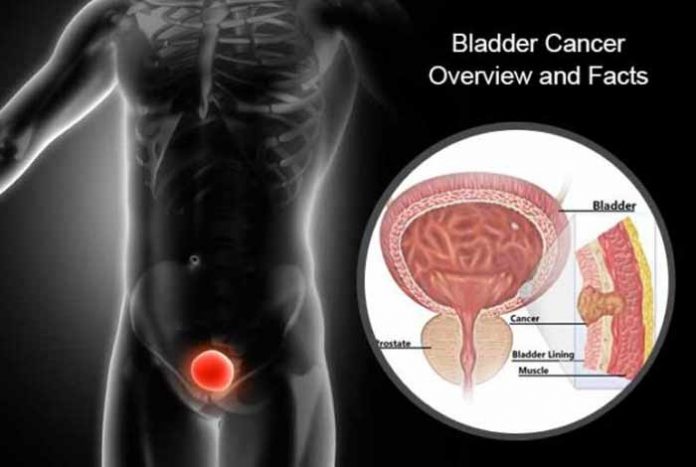
Overview and Facts:
Bladder is an organ in the lower portion of the abdomen or pelvis. Kidney produces urine, while bladder collects and stores the urine. A tube called, ureter connects bladder with the kidneys. The wall of the bladder contracts when the saturation point of holding the urine is attained. At the same juncture, urinary control muscles in the urethra relax and expels the urine.
Cancer happens when cells in the body undergo a degenerative or a malignant change, which causes abnormal growth and multiplication of cells. Basically, bladder cancer is a mass of these malignant cells. Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder. It occurs when cells in the urinary bladder grow without control. As more cancer cells develop, they form a tumor and spread to the other parts of the body.
There are different layers in the bladder walls. Different types of cells make up the bladder walls. Most of the bladder cancers originate from the inner lining of bladder, i.e., urothelium or transitional epithelium. The cancer cells have the potential to spread to other areas of the body through a process, known as metastasis. Metastasis means cancerous cells spread through circulation of tissue fluid along the blood stream. The tissues and organs accumulate these fluids, where cancerous cell grow uncontrollably and causes harm to these locations. It must be noted that if bladder cancer cells metastasize, i.e., spread to other body parts like lung, then it would be treated as metastatic bladder cancer, and not as a lung cancer.
Types and Symptoms of Bladder Cancer:
Types of Bladder Cancer:
- Urothelial Carcinoma: Most commonly occurring bladder cancer in the U.S. The normal cells in the innermost lining of the bladder – urothelium – undergo changes that lead to uncontrolled growth of cancerous cells.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This cancer comprises cells that are formed as a result of inflammation of the bladder, which occurs over a period of months or years.
- Adenocarcinoma: This cancer develops from cells that make up glands releasing fluids like mucus.
- Small Cell Carcinoma: Very few cancers are small cell carcinoma, which starts in nerve cells, known as neuroendocrine cells. This needs to be treated with chemotherapy.
- Sarcoma: These is a rare cancer, which starts in the muscle cells of bladder.
Bladder cancers are also categorized on the basis of how they invade the bladder.
- Non-Invasive Bladder Cancers: These cancers are in the inner layers of the cells that have not reached the deeper layers.
- Invasive Bladder Cancers: This type of cancers grows in the deeper layers of bladder wall. They also spread to other areas of the body, and are difficult to treat.
A bladder cancer can be described as superficial or non-muscle invasive. Also, there are two subtypes of bladder cancer:
- Papillary Carcinomas: These grow as finger like projections from the surface of the bladder leading to the hollow center. These grow towards the center of the bladder without projecting into deeper layers.
- Flat Carcinomas: These cancers don’t grow towards the hollow part, but in the inner layers of bladder cells.
Bladder cancer commonly occurs in older age. Around 90% of the cases come from people above the age of 55. Average age of diagnosis is 73 years. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer as compared to women. Moreover, Whites are more prone to getting bladder cancer as against Blacks.
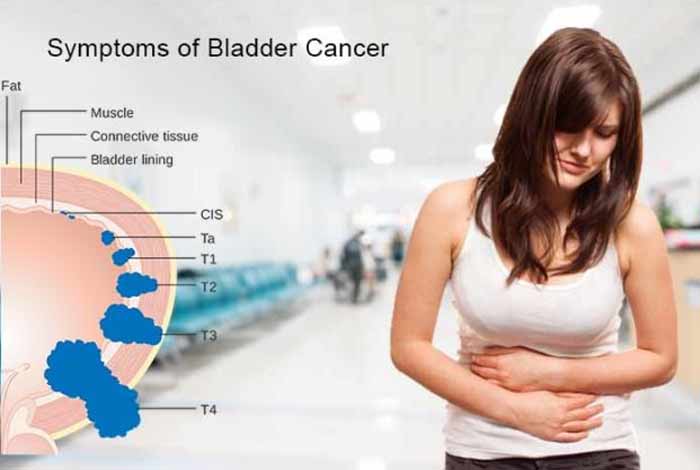
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer:
1. Blood in the Urine: It is one of the first signs of bladder cancer. There is enough blood in the urine to change its color to pink, orange or red. Sometimes urine may be normal, but you may find small amounts of blood in the urine test analysis. This condition is known as, hematuria. Blood may be present periodically, i.e., may not be present on consecutive days. Early stages of bladder cancer have blood as the symptom, but there may be little to no pain.
