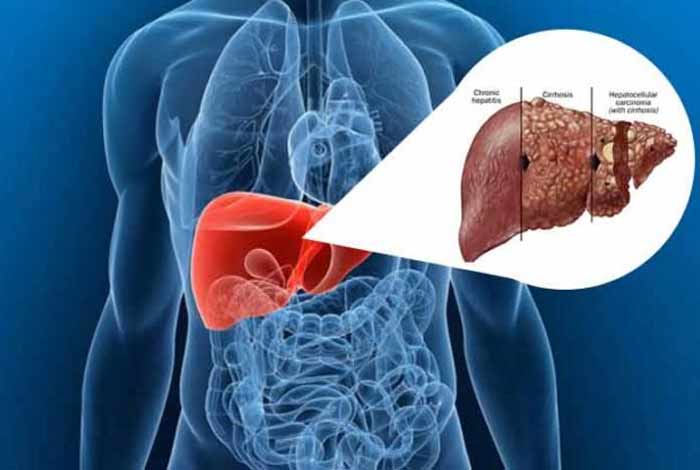
Types and Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis
Depending on the causes of liver cirrhosis, it can be classified into following types:
Laennec’s Cirrhosis: In this, cirrhosis generally occurs due to chronic alcoholism. It is the most common form of liver cirrhosis and occurs in about 30-50% of the cirrhotic patients.
Biliary Cirrhosis: It arises from a slow, progressive injury to the bile ducts, which causes obstruction to the flow of bile and bile toxins.
Postnecrotic Cirrhosis: It is characterized by destruction of the whole lobules of liver along with the collapse of reticular framework, leading to formation of scars. It results from different types of hepatitis.
Pigment Cirrhosis: It arises in patients suffering from hemochromatosis, i.e., too much iron in the body.
Cardiac Cirrhosis: It is caused due to failure of the right side of heart.
Idiopathic Cirrhosis: Idiopathic cirrhosis occurs due to unknown reasons.
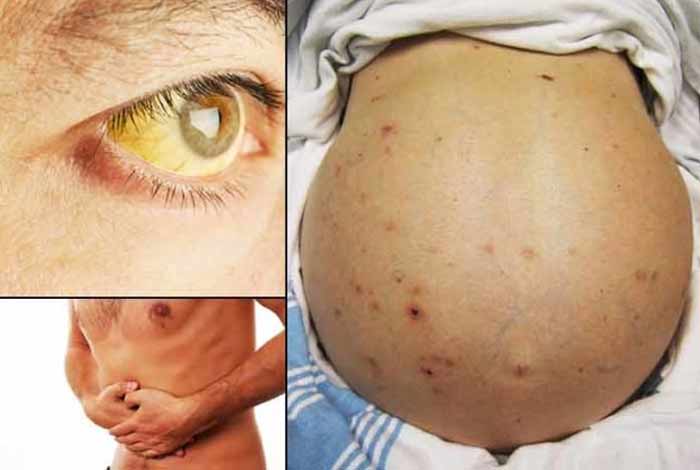
Liver cirrhosis does not show any symptom in the early stages of disease. It can only be detected in routine health check up. As the diseases progresses, following symptoms can be experienced:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Bloating of the abdomen due to ascites, which is a buildup of fluids in the abdomen
- Edema or swelling in the feet, ankles or legs
- Jaundice
- Spider angiomas, which is development of spider like blood vessels on the skin
- Itchy skin
- Bruising
- Confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech
- Breast enlargement in men
- Testicular atrophy in men
- Redness in palms
- Vomiting blood
- Dark, tarry-looking stools
Stages of Liver Cirrhosis
There are two stages of liver cirrhosis: compensated and decompensated.
- Compensated: In this stage, there are no symptoms of the disease. Healthy tissues outnumber scarred tissue and the needs of the body are met.
- Decompensated: Decompensated liver cirrhosis occurs when there is development of jaundice, variceal hemorrhage or hepatic encephalopathy. There are very less chances of survival in these patients without liver transplant.
