Overview and Facts
Bronchitis is a condition of lungs. It refers to the inflammation of bronchi – medium and large-sized airways situated in the lungs – whose function is to carry air to and from the lungs. Bronchitis decreases the ability of an individual to breathe air and oxygen.
Normally, bronchial walls produce mucus – a slimy, greasy substance – which traps minute dust and similar particles that can cause irritation. In bronchitis, mostly due to some infection, bronchi get inflamed or irritated, which causes a person to produce mucus in excess. Coughing is the body’s response to shift that extra mucus.
As per American Lung Association, around 10 million Americans were suffering with bronchitis in 2011. More than 70% of the cases were of the age 45 years and above. The risk of contracting bronchitis increases with age. Women have twice the likelihood of contracting bronchitis as compared to men.
Some races are more susceptible to getting bronchitis as compared to others. Non-Hispanic Whites are more prone to develop bronchitis as compared to non-Hispanic Blacks. Figures show around 7.5 million non-Hispanic Whites had bronchitis in 2011 as compared to 1.3 non-Hispanic Blacks. Also, around 10 lakh Hispanics were known to have bronchitis in the same year.
Types and Symptoms of Bronchitis
Types of Bronchitis:
Bronchitis can be broadly classified into two types, as discussed below:
- Acute Bronchitis: Airways become inflamed temporarily, which lasts up to 3 weeks. There is cough and mucus production. It can affect almost anyone, but it mostly affects children below the age of 5 years. It is more common in winters and occurs as an aftereffect of flu, sore throat or cold. Also known as chest cold, it gets corrected after some time on its own. The cough may remain for some weeks, but this also improves on its own.
- Chronic Bronchitis: It persists for 3 months in a year, and appears consecutively twice, i.e., two years back to back. Emphysema (characterized by shortness of breath) together with bronchitis is called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is one of the leading conditions of the lungs.

Symptoms of Bronchitis:
For both acute and chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms are as follows:
- Cough
- Discolored mucus (sputum) production; generally white, yellow and sometimes, may be full of blood
- Breath shortness
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Discomfort in the chest
- Fever and chills down the spine
- Wheezing
- Tightening of the chest
- Sinus and blocked nose
- Sore throat
- Headaches
In acute bronchitis, one may experience headaches or body aches. These symptoms go away on their own in about a week’s time. But, cough may stay on for some time. In chronic bronchitis, one may have time periods when the symptoms become really bad.

Risk Factors of Bronchitis
Following are some common risk factors of Bronchitis:
- Inhalation of smoke that is whether one smokes or lives with someone who smokes
- Dust, chemicals and fumes exposure
- Malnourishment; particularly in children
- No pertussis immunization
- Chronic sinusitis
- Pollutants in the air
- Allergy-causing substances
- Less resistance to disease
- Regular and frequent infection of the respiratory tract
- Gastric reflux — repeated incidence of heartburn that can irritate the throat, making a person more susceptible to develop bronchitis.

Do I have Bronchitis?
Pneumonia, which is inflammation of the lungs, has some symptoms similar to bronchitis. These include:
- Continued high fever
- Persistent cough often with yellow or gray mucus
- Chills that give sensation of shaking
- Breath shortness
- Pain in the chest
- Confusion; more generally found in older people
While the symptoms of pneumonia are similar to those of bronchitis, the former is much more serious than the acute type of the latter. The difference between bronchitis and pneumonia is that bronchitis is inflammation of the airways, whereas pneumonia is inflammation of lungs.
Moreover, the symptoms of bronchitis are also similar to common cough, cold and flu. Symptoms may also be present as in asthma and other lung conditions. So, it’s best to consult a doctor for complete and proper diagnosis of the condition.
Causes and Prevention of Bronchitis
Causes of Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is caused by virus or bacteria. However, viral bronchitis is more common. In most cases, it is caused by the very same virus that causes common cold and flu. The virus is present in the droplets that come out of the nose and mouth when someone sneezes or coughs. Bronchitis can be caused by dust and other particles that irritate the bronchial tubes. Acute bronchitis sometimes occurs after a cold or viral infection. Smoking cigarettes is the most common cause of chronic bronchitis.
Inhalation of irritants in the workplace, pollution and secondhand smoke are the common causes of bronchitis. Further, inhaling fumes or dust can worsen the symptoms of chronic bronchitis. Chemical solvents may also exacerbate the condition.
Several viruses like influenza A and B, referred to as the flu can also lead to bronchitis. There are many bacteria also at play like Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Mycoplasma pneumoniae that causes pneumonia and are known to responsible for bronchitis.
Elderly people are at a greater risk. Besides, those with weakened immune system, smokers, individuals with COPD and anyone exposed to irritants that harm the lungs are all more likely to suffer from bronchitis.

