Given our present lifestyle and food choices, all of us are under the constant threat of getting Diabetes. When the threat is looming so hard on us it becomes absolutely necessary to know all about Blood Sugar Level and how to keep them under check so that this devastating silent killer doesn’t affect us.
So, let’s know all about Blood Sugar and why is it important to keep it in check.
- What is blood sugar?
- What regulates this blood sugar in our blood?
- What if this regulation doesn’t work. What happens then?
- What are the normal blood glucose level ranges in our body?
- What is a blood sugar test?
- Usefulness of Blood Sugar Test
- Risks of Blood Sugar Test
- When to test for blood sugar
- How are blood glucose tests performed?
- Who should undergo diabetes testing?
- Blood Tests for Diabetes
- Conclusion
What is blood sugar?
Blood sugar is the sugar that is transported through our bloodstream to different cells in our body so that these cells generate energy from it to keep us alive. Glucose is a simple form of sugar that is transported by our blood and it is the only form of sugar that can be utilized by our body for generation of energy.
So, blood sugar always means blood glucose.
Where does our blood get this sugar from?
When we eat food, it gets digested in our body and gets converted into glucose. This glucose goes straight from our digestive system into our bloodstream.
What is the use of this blood sugar?
This glucose gets transported by our blood to all the cells in our body and is the food for our cells. Once inside the cells it gets converted into energy by the enzymes present in the cells and this energy is then utilized by us to do our day to day activities.
What regulates this blood sugar in our blood?
The level of sugar or glucose in our body is regulated so that they are neither too low nor too high. This regulation is done by pancreas by secreting two hormones insulin and glucagon.
When we eat food, it gets digested and converted into glucose. This glucose is taken up by our blood and the concentration of glucose increases in the blood. This increased blood sugar level acts as a signal for pancreas to secrete insulin. This insulin is a must for glucose to enter into cells. Secretion of insulin lowers blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by the cells
Extra glucose is stored in the form of glycogen in the liver. And if we haven’t eaten for a while and our blood sugar concentrations are low then pancreas secretes hormone glucagon which breaks down glycogen in liver to release glucose.
What if this regulation doesn’t work. What happens then?
Normally the blood sugar levels in the body are regulated but sometimes this regulation gets disturbed due to a number of reasons which can lead to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Hyperglycemia is a condition where the levels of glucose in blood are way above the normal level. Prolonged high levels of sugar in blood have a devastating effect on the whole body. Diabetes is a very common cause of hyperglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is a condition where blood sugar levels are below normal. Hypoglycemia can be fatal if the blood sugar levels become critically low and a person can go in coma or even die.
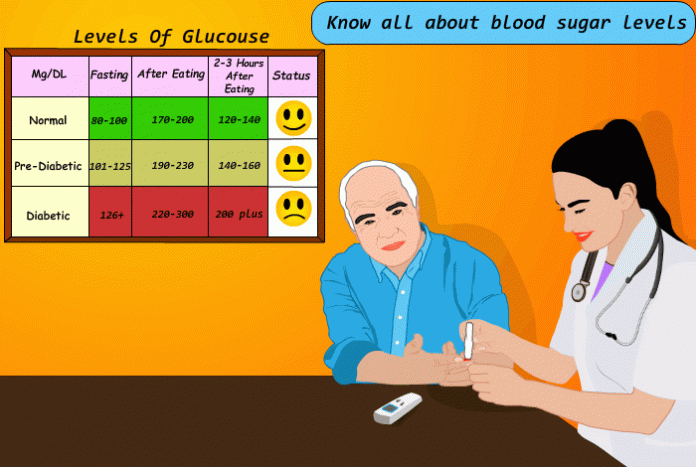
What are the Normal Blood Glucose Level ranges in our body?
Normal blood glucose level varies throughout the day. A fasting blood glucose level on awakening should be below 100 mg/dL. Before meal, the average blood glucose level for a normal person should be between 70-90 mg/dL. Postprandial blood glucose level is measured 2 hours after consuming food and should be less than 140 mg/dL.
American Diabetes Association (ADA)[1]advises to keep blood glucose levels between 80-130 mg/dL before meals and below 180 mg/dL 1-2 hours after meals in diabetics.
Most diabetic people aim for having a blood glucose level near the normal blood glucose levels of non-diabetic patients. Lower numbers of blood glucose level require careful monitoring of diet and regular exercise.