Risk Factors of Liver Cirrhosis
People, who are at a risk of developing liver cirrhosis are:
- Alcoholics
- Patients with long-term liver disease like hepatitis B or C
- Patients with inherited liver disease such as hemochromatosis
- Patients with defective immune system
- Obese
- People exposed to toxins through ingestion, inhalation or skin absorption
- Patients with bile duct disorders
- Patients with severe reaction to certain prescription or over-the-counter medication
Age and gender also play a vital role in developing liver cirrhosis. Women between the age groups of 35-60 years are at a high risk of developing primary liver cirrhosis, whereas men in the age group of 30-40 are at a higher risk.

Do I have Liver Cirrhosis?
If you observe swollen and tender abdomen along with jaundice, changes in urine and stool color, irritated skin, increased nausea and vomiting along with fluid retention in the body, then there is a chance you might have liver cirrhosis. If you observe changes in your appetite along with confusion and drowsiness, then you should seek medical advice.
However, these symptoms are also indicative of other conditions like hepatitis, hypothyroidism or Crohn’s disease, which can only be diagnosed correctly by a doctor.

Causes and Prevention of Liver Cirrhosis
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis:
Following are the factors that can cause liver cirrhosis:
- Chronic Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C occurs due to a viral infection of hepatitis C virus (HCV). II is characterized by inflammation of the liver along with liver damage. Chronic hepatitis C causes liver damage, which over the years, can lead to liver cirrhosis.
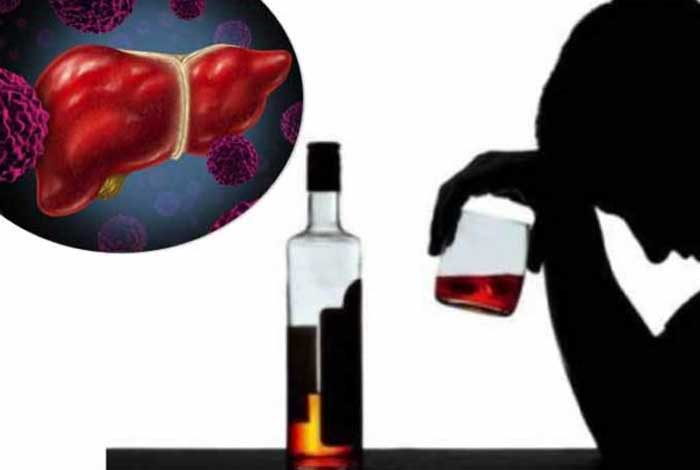
- Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Heavy alcohol consumption causes fat deposition and inflammation in the liver, which gradually leads to liver cirrhosis.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): In NAFLD, there is deposition of fat in the liver, which is not due to alcohol consumption. When this deposition of fat is accompanied by inflammation and liver cell damage, it leads to NASH. These conditions lead to fibrosis, which ultimately results in liver cirrhosis.
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B is caused due to the infection of hepatitis B virus which causes inflammation of the liver and damages it. It also causes liver fibrosis which in the end develop into liver cirrhosis.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: In this, the immune system attacks the liver cells and damages them. The liver tries to repair itself, forming scar tissues. In the long run, this leads to liver cirrhosis.
- Diseases that Damage, Destroy or Block Bile Ducts: Some of the diseases such as primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, Alagille syndrome, biliary atresia, cystic fibrosis, affect the bile duct causing it to become inflamed and damaged. This ultimately leads to cirrhosis.
- Inherited Diseases Affecting Liver: Diseases like hemochromatosis and Wilson disease are types of inherited diseases that interfere with the functioning of liver and leads to cirrhosis.
- Rare Viral Infection of Liver: Hepatitis D and E are rare infections of liver caused due to virus. Only people with a compromised immune system acquire these infections that result in liver inflammation and damage to liver cells, eventually leading to liver cirrhosis.
Other Causes:
- Reaction to medications
- Prolonged exposure to toxins
- Parasitic infections
- Chronic heart failure with liver congestion
While trauma or short-term injuries to the liver do not cause cirrhosis, it is only prolonged damage to liver cells that leads to cirrhosis.
Prevention of Liver Cirrhosis:
The only way to prevent liver cirrhosis is to diagnose liver damage and take necessary steps to stop further deterioration of the organ
Following steps might be taken to prevent liver damage:
1) Decreased Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol-related liver cirrhosis occurs due to heavy intake of alcohol for ten years or more. Women, who indulge in heavy drinking are more likely to develop liver cirrhosis than men.
