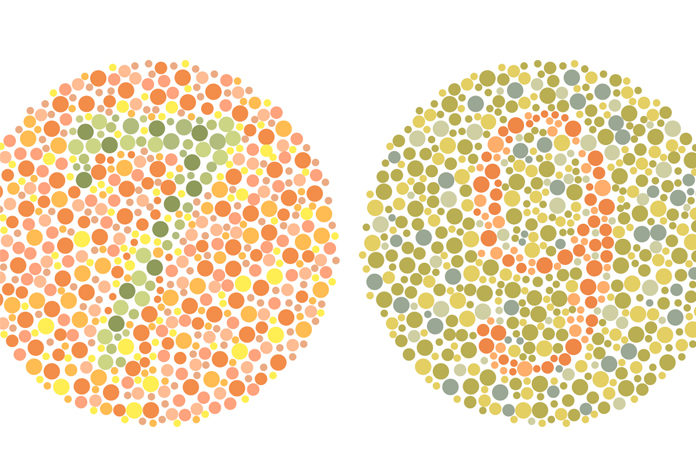

Overview and Facts
Color blindness is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish between certain colors. It is also known as color vision deficiency. Color blindness can hamper daily activities. Various activities such as watching traffic signals, selecting clothes, purchasing fruits become more challenging with color blindness. The problems associated with this condition are not very severe, and most people are able to adapt to it easily. However, people who have total color blindness have decreased vision and may feel uncomfortable in bright environment When a person has color blindness, he/she may not be able to differentiate between various colors like green and red or yellow and blue. The affected person is more likely to get confused with red and green color and hence it is the most common form of color deficiency. Blue and yellow color deficiency is rare, and it equally affects men and women. The term color blindness is not correct. This is because when we talk about color blindness we are referring to color vision deficiency and not exactly color blindness. Color vision deficiency is a more appropriate term, but color blindness is more convenient, hence it is commonly used.
Color blindness is more common in men than in women. This is because men, unlike women, have only one X chromosome. The muted or altered gene responsible for color vision deficiency is present on the X chromosome. Women with a muted X chromosome does not suffer from the disease because the second X chromosome in them is normal.
Red-green color blindness can’t be passed on to sons from father. There are many people suffering from complete color blindness known as achromatopsia or rod monochromacy. If a woman is color blind with red-green color deficiency, all her sons will be colorblind. 99% of people with color blindness have red-green color blindness.
People with normal vision can differentiate between more than 100 different hues while with color blindness the number comes down to 20. Colored lenses and glasses can help discriminate colors, but it cannot provide normal color vision. Based on severity, color blindness can be divided into four categories: Slight, moderate, strong, absolute.
Daltonism is a form of color blindness in which a person is not able to distinguish between certain colors, especially red and green. This name is kept after the scientist John Dalton.
As per the Prevent Blindness America, around 8% of males are affected by the condition and less than 1% of females have vision problems related to color blindness. Around 0.5% of women have color blindness.
Types and Symptoms of Color Blindness
Types of Color Blindness
1. Red-Green Color Blind: It is the most common type of the condition: It is further divided as:
- Protanomaly: This is caused by defective long-wavelength-sensitive cones (L-cones). This reduces sensitivity to red colors.
- Protanopia: It is a severe form of color blindness as it is caused by absence of L-cones. This reduces the ability of the eye to see red colors.
- Deuteranomaly: It is caused by defective middle-wavelength-sensitive cones (M-cones). This reduces the ability to distinguish red and green colors.
- Deuteranopia: It is caused by the absence of M-cones. This leads to inability to distinguish between red and green colors.
3. Blue-Yellow Color Blindness: This is further categorized into the following types:
- Tritanomaly: This is caused by the weakening of short-wavelength sensitive cones (S- cones) which reduces the ability to differentiate between blue and yellow shades.
- Tritanopia: It occurs because of the absence of S-cones. Some blue hues are confused with green and yellow shades are confused with violet.
4. Total Color Blindness: This condition can be classified into the following types:
- Rod Monochromacy: This condition is marked by inability in distinguishing any color. This happens when retinal cones are absent or not functioning. It is correlated to photophobia or sensitivity to light and poor vision.
- Cone Monochromacy: It is a form of complete color blindness and occurs rarely. However, vision remains normal in this condition.
Color blindness can be either inherited or acquired. Based on this, two types of the condition occur as given below:
- Inherited Color Blindness: It is very common and is due to genetic defects. This means that the condition runs in families. Someone having color-blind family members is more develop the condition.
- Acquired Color Blindness: Diseases damaging the retina or optic nerve of the eyes can cause acquired color blindness.