Measuring Blood Glucose Level
In the U.S., blood glucose level is normally measured in milligram per deciliter (mg/dL). However, in Canada and U.K., it is reported in millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Canadian or British units of measuring blood glucose levels can be converted into American units of measurement by multiplying it with 18.
What is HbA1C?
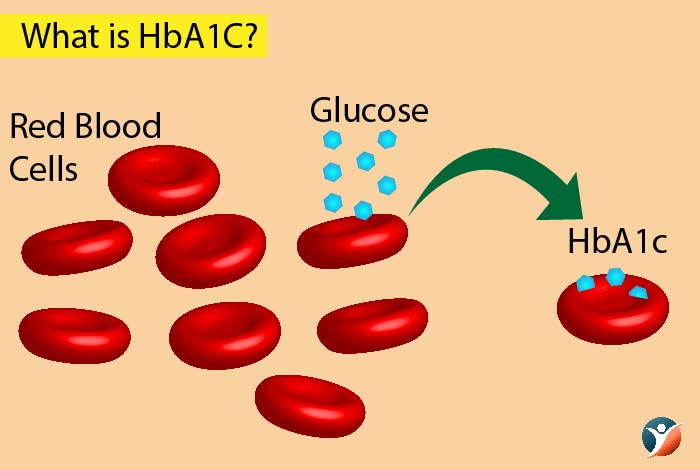
The term HbA1C refers to hemoglobin that is attached to glucose. Hemoglobin is a red pigment that transports oxygen throughout the body and and gets joined with glucose to form glycated hemoglobin. By determining the level of HbA1C in the body, we can determine the average blood glucose level for past several weeks or months. This is because hemoglobin has an average life span of 120 days and therefore by using glycated hemoglobin molecule, we can determine the blood glucose level of the last 120 days approximately.
HbA1C is expressed in the form of percentage. Non-diabetic people have an HbA1C level below 5.7%. The ADA recommends that diabetic people should aim to maintain their HbA1C level lower than 7.0%.
Keeping a check on the blood glucose level is extremely important to manage your diabetes. For this, blood tests are done to determine the level of glucose in the blood.
What is a blood sugar test?

A blood sugar test refers to a procedure that is done to determine the amount of glucose present in the blood. This test might be ordered by the doctor to diagnose diabetes. People who suffer from diabetes can also do these tests in order to monitor their blood glucose levels.
Blood sugar test gives instant information about the following parameters:
- Diet and exercise routine
- Whether the anti-diabetic medicines are working
- High or low blood glucose levels
Doctors might also prescribe this test in order to determine whether a person is healthy, prediabetic or diabetic.
The risk of developing diabetes increases when the following criteria are met:
- Age is 45 years or more
- Overweight or obese
- Not being active physically
- High blood glucose, triglycerides levels
- Low good cholesterol levels
- History of gestational diabetes
- Gave birth recently and the baby weighed more than 9 pounds
- History of insulin resistance
- Asian, Hispanic, African, Pacific Islander or Native American origin
- Family history of diabetes
Blood test for determining glucose levels can be done at home or at a clinic.
Usefulness of Blood Sugar Test
A blood glucose level test can be done in order to determine whether a person has diabetes or prediabetes. The test will determine the amount of glucose in the blood.
The food eaten by the person has carbohydrates, proteins and fat, which are broken down into smaller units by the digestive juices present in the digestive tract. When carbohydrates are broken down, they form glucose which is the primary source of energy for all the cells of the body. Insulin is a hormone that is secreted by the pancreatic cells in order to assist the cells in taking up glucose for energy.
In people with insulin-dependent diabetes, there is deficiency of insulin in the body due to which the cells are not able to take up glucose from the body. This causes the blood glucose levels to rise in the blood, which can be determined with the help of blood glucose level test.
Risks of Blood Sugar Test
There are no side effects of blood glucose tests. Some people might feel swelling, soreness or bruising at the site of puncture which generally goes away in a day.
Types of Blood Sugar Tests
There are two ways in which blood sugar tests can be performed.
Self-monitoring by using a glucometer which involves pricking of a finger to draw blood.
Testing at Laboratory where blood is drawn for testing.
A fasting blood sugar (FBS) test is done to measure the blood glucose levels or glycosylated hemoglobin. Otherwise, a hemoglobin A1C tests are done to determine the levels of glucose for the last 90 days. These results will determine whether a person has prediabetes or diabetes.