2) Protection Against Hepatitis: Hepatitis, caused by virus, leads to liver inflammation and damage. These infections in their chronic forms result in liver cirrhosis. Vaccination can be an option for people, who are at a high risk of developing the hepatitis infections.
3) Monitoring Diet: Fatty buildup in the liver can cause NASH, which might lead to cirrhosis.
4) Physical Exams: People living in areas, where hepatitis B and C are common, should have regular check-ups and be screened for cirrhosis.

Diagnosis and Tests of Liver Cirrhosis
Following tests are performed to diagnose liver cirrhosis:
Medical and Family History
Family and medical history is taken into consideration as the foremost thing for diagnosing liver cirrhosis.
Physical Examination
Physical examination is performed to diagnose cirrhosis. A patient’s body is examined physically, and the sound from his abdomen is heard using a stethoscope. The medical health provider looks out for signs of hardness of liver or for presence of ascites, which might cause the abdomen to enlarge.
Blood Test
Blood test might be performed to analyze levels of liver enzyme and blood cell counts. It can be used to find the reason for liver cirrhosis like whether it is caused due to an infection of hepatitis B or C. It is also used for measuring the severity of cirrhosis by measuring the level of bilirubin (indicates the amount of bile pigment in the blood), creatinine (indicates the kidney function), and the international normalized ratio (determines the blood’s ability to clot).
These results are collectively used to calculating Model for End-stage Liver Diseases (MELD) score. It is used to predict 90-day survival rate of patients having an end-stage liver disease. It also determines whether the patient is eligible for liver transplant.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are used to determine the signs of advanced liver cirrhosis, such as deformities on liver surface, splenomegaly and gastric varices. It also helps in determining signs of complications like ascites and liver cancer.
Ultrasound
It is used to create the image of the organ using sound waves to examine the liver.
CT scan
In this test, X-rays and computer technology are used to create images of liver. For the test, the patient is made to drink a solution and an injection of a special dye is given to the patient.
MRI
In this test, images of liver are created using radio waves and magnets. It produces detailed image of a person’s liver.
Elastography
It this test, ultrasound or MRI is used to determine stiffness of liver occurring due to scar tissue formation. It helps in determining the severity of scarring and its progression.
Liver Biopsy
In this test, a tissue from the patient’s liver is taken and analyzed for damage. It is used to confirm liver cirrhosis.
Endoscopy
In this test, a thin, flexible tube with a camera at its end is introduced through the patient’s mouth into his stomach. The images captured of esophagus and stomach are analyzed for swollen veins or varices, which indicate cirrhosis.
Other Tests
- Blood tests may be performed for determining blood ammonia levels, blood sugar levels, magnesium levels, potassium levels, sodium levels and so on.
- Blood tests are also performed to check inflammation of liver by performing aspartate aminotransferase test (AST), alanine aminotransferase test (ALT), lactate dehydrogenase test (LDH), alkaline phosphatase test (ALP) and gamma galactosyltransferase test (GGT).
- Blood tests are performed to determine the function of liver. These tests determine the levels of albumin, total serum protein and bilirubin as well as partial thromboplastin time.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatogram (ERCP) is used to look inside the liver bile ducts, pancreatic ducts and gallbladder. It is used to rule out primary sclerosing cholangitis as a cause of liver cirrhosis.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) testing is done to screen patients of liver cancer.
Treatment and Care of Liver Cirrhosis
In the early stages of cirrhosis, treatment is aimed at slowing down the progression of disease. In the later stages, the treatment aims at managing the complications. The patient might even require hospitalization.
Treatment includes the following:
1) Abstinence from Alcohol and Substance Abuse
People with chronic alcoholism are suggested to stay away from alcohol or substance abuse as both are known to cause liver damage.
2) Viral Hepatitis Vaccination and Screening
Patients suffering from cirrhosis should be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B as infection from any of these viruses can cause worsen the condition. Liver cirrhosis patients should be screened for hepatitis C as well.
3) Treating Causes of Cirrhosis
Hepatitis B and C can be cured in some cases by using antiviral medicines. Auto-immune hepatitis is cured by using corticosteroids, that suppress the immune system. Hemochromatosis and Wilson diseases can be cured if they are detected in early stages. Liver diseases arising due to blockage or loss of bile ducts can be cured by prescribing ursodiol (UDCA) which is a nontoxic bile acid which can be taken orally. It replaces the toxic bile acids produced in the liver due to blockage of bile ducts.
