
Overview and Statistical Facts of Insomnia
Sleep is a condition of mind and body, which occurs routinely and persistently for several hours, every day. During sleep, consciousness alters, voluntary muscles relaxes and interaction with the surroundings reduces. Lack of sleep can take a toll on a person’s health, work performance and overall quality of life.
Insomnia or sleeplessness refers to a sleep disorder in which people face trouble falling asleep or staying asleep even when the person has a chance to do it. People with insomnia experience ‘early morning wakening’ or are unable to have restorative sleep. They experience daytime fatigue, confusion, mood disturbances and irritability.
Most adults experience insomnia at some point of their lives. Insomnia cannot be defined by the number of hours of sleep a person gets, because sleep requirements and practices differ a lot among people.
Insomnia affects people in all age groups. Women have 50% more chance of developing insomnia than men. Its incidence tends to increase with age. This sleep disorder is more common in people belonging to lower socio-economic groups, post-traumatic stress disorder patients, people with other mental disorders and chronic alcoholics.
Lately, insomnia has emerged as one of the most common and best-known conditions among all sleep disorders. In the U.S. itself, 50 to 70 million people suffer from some kind of sleep disorder. It has been estimated that 1 out of every 3 adults in the U.S. get less than 7 hours of nighttime sleep on a regular basis. About 40% of people in the U.S. have been reported to suffer from insomnia. There are approximately 10 million people in the U.S., who use prescription sleep aids for falling asleep.
Insomnia costs the U.S. economy more than 15 billion USD annually as health care costs. It has been estimated that American industries lose around 150 billion USD each year due to sleep-deprived workers. Moreover, insomnia is also one of the leading causes for road accidents. To spread awareness about this disorder, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has declared March 10th as ‘Insomnia Awareness Day.’

Types and Symptoms of Insomnia
Insomnia can be classified in various ways.
A. Classification According to Time:
1. Transient Insomnia: When the symptoms of insomnia last up to three nights, it is called transient insomnia.
2. Acute or Short-Term Insomnia: Acute insomnia lasts for a short period of time; generally lasting for several weeks.
3. Chronic Insomnia: It is the type of insomnia that lasts for several months and sometimes years. It generally arises due to some underlying conditions.
B. Classification According to Cause:
1. Primary Insomnia: It arises when no medical condition is responsible for sleeplessness.
2. Secondary Insomnia: It develops when asthma, chronic pain, depression, cancer, heartburn, arthritis or any other health condition is responsible for sleeplessness. Certain medicines, or indulging in alcohol or substance abuse can also be a probable cause of this type of insomnia.
C. Classification as given by The American Academy of Sleep Medicine:
1. Adjustment Insomnia: It is also called acute or short-term insomnia, and is usually caused due to stress. The symptoms vanish as soon as the stress-inducing factors go away, or the person gets adapted to the stress. It is to be noted that stress does not always stem from a negative experience, but a positive situation can also make a person too excited to sleep.
2. Behavioral Insomnia of Childhood: It is commonly found in children, who do not go to bed unless forced by a parent or guardian. If strict bedtimes are not enforced, the child might lay awake for several hours at night.
3. Idiopathic Insomnia: This is said to occur, when a particular cause cannot be defined for an insomnia that starts during infancy or childhood, but continues in the adulthood.
It is not caused by any of the following reasons:
- Medical problems
- Psychiatric disorders
- Stress events
- Medication use
- Other behavior
- Other sleep-disorders
It might be caused due to some imbalances in the body like overactive awakening system and/or underactive sleep system. However, the real cause of this type if insomnia is still not clear.
4. Insomnia due to Drug or Substance Abuse: This type of insomnia occurs directly due to consumption of caffeine, alcohol or certain medicines. It generally goes away once a person stops using them.
5. Insomnia due to Medical Condition: Several medical conditions can also cause insomnia. The course and severity of insomnia is directly proportional to the severity of medical condition.
6. Insomnia Non-Organic, Unspecified: When substance use and other physical causes of insomnia have been ruled out, the condition is regarded as non-organic, unspecified insomnia. This name is given on a temporary basis until the exact cause of insomnia is determined. It is generally caused due to some underlying mental health disorder, sleep disruptive behavior or psychological factors.
7. Insomnia due to Mental Disorder: Insomnia can also occur due to some mental disorders like depression and Parkinson’s.
8. Insomnia due to Inadequate Sleep Hygiene: Inadequate sleep hygiene can cause problem is sleeping.
9. Paradoxical Insomnia: It is a severe form of insomnia, which occurs without any evidence of sleep disturbances. The severity of daytime effects due to insomnia could vary. These insomniacs report little or no sleep along with an intense awareness about external environment or internal processes that are consistent with being awake. It generally indicates a state of hyper arousal. These people overestimate the time taken by them to fall asleep and underestimate their total sleep time.
10. Psycho-Physiological Insomnia: This type of insomnia occurs due to excessive worrying about falling asleep. It might start suddenly after some event or might develop over years. These people become tensed about their sleeplessness and associated tiredness the next day; which adds to their insomnia.
11. Organic Insomnia, Unspecified: Any medical condition, physical disorder or substance abuse can lead to this type of insomnia. However, this is said to occur until the exact cause is not identified. Further tests are required to pinpoint the specific reason for the same. In other words, the name is used on a temporary basis until the correct diagnosis is made.
Symptoms of Insomnia:
Incidentally, insomnia in itself can point towards an underlying health condition. However, following are the symptoms associated with insomnia:
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Waking up frequently during night
- Daytime fatigue or sleepiness
- Irritation, depression or anxiety
- Poor concentration and focus
- Being uncoordinated; increased accidents and errors
- Tension headaches
- Difficulty in socializing
- Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and stomach ache
- Worrying about sleeping
- Feeling unrefreshed upon waking
- Waking up too early