When to test for blood sugar
When and how to get a blood sugar test depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment program.
1. Type I Diabetes

As per the American Diabetes Association (ADA),[2]if a patient is managing type I diabetes with insulin therapy, the patient is required to monitor the blood glucose levels after the following activities like
- Eating a meal
- Exercising
- Sleeping
- Critical tasks like babysitting or driving
2. High Blood Sugar
If a patient has high levels of glucose, he will experience extreme thirst and urge to urinate. These symptoms indicate high blood glucose and there might be a need for change in treatment plan. If diabetes is under control and these symptoms are still there, it indicates sickness or stress. Exercising and maintaining carbohydrate intake might help in decreasing blood glucose levels.
3. Low Blood Sugar
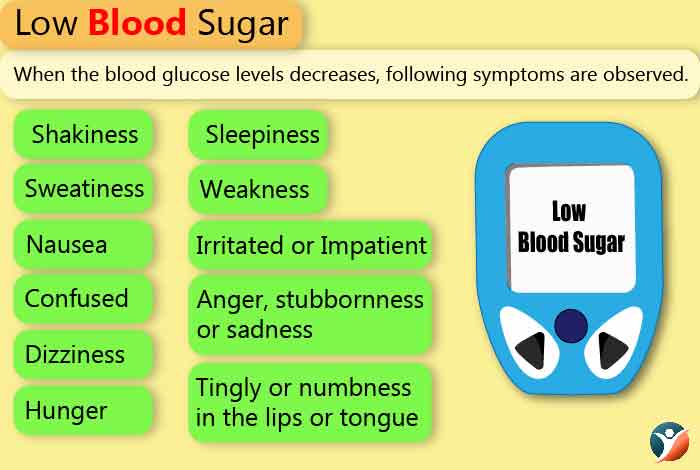
When the blood glucose levels decrease, following symptoms are observed:
- Shakiness
- Sweatiness
- Irritation or Impertinence
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Hunger
- Nausea
- Sleepiness
- Tingly or numbness in the lips or tongue
- Weakness
- Anger, stubbornness or sadness
Delirium, unconsciousness or seizures are some of the other symptoms that are observed with low blood sugar levels or insulin shock.
Patients who daily take insulin injections should ask their doctors to prescribe glucagon that will prevent them from having severely low blood glucose level.
4. Pregnant Women
During pregnancy, some women develop gestational diabetes. This happens when there is a disbalance in the way mother’s body uses insulin. This causes glucose to get accumulated in the blood.
If a woman develops gestational diabetes, she is required to get her blood glucose level tested at regular intervals. Gestational diabetes generally goes away after childbirth.
5. No Scheduled Testing

Home testing of blood glucose level might be unnecessary if a patient has type II diabetes and maintains his blood glucose levels through diet and regular exercise.
How Are Blood Glucose Tests Performed?
In order to get a sample, a needle is inserted into the veins and blood is drawn. The patient is asked to fast for nearly 12 hours before fasting blood sugar (FBS) test.
No fasting is required before A1C test.
1. Home Tests

By using a glucometer, blood sugar levels can be measured at home. The exact procedure of finger stick glucose tests varies as per the type of glucose meter. The home kit caries instructions on how to use it. Generally, the procedure involves pricking the finger to get a drop of blood which is then put on the glucose meter strip, which is inserted into a machine. The results get displayed within 10-20 seconds.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitoring

A device can also be worn by the patient for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). The glucose sensor is inserted under the skin which continuously reads blood glucose level in the body. It alerts the person when the glucose level becomes too high or low.
These sensors can last for a number of days before these required to be replaced. However, these devices are not very reliable when it comes to identifying acute problems like low blood glucose levels. For checking instant glucose level, patients should trust glucometer.
What Do Results of Blood Sugar Test Mean?
Depending on the condition and the timing of test, following are the blood glucose levels that are observed:
| Time | People Without Diabetes (mg/dL) | People with Diabetes (mg/dL) |
| Before breakfast | Under 70-99 | 80-130 |
| Before lunch, dinner and snacks | Under 70-99 | 80-130 |
| Two hours after eating | Under 140 | Under 180 |
| Before sleeping | Under 120 | 90-150 |
A more specific target range for blood glucose level will depend on the following conditions of the patient:
- Personal history
- Time period for which the person has diabetes
- Presence of diabetes complications
- Age
- Pregnancy
- Overall health
Diagnostic Results
| Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes | |
| FBS Test | Under 100 mg/dL | Between 110-125 mg/dL | Greater than or equal to 126 mg/dL |
| A1C Test | Under 5.7% | 5.7-6.4 % | Greater than or equal to 6.5 % |
Who should undergo Diabetes Testing?