Symptoms of Color Blindness:
The main symptom of color blindness is the inability to distinguish between colors or making mistakes while identifying colors. If one feels that his/her child may be color blind, the main signs to notice are:
- Choosing wrong colors, for example, choosing purple for tree leaf color or other dark colors.
- Filling out wrong colors in coloring sheets or books
- Denying that there may be any color issues
- Sensitivity to bright lights
- Complaints that eyes or head hurt when they look at something which has a red or green color touch to it
- Being able to see only a few shades of colors while the one not affected by color blindness can see thousands of colors. In some rare cases, only black, gray and white colors are visible
- Being able to see some colors and not others
- Difficulty in reading
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Pain in eye

Risk Factors for Color Blindness
- Men are at a higher risk of having color blindness as compared to women who rarely exhibit the condition.
- It is also commonly seen in men of Northern European origin.
- Conditions of the eye like macular degeneration, i.e. damage of the central part of the retina, and glaucoma, a condition which damages optic nerves, may increase risk of acquired color deficiency.
- It may also come as a side effect of certain drugs. The drug hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) can lead to color blindness. This drug is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Chronic alcoholism, cancers like leukemia, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, all increase the risk of developing color blindness.
Do I Have Color Blindness?
One may be having color blindness if he or she is not able to distinguish between certain colors. A family history of the condition increases the chance of developing color blindness. A person who experiences eye strains after seeing a particular color, he/she must go for a color blindness test.
Causes and Prevention of Color Blindness
Causes of Color Blindness:
- Genetics: Color blindness is a genetic condition. It is usually passed down from parents to children. The gene responsible for the condition is carried on the X chromosome and because of this reason, it is more common in men than in women. Most people with color blindness get the disease from the mother who is usually a carrier of the condition but is not color blind herself. These effects are due to lack of cones, a photoreceptor that helps in color vision. () These cells are found in retina and are light sensitive. Cones help in distinguishing red color from green and blue.
- Acquired: The disease may also be acquired as a result of long-standing diseases like diabetes, liver and eye diseases, multiple sclerosis. Generally, color vision issues that are caused in later life happen as a result of trauma, toxic effects of drugs, metabolic or vascular diseases.
- Injury to the Eye: Acquired loss of color vision can happen as a result of damage to the retina or optic nerve.
- Aging: In people over the age of 60 years, physical changes occur along with a decrease in person’s ability to distinguish between colors. The lens becomes dark or yellow over time. This causes problems to older adults in seeing dark colors.
- Accidents: The accidents leading to damage of the retina or strokes that affect some area of the brain/eye can lead to color blindness.
- Medications: These include antibiotics, anti-TB drugs, medicines of high blood pressure, drugs used for treatment of nervous disorders can all lead to color blindness.
Industrial and Environmental Chemicals: Chemicals containing lead, carbon monoxide, carbon disulfide can all lead to color blindness. - Shaken Baby Syndrome: Damage to the retina and brain can cause permanent loss of color vision.
- UV Damage: Unprotected exposure to UV rays can lead to degeneration of the retina leading to loss of color vision.
- Cataracts: Lens clouding causes light to diffuse before reaching the retina. Good color vision can be restored by cataracts surgery as the cloudy lens is removed.
Prevention of Color Blindness
Hereditary color blindness cannot be prevented. However, acquired color blindness can be prevented if all possible causes are avoided. Thus, there is no way to prevent color blindness which is present in the child from birth. But, one can reduce the chances of having color blindness in later life. To reduce the risk of acquired blindness, one must go for regular eye exams and follow a healthy lifestyle.