Prevention of Bronchitis:
The following are prevention methods for bronchitis:
- Do Not Smoke: It is well known that smokers are more likely to develop bronchitis. When one stops smoking, he/she may cough up more mucus for some time. But, this is a good sign as the lungs are working their way to clear up the mucus. Cough will eventually go away as the lungs start to heal.
- Eat Onions: Onions contain some powerful compounds like quercetin, which is a part of the bioflavonoid family and help in protecting the lungs against infection.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Breathing smoke of someone else can lead one up to developing bronchitis.
- Breathe in the Mist: This will help in thinning out the mucus, which makes it easier for the lungs to clear themselves. Breathing steam by wrapping a towel over the head and mouth dipped in a hot bowl of water also provides the necessary moisture required by the airways to remain clear.
- Drink Enough Water: It thins the mucus secretions in the lungs, thus making it easier for it to throw the mucus out.
- Blow Balloons: Therapists will have their patients breathe deeper and blow harder than normal as this will help mucus out of lungs.
- Spice It Up: Curries, red peppers and other spicy foods that make eyes watery or gives a running nose also prevent thickening of mucus.

Diagnosis and Tests of Bronchitis
It may sometimes get difficult to tell apart bronchitis from common cold as symptoms may be quite similar. A person is therefore examined physically using a stethoscope to listen to the lungs while one breathes. The following test may be advised by the doctors:
- Chest X-Ray: This test lets the doctor to know whether the patient has pneumonia, bronchitis or any other condition related to cough. This is even more important if one smokes.
- Sputum Test: It is the test of the mucus that one throws up while he/she has the condition. Sputum is tested for allergies. It can be tested to see if these conditions can be treated using antibiotics.
- Pulmonary Function Test: In this test, a device called spirometer is blown by the patients. This gives the measure of how much air can be held by the lungs and how fast the air can be expelled by the same. It is a test for asthma or emphysema.
Treatment and Care for Bronchitis
Most cases of acute bronchitis get better on their own. The symptoms go away in a few weeks. However, since most cases of bronchitis are due to viral infections, antibiotics are not much effective.
Antibiotic may be prescribed if bacterial infection is suspected. Doctor may recommend medications like:
- Cough Medicines: Cough suppressants may be taken at night before going to bed if cough gets bad during night and does not let the patient to sleep.
- Other Medicines: In case of asthma, allergies and COPD, doctor may prescribe inhalers for opening the air passages in the lungs that have become narrow.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
Pulmonary rehabilitation may come to one’s rescue if one has chronic bronchitis. In this a respiratory therapist tells the person how to breathe more easily and this will improve the ability to breathe and exercise more easily.

OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Bronchitis
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications for Bronchitis:
As OTC medication, one can take acetaminophen or non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for treating bronchitis. Mucolytics or cough suppressants can be taken for thinning the mucus, so that it can easily be coughed out as sputum or phlegm. Some studies have shown that OTC medicines can have dangerous side effects and must be used with precautions. Acetaminophen overdose can be poisonous for the body. This has been associated with liver injury and even death. NSAIDs have many side effects like stomach ache, vomiting and nausea.
There are two main types of over-the-counter medicines available for bronchitis:
- Cough suppressants that work on dry cough by blocking cough reflexes
- Cough expectorants that help in thinning the mucus and separate it from wet cough.