Risk Factors of Insomnia
Insomnia is a condition which can occur at any age, and affects women more than men.
Some of the factors that increase the risk of developing insomnia are:
- High levels of stress
- Lower income
- Traveling to different time zones
- Medical conditions
- Sedentary lifestyles
- Emotional disorders like depression and distress related to a traumatic life event
- Changes in work hours or night shifts
- Old age; individuals above 60 years
- Use of illegal drugs
- Pregnant women
- Menopausal women
- Alcoholics

Do I Have Insomnia?
If you find it difficult to fall asleep or experience frequent night time awakenings or wake up too early in the morning, then you might have insomnia. If you find thoughts running through your mind that are keeping you awake at night, or you feel afraid while going to sleep and find it difficult to relax completely; then there is some problem with your sleep.
Even after sleeping for sufficient hours in a day, you don’t feel refreshed or have muscle and joint stiffness along with aches all over the body, then without delay, you must consult a doctor specializing in sleep medicine.
Sleeplessness can be caused due to a number of factors and there are high chances that by eliminating those factors, you can manage to get good sleep.

Causes and Prevention of Insomnia
Causes of Insomnia:
Insomnia can be a primary disorder or might occur due to any underlying medical condition. By treating the underlying cause of insomnia, patient can again have peaceful sleep but in some cases, it can last for years.
Some of the common causes of insomnia are:
- Stress: Excessive worrying about everyday activities can increase anxiety and stress that might result in sleepiness. Death of a loved one, divorce, job loss and other stressful life events can also lead to insomnia.
- Travel or Work Schedule: The body’s circadian rhythm acts as an internal clock for maintaining balance in sleep wake cycle, metabolism and other important functions. Any disruption in this rhythm can result in insomnia. People, who travel in different time zones, or work late or early shifts, or have frequently changing shifts are known to suffer from insomnia.
- Poor Sleep Habits: Irregular bed timings, naps, involvement in stimulating activities just before bed, using bed for work or eating, watching TV, playing computer or video games and other such activities that could disrupt sleep-wake cycle might lead to insomnia.
- Heavy Meals before Bedtime: People can experience discomfort while lying down in bed after a heavy meal. It can also cause heartburn, and back-flow of food and acid from the stomach into esophagus, which can keep the person awake in bed.
- Mental Health Disorder: Anxiety disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder, depression and other mental health conditions can disrupt a person’s sleep cycle.
- Medications: Antidepressants, anti-asthmatics, anti-hypertensives and other such medicines can cause insomnia. Some of the pain relievers, allergy and cold medications, and weight-loss products contain high amounts of caffeine and other stimulants that can cause insomnia.
- Medical Conditions: People suffering from chronic pain, diabetes, asthma, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, cancer and other chronic diseases often suffer from insomnia.
- Sleep-Related Disorders: Sleep apnea is a condition in which a person has difficulty in breathing periodically throughout the night, which could disrupt his/her sleep. Another condition, called Restless legs syndrome causes unpleasant sensations in the patient’s legs, making it difficult for a person to move his/her legs. These conditions prevent a person from having a good sleep.
- Caffeine, Nicotine and Alcohol: Consumption of coffee, tea and other drinks containing high amounts of caffeine can prevent a person from falling asleep as caffeine acts as a brain stimulant. Similarly, nicotine present in tobacco products also acts as a stimulant and keeps a person awake. Alcohol, on the other hand, can cause drowsiness and help a person in falling asleep, but it prevents deeper stages of sleep and might even cause frequent awakenings throughout the night.
- Environmental Conditions: Unsuitable environmental conditions like excessive noise and, too high or too low room temperature can also cause insomnia in some people.
- Drug Withdrawal: Withdrawing from substance, alcohol or sedatives can also lead to insomnia.
Chronic insomnia occurs when there is some underlying medical condition, or if a person indulges in substance abuse. Treating the medical condition might help in improving the overall sleep quality, but in some cases, insomnia can persist even after the condition is cured.