Diagnosis and Tests of Color Blindness
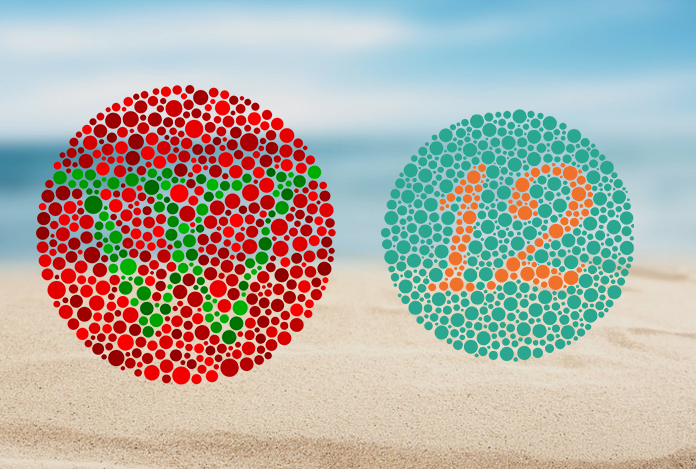
Inherited color vision deficiency (CVD) can be diagnosed using simple screening tests. The H-R-R (Hardy-Rand-Rittler) and Ishihara color plates can be used for evaluation of type and degree of color blindness. In Ishihara color test, plates are used which are numbered 1-17 and plates from 18-24 contain one or two lines. In order to pass the test, the patient must correctly identify the number and trace the wiggly lines. In both the tests, the patient is asked to identify colored shapes and numbers that vary in color and intensity. The deficiency is measured and detected based on the responses of the patients.
There is another test known as the Farnsworth-Munsell D15 Color Vision Test and the Farnsworth-Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision Test. This test evaluates or checks the ability of a person to identify color gradations. The patient is asked to place the discs of various colors in order.
An eye specialist may perform a test to know if a person has color blindness. In this test, the patient is shown a pattern of multi-colored dots. If one does not have color blindness, he/she will be able to see numbers and shapes in the dots. If one has color blindness, he/she may not be able to find numbers or shapes in the dots. Nothing may be visible to such a person.
There is another type of test in which the patient is asked to arrange colored chips in order in accordance with the similarity of the colors. People who have color vision problems face difficulty in arranging the colored chips correctly.

Treatment and Care of Color Blindness
Treatment of Color Blindness:
Currently, there is no treatment for color blindness. Color filters or contact lenses can be used in some situations for improving the brightness of colors. Wearing colored contact lenses can help see the difference between colors. However, these do not provide normal color vision and can often distort images.
One can go for glasses that prevent glare. People having severe issues related to color vision are better able to see differences between colors when there is less brightness and glare.
Gene therapy for color blindness is a therapy that converts color blind individuals to trichromats by inserting a photopigment gene in them.
Curing color blindness cannot be cured completely. People are color blind as a result of defective genes on the X chromosome. Gene therapy which repairs the damaged chromosome can help in some cases. Light filtering lenses can help color blind people differentiate between certain colors.
Ayurvedic treatments like Tarpana is very useful in the treatment of color blindness. Intake of Triphala Ghrita is quite beneficial in the treatment of the condition.
Herbal medicines like Divya Amrit Rasayana and Saptamrit Lauh provide nutritional value to the eye. Thus, these can be used.

Care for People with Color Blindness:
If you know of someone having color blindness or if your child is having the condition it is advisable to take the following steps:
- Informing the child’s school that he/she has a color vision problem. So, learning material must be provided accordingly
- Family or friends can help them choose cloth and see whether food is safe for consumption
- Ensuring adequate and good quality of lighting to help them distinguish colors
- Adjusting devices and systems like computers and change their settings to make it easier for usage. Mobile phone apps can be used for detection and identification of colors

OTC and Self-Management Methods Available for Color Blindness
There is no OTC medication available for treating color blindness. Further, there are no eye drops available which can be used for management of symptoms. However, there are some self-management methods that have been discussed below:
Self-Management Methods for Color Blindness:
- Taking Proper Diet: Diet matters a lot as far as health of the eye is concerned. Eat a lot of green leafy vegetables that give nutrients like lutein and zeaxanthin. These are good for the eyes. Also, vitamin A found in orange and brightly colored vegetables, and fruits like carrots improve the health of the eye. Adding fruits like oranges and strawberries also help as these are a source of vitamin C and antioxidants like Omega-3 fatty acids. These are also good for the eyes.
- Going for Eye Examination: Regular eye check-up may help in early detection of the condition. It is best to take advise of a doctor and timely treatments can help prevent complications.
- Quit Smoking: When you smoke, cyanide from the smoke enters the blood and ruin your eyes. Smoking subjects you to a greater risk of having eye conditions like color blindness.
- Protecting the Eyes from Sun: Wear sunglasses for protection from UVA and UVB rays.
- Avoiding too much Work on Computer: Working long hours on computer can lead to various complications like color blindness. So, it is advised to avoid spending more time on computers.

Natural Ways to Cure Color Blindness
- Amla juice is good for the eyes. One must incorporate it into one’s diet.
- Green leafy vegetables and balanced diet is also beneficial for the eyes and is effective in color blindness.

Health Tip by Experts
Controlling lighting in home and workplace can provide comfort in color blindness. Natural light is the best. Bright light and glare should be avoided in color blindness. Finally, proper diet helps a lot in maintaining good health of the eyes.