4) Treating Symptoms and Complications of Liver Cirrhosis
Itching and Abdominal Pain: Itching and pain in the abdomen can be managed by taking medicines which help in relieving these symptoms. However, these should only be taken under medical supervision.
- Portal Hypertension: Beta blockers or nitrates are prescribed for treating portal hypertension. Beta blockers slow down the heart and lower the blood pressure, whereas nitrates widen the blood vessels, thereby allowing more blood to flow through the veins.
- Varices: Beta blockers are used to decrease the pressure in varices and decrease the probability of bleeding. Immediate upper endoscopy is required if bleeding occurs in stomach or esophagus. Endoscope can be used to place a special band around the varices, which causes the cells to die and fall off.
- Edema and Ascites: Diuretics are used to remove fluid from the abdomen to treat edema and ascites. Antibiotics might be prescribed for treating any bacterial infection in the abdominal fluid.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: It refers to neuropsychiatric abnormalities that occur in the brain of people suffering from liver problems. It is treated by cleansing the bowel with lactulose, which is a laxative. Antibiotics might also be given along with lactulose to treat any bacterial infection. The condition gets better with the improvement in other complications of liver cirrhosis.
- Hepatorenal Syndrome: Liver cirrhosis patients, who develop renal symptoms are made to undergo regular dialysis to filter waste and extra fluids. Medicines are also prescribed to improve blood flow through kidneys.
- Osteoporosis: Bis-phosphates are prescribed to improve bone density.
Gallstones and Bile Duct Stones: Surgery and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography might be used to remove gallstones and bile duct stones, respectively. - Liver Cancer: Liver cancer screening test is performed every 6 to 12 months from the early detection of cancer. Treatment of cancer is more effective when it is diagnosed at an early stage.
- Liver Transplant: Liver transplant is suggested when liver cirrhosis leads to liver failure or when the treatment of cirrhosis is ineffective.
In this procedure, the diseased liver is removed from the patient’s body and replaced with a healthy whole or part of the liver from a donor.
Liver cirrhosis does not show symptoms in the initial phases. Regular health check-ups is hence required for early diagnosis. Lifestyle changes, such as abstinence from alcohol and substance abuse should be done. People suffering from chronic alcoholism might require assistance to completely give up alcohol. People with a high risk of developing liver cirrhosis should take care of their liver and try to minimize the risk factors responsible for liver damage.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Liver Cirrhosis
Over-the-counter medication is strictly prohibited in patients with liver cirrhosis. Any medication should be taken only under medical supervision.
For self-managing the disease, lifestyle changes should be employed. This may involve abstinence from alcohol and substance abuse along with prevention from viral hepatitis. Healthy diets should be taken, and weight should be managed effectively. Obese patients must try to achieve a healthy body mass index (BMI).

Natural Ways to Cure Liver Cirrhosis
Patients suffering from liver cirrhosis should try to cleanse their liver regularly. Following foods can be included in the diet that helps in naturally detoxifying the liver:
- Dark green, leafy vegetables
- Citrus fruits
- Sweet potatoes
- Bananas
- Avocado
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Lemon juice
- Raw apple cider vinegar
- Following foods should be avoided as they can stress the liver:
- Refined carbohydrates containing gluten
- Sugar
- Too much caffeine
- Fried foods
Following are the liver-supporting vegetables:
- Cauliflower
- Broccoli
- Celery
- Asparagus
- Carrot
- Cucumber
- Herbs like parsley, mint, cilantro and basil
Following supplements can be taken that help liver to produce proper bile and enzymes:
- Milk thistle, known as the “king of detoxifying herbs”
- Turmeric
- Probiotics

Health Tip by Expert
Liver cirrhosis is an irreversible condition that can be prevented by following a healthy lifestyle and protecting oneself from hepatitis-causing viral infections. Alcohol consumption should be monitored, and substance abuse should be avoided. People, who indulge in heavy intake of alcohol, should get their liver checked at regular intervals, so that liver damage can be diagnosed at an early stage. Weight management should be done by obese people.