Prevention of Insomnia:
Insomnia can be prevented by adopting following measures:
- Relaxation techniques can help in decreasing stress and anxiety and promote good sleep.
- Loud noises, extremely low or high temperatures and bright lights in the bedroom should be avoided as they hinder good sleep. Bed should only be used for sleeping and no other activity like eating or working.
- People with insomnia should fix their sleep times to maintain their circadian rhythm.
- Large meals, strenuous exercises and other such activities which can result in sleeplessness should be avoided just before bedtime.
- Foods containing stimulants like caffeine should be not be consumed before going to sleep.
- Listening to soothing music or reading can also help a person in falling asleep.
- Daytime naps should be avoided unless it is directed by a doctor.
- Sleep hygiene should be maintained.
- Laptops, mobile phone and other electronic gadgets should not be used during bedtime.

Diagnosis and Tests for Insomnia
Insomnia is diagnosed by performing the following tests:
- Physical Examination: In patients, where the reason for insomnia is not apparent, a physical examination is performed to check for any underlying medical condition. Also, the size of neck, oral and nasal air passages are measured along with a thorough examination of heart and lungs. The patient is also asked for any recent weight gains and snoring.
- Sleep Study: An overnight sleep test might be performed in specialized ‘sleep labs’ by doctors specializing in sleep medicine and pulmonary specialists. A number of tests are performed to monitor brain waves, breathing pattern, eye and body movements, heartbeat and other activities while the patient is asleep. However, the sleep test is not a part of routine, initial test for insomnia.
- Sleep Habits Review: The patient’s complete sleep-wake pattern and level of daytime sleepiness is determined by the physician. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale, comprising a short questionnaire, is employed to assess the daytime sleepiness. The patient is also asked to maintain a sleep diary to collect proper information about the condition.
- Patient history: The doctor might take an extensive history of the patient about his alcohol and drug use, stressful work or social situations, sleeping habits of bed partner, work shifts, and routine medications being taken.
- Actigraphy: This technique is used to determine sleep-wake pattern over time buy using a device called actigraph. These are small devices that can be worn on the wrist to measure movements. Actigraph provides objective data about daytime activity of a patient.
Treatment and Care of Insomnia
Treatment of Insomnia:
To manage insomnia, its cause(s) should be taken into consideration. Sleep habits should be changed and any underlying condition like stress, disease or use of medicines should be addressed. If these changes do not help, the doctor might recommend medicines, cognitive behavioral therapy, or both for the treatment of insomnia.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
This therapy helps a person in controlling or eliminating negative thoughts and actions that can be stressful for a person and keep him awake during the night. It is generally recommended as the first line treatment for insomnia. This therapy is nearly as effective as sleep medication.
Through this therapy, patients are taught to recognize and change their beliefs that are affecting their sleep. It plays an important role in breaking the cycle in which a person is unable to sleep, because he/she keeps on worrying about getting asleep.
Some of the strategies that are taught in this therapy include:
- Stimulus Control Therapy: In this method, a person is taught how to remove those factors that can prevent a person from falling asleep. He/she is coached to maintain a consistent bedtime and wake time, avoid naps during day, and use bed only for sleeping. Also, the patient is instructed to leave the room if he/she is unable to fall asleep within 20 minutes and return only when sleepy.
- Relaxation Techniques: Breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation and biofeedback are some of the relaxation techniques that can be used to reduce anxiety in bed. These techniques help control breathing, heart rate, mood and muscle tension.
- Sleep Restriction: Through this therapy, a person is instructed to decrease the time spent in bed, and avoid naps during the day time. This can lead to sleep deprivation, and eventually, increased tiredness the next night.
- Remaining Passively Awake: This therapy is also called paradoxical intention, in which a person is directed to get in bed and try to stay awake rather than sleep. This helps in reducing anxiety about sleep.
- Light Therapy: Light can be used to adjust internal or biological clock. A person is recommended to go outside when there is light outdoors during evening or use a light box.
2. Medication
Doctors might prescribe hypnotic medications to help patients fall asleep, stay asleep, or both. Usually, these drugs are not recommended for more than a few weeks, but some are prescribed for long-term use. Major classes of medications prescribed for insomnia include benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepines and melatonin receptor agonists. Some of the commonly prescribed drugs are zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon and ramelteon.
Care for People with Insomnia:
Insomniacs can manage their sleeplessness by following a strict routine for their sleep and maintaining proper sleep hygiene. Being active during daytime and avoiding naps can help in falling asleep easily at night. Decreased intake of caffeine, alcohol and nicotine can aid in improving sleep quality. Family and friends can help a person in getting rid of his/her stress. Any medication that is causing sleeplessness, can be discussed with a doctor. Acupuncture, yoga, Tai chi or meditation are some of the alternative medicines that can help a person to effectively manage insomnia.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods of Insomnia
OTC Medications for Insomnia:
Over-the-counter (OTC) medicines containing antihistamines can induce drowsiness in people, but these are not meant for regular use as these can cause daytime sleepiness, confusion, cognitive decline and dizziness. Some of these medications are diphenhydramine and doxylamine. Also, melatonin is an OTC supplement available for managing insomnia for a few weeks.
Self-Management Methods for Insomnia:
For self-managing insomnia, following steps can be taken:
- Sticking to a sleep schedule
- Being physically active
- Avoiding or limiting daytime naps
- Avoiding or limiting caffeine and alcohol intake
- Avoiding nicotine and nicotine containing products
- Treating pain
- Avoiding large meals just before bedtime
- Checking medications that might be causing insomnia
- Ensuring adequate exposure to natural light
- Having a pleasant sleep environment
- Maintaining healthy sleep-wake cycle