Self-Management Methods for Bronchitis:
Some common ways to self-manage the symptoms of bronchitis are listed below:
Avoid Things that Irritates the Lungs: Cut out on smoking. Also, during exposure to chemicals, paints, household cleaners, take necessary preventive measures like using mask.
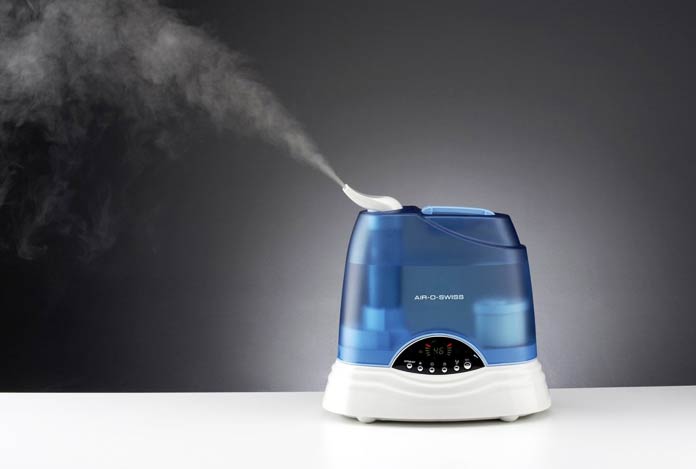
- Use Humidifier: Warm and moist air helps in thinning the mucus and allows it to be coughed out of the airways. Make sure that the humidifier is clean and there is no bacteria or fungi in the water container.
- Consider Using a Face Mask: If cold air exacerbates the cough and cold, do wear a cold air face mask while going outside.

Natural Ways to Cure Bronchitis
Some natural ways to treat bronchitis are discussed below:
- Raw Honey: Raw Honey is a rich source of vitamins, enzymes and minerals. It helps soothe inflammation, and when one is coughing, it treats sore throat too. A combination of 3-4 tablespoons of honey with half a tablespoon of cinnamon makes for a wonderful anti-inflammatory product that works in bronchitis and allergies.
- Oregano Oil: It is a very strong natural antibiotic. Its main ingredient, carvacrol, works on inflammation and chest congestion. It is useful in treating illnesses of the respiratory tract that are caused by bacteria and viruses. In order to use this oil, mix it with a carrier oil like olive oil in the ratio of 1:1. Take two drops of the mixture in mouth and gulp it with water. Capsules of this combination are also available.
- Garlic: It has antiviral and antibiotic properties. It has a compound, called allicin, which helps reduce inflammation. Also, there are vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, copper and iron in it; hence, quite beneficial for health.
- Turmeric: This has a compound, known as curcumin, which imparts turmeric the golden color. Curcumin is known to treat respiratory conditions like bronchitis. In a study, patients with bronchitis were divided in two groups. One group was given standard medicine and the other group received turmeric/curcumin capsules along with standard medicine. The condition of the patients, who received turmeric capsules, was found be better than those, who were solely on standard medication.
- Salt Water: Gargling with salt water thins the mucus and soothes the inflammation of sore throat. It also helps in reducing mucus, which is a cause of irritation in the throat.
- Ginger: It has been naturally found to treat bronchial irritation. It has anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. If one has cough, he/she may boil ginger in water and have the mixture at least 3 times a day.
- Epsom Salt: For individuals with bronchitis, Epsom salt baths are recommended at least two times a day. Add Epsom salt to a hot bath and soak it for half an hour. This will soothe inflammation.
- Lemon Water: When one has bronchitis, he/she is advised to drink plenty of lemon water or tea. This helps thin the mucus, so that it would be easy to expel it out from the body. It also has vitamin C, which boosts the immune system.
- Cayenne Pepper: This has the potential to break the phlegm that forms in bronchitis. One can consume it with water. Repeat the consumption twice a day to see magic.
- Drink Mullein Tea: This herb soothes mucus membranes and removes mucus from the lungs. To make the tea, boil mullein leaves for about 10 minutes in warm water. Drink about three cups a day. This will help in easing away symptoms of bronchitis.
- Steam Bath: Steam soothes the lungs and throat, thus providing relief from irritation caused due to chronic coughing.

Health Tip by Expert
To open the airways, sit in a steamy bathroom or use a humidifier and stay away from things that irritate the lungs like tobacco smoke.