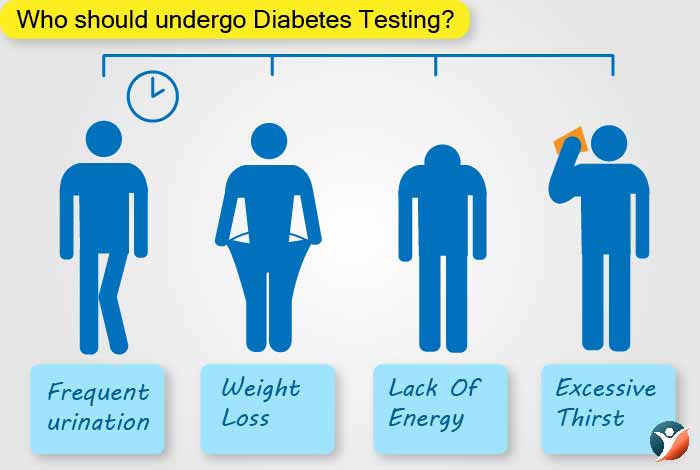
In the early stages, diabetes might not show any symptoms. A person should get his blood glucose level checked if they observe the following symptoms:
- Extreme thirst
- Feeling tired all the time
- Have sores or cuts that do not heal
- Feeling very hungry, even after eating
- Blurry vision
- Urinating more often usual
Some people who do not experience any symptoms should also get themselves tested for diabetes as per the American Diabetes Association (ADA) [3] if a person meets the following criteria:
- High risk of ethnicity (Latino, Native American, Pacific Islander, African American, Asian American)
- High blood pressure
- Low HDL cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Heart diseases
- Family history of diabetes
- Personal history of abnormal blood glucose levels
- Signs of insulin resistance
- No regular physical activity
- Woman having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or gestational diabetes
- Aged 45 years or more
Getting a blood glucose level test around the age of 45 years will help in establishing a baseline for blood sugar level. Since the risk of developing diabetes increases with age, it is important to identify the chances of developing the disease.
Blood Tests for Diabetes
Following are some of the tests that need to be performed for testing blood glucose levels:
1. A1C Test
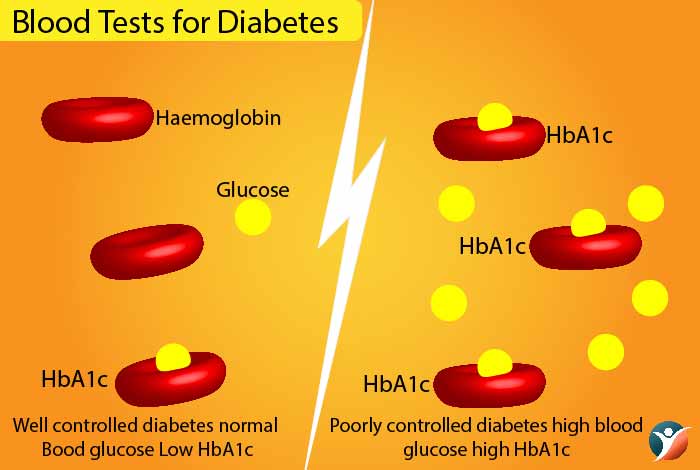
Blood test helps in determining the levels of blood glucose in the body. It is one of the common tests that are performed to estimate the blood sugar level over a period of time and it does not require fasting. This test is also known as glycated hemoglobin test which measures the amount of glucose that gets attached to red blood cells in the body over a period of 2-3 months.
The lifespan of red blood cells is nearly 3 months, this test measures the average blood sugar level for the last 3 months. The test requires that a small amount of blood be drawn out for analysis. The results get measured in the form of percentages:
| HbA1C Reading (%) | Inference |
| < 5.7 | Normal Reading |
| 5.7- 6.4 | Prediabetes |
| > 6.5 | Diabetes |
National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP)[4] standardizes these lab tests and therefore no matter where the test gets performed, the method by which the test gets performed remains same. As per National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,[5] the tests that are approved by NGSP are considered enough to diagnose diabetes.