Natural Ways to Cure Insomnia
Following remedies can be used to manage insomnia naturally:
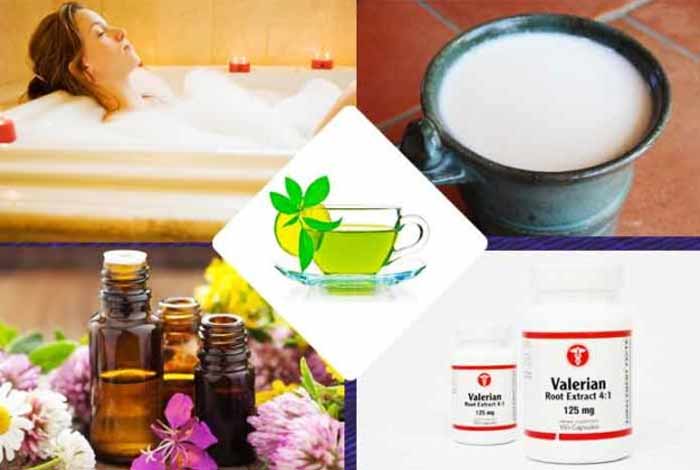
- Valerian: It is a dietary supplement that has been known to possess mild sleep-inducing properties due to the presence of valerenic acid and valerenol – the active ingredients found in Valerian root. It is known to increase the amount of a neurochemical in the brain, called gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps regulate nerve cells and decreases anxiety.
- Essential Oils: Essential oils obtained from lavender and chamomile can help in relaxing a person and induce sleep. Chamomile is one of the best medicinal herbs that help fight against anxiety and promote relaxation. Certain aromatics present in lavender oil help relax the body.
- Raw/Warm Milk: Consuming raw milk before bedtime can help in having a good sleep. Milk contains an amino acid, called tryptophan that helps in secreting serotonin, which causes drowsiness in people. However, some researchers debate this reason for the sleep-inducing properties of milk. Some experts consider psychological aspect of milk being the main reason for inducing sleep. Milk brings back feeling of comfort and remembrance; thereby calming a person and stimulating secretion of serotonin that lead to sleepiness.
Honey can also be added in the milk for enhanced effect. - Warm Bath: Warm baths can help a person in falling asleep. After a warm bath, when a person enters a relatively cooler bedroom, his/her body temperature falls. This signals the body to rest. Essential metabolic functions like heart rate, digestion and breathing decrease and the person turns sleepy.
- Green Tea: L-theanine is an amino acid found in green tea that helps in decreasing anxiety and brings overall relaxation. It decreases heart rate and immune responses to stress. It stimulates release of feel-good hormones and induces brain waves that are linked to relaxation.

Health Tip by Experts
Insomnia is a condition that affects almost everyone at some point of time. It can easily be managed by following good sleep hygienic practices. If there is any underlying medical condition that is causing insomnia, it should be discussed with a doctor.
Being physically active and getting exposed to daylight also helps in maintaining sleep-wake cycle. When traveling across different time zones, enough time should be given to the body, so that it can adjust its internal clock. Insomnia can be easily managed with CBT. Sleep-inducing medicines have a habit-forming tendency, and should not be used for long.