Some people can have varied results to the A1C tests like pregnant women and people who have a special variant hemoglobin that gives inaccurate test results. In these circumstances, other tests are prescribed.
2. Random Blood Sugar Test
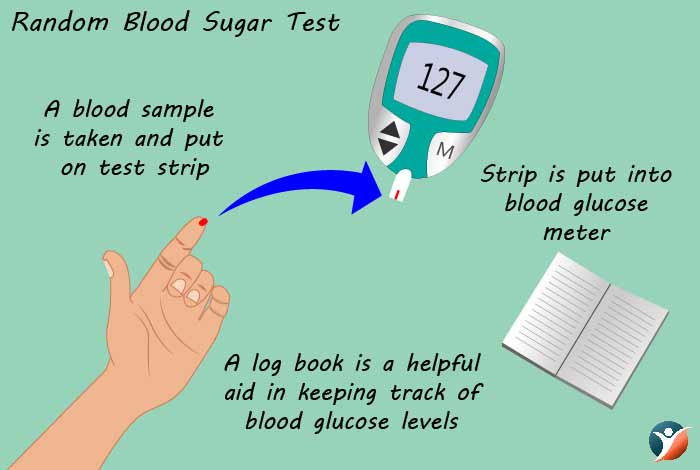
A random blood sugar test can be performed any time, irrespective of the food taken by the person. This gives an instant value of blood glucose level in the blood.
| Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Inference |
| > = 200 | Diabetes |
| 140-199 | Prediabetes |
3. Fasting Blood Sugar Test
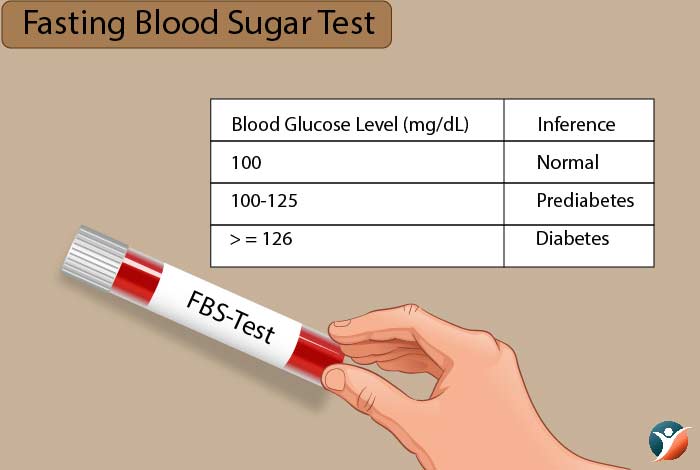
Fasting blood glucose levels are tested after a person has fasted for at least 8-12 hours before the test.
| Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Inference |
| 100 | Normal |
| 100-125 | Prediabetes |
| >= 126 | Diabetes |
4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
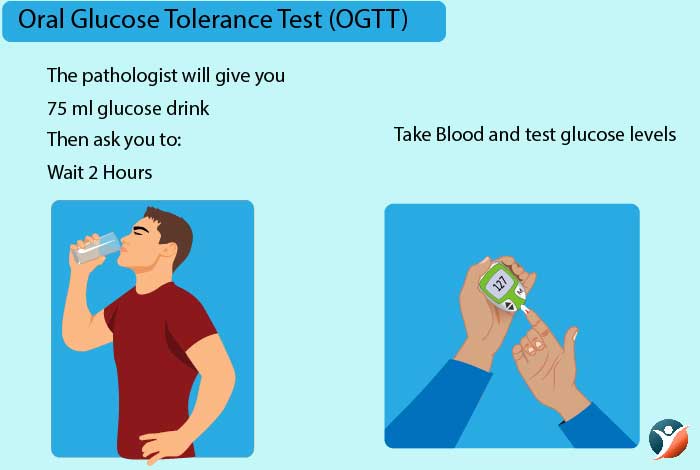
Oral glucose test is performed over a course of 2 hours. A person’s blood glucose level is evaluated initially and then he is given a sugary drink. After 2 hours, the blood glucose levels are again tested.
| Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Inference |
| < 140 | Normal |
| 140-199 | Prediabetes |
| > 200 | Diabetes |
Conclusion
Blood glucose level defines whether or not a person has the metabolic disorder of diabetes. If there is any chance of developing this disease, blood sugar level should be checked regularly. For people suffering from diabetes, it is extremely important to maintain near-normal blood glucose levels in order to avoid development of diabetes-related complications.