2. Irritation During Urination: Bladder cancer can cause changes in urination like need for urination more than what is normal. There may be burning sensation or pain during urination. There may be other reasons for these symptoms. But, you need to find and treat the exact cause.
3. Other Symptoms: Bladder cancer may have other symptoms like not being able to urinate, loss of appetite, weight loss, lower back pain, bone pain, etc.
4. Depends on the Affected Part: For example, if cancer has spread to lungs, then there may be cough or shortness of breath. If it has spread to the liver, it may cause abdominal pain or jaundice. Likewise, if has spread to the bones, it may cause bone pain or fracture. Pelvic pain is another common symptom of bladder cancer.
Risk Factors:
- Smoking: It is a very important risk factor of bladder cancer. Smokers have three times more likelihood of developing this cancer as compared to non-smokers. About 50% of bladder cancer cases results from smoking.
- Workplace Exposure to Chemicals: Certain industrial chemicals like aromatic amines like benzidine and beta-naphthylamine used in dye industry can cause bladder cancer. Workers in industries that use certain organic chemicals like rubber, paint, textiles have a higher risk of bladder cancer. Exposure to chemicals compounds and aggravates the effect of smoking and lead to bladder cancer.
- Certain Medicines and Herbal Supplements: As per FDA, using diabetes medicine pioglitazone (Actos) for over a year is associated with increased risk of bladder cancer. Dietary supplements containing aristolochic acid is known to increase the chance of urothelial cancers like bladder cancer.
- Drinking Water Containing Arsenic: Presence of arsenic in drinking water is related to increased risk of bladder cancer. It depends on the source of water, i.e., from where you get your water.
- Not Consuming Enough Fluids: People, who do not take lots of fluid, particularly water, have greater chances of having bladder cancer.
- Age and Gender: The risk of bladder cancer increases with age. Nearly 90% of the people with bladder cancer are above the age of 55. Bladder cancer is more common in men than in women.
- Chronic Irritation and Infections in Bladder: Urinary infections, stones in kidney and bladder is associated with bladder cancer, but it is not clear whether they actually cause the cancer.
- Birth Defects: Belly button and bladder are connected before birth. This is known as urachus. If part of this connection remains after birth, it could be cancerous. Cancer starting in urachus are adenocarcinomas that are made up of cancerous cells.
- Genetics and Family History: People, who have family members having bladder cancer are at a greater risk of developing the same. They may share changes in some genes that makes it difficult to break down certain toxins.
- Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy: Consuming chemotherapy drug, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) can cause irritation to the bladder and increases the risk of bladder cancer. In order to protect the bladder from irritation, it is advised to drink lots of fluids. People, whose pelvis has been treated with radiation are more likely to develop bladder cancer.
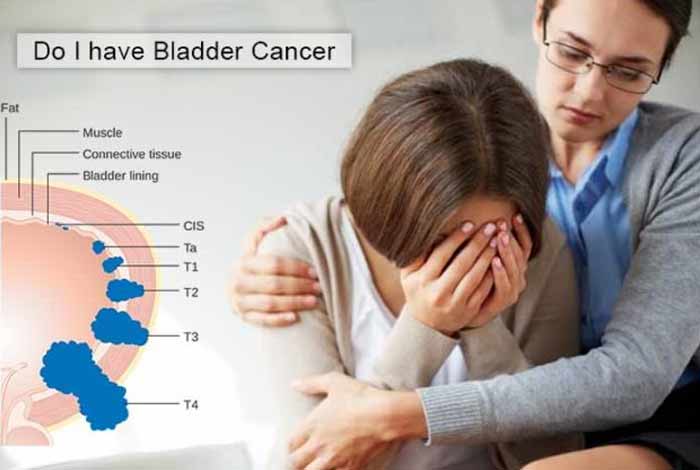
Do I have Bladder Cancer?
Blood in the urine does not always mean you have bladder cancer. Mostly, it is caused by other things, such as infection, benign tumors (non-cancerous in nature), stones in bladder or kidney, or other kidney diseases.
To find out whether you have bladder cancer or not, your doctor will perform a complete medical checkup. He will evaluate your risk factors and will do a physical exam. Hematuria, the condition of blood in urine, occurs in 90% people, who have bladder cancer.
When a woman finds blood in her urine, she may ignore it for a while thinking it is menstrual blood or symptoms of menstruation. Blood in the urine can also be easily misdiagnosed as post-menopausal bleeding or infection in the urinary tract (UTI). Thus, the most common symptom of bladder cancer – blood in the urine –is also a common sign of UTI. Other UTI symptoms include irritation or pain while urinating. Sometimes, an urgency to pass urine could also be a symptom of bladder cancer.
Because UTI and bladder cancer have similar symptoms, it may be difficult to diagnose bladder cancer. Thus, when a woman has UTI or is getting blood in the urine, it is recommended to consult an expert.
Causes and Prevention of Bladder Cancer:
1. Causes of Bladder Cancer:
This happens when the bladder cells grow abnormally. These cells, instead of growing and dividing normally, develop mutation. This causes the cells to grow abnormally without dying. A mass of these abnormal cells forms a tumor or cancer.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: It is a major risk factor. Smokers are three times more likely to develop bladder cancers than non-smokers.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to chemicals, such as in cases of people working in environments, where they are predominantly exposed to chemicals like aromatic amines. Exposure to arsenic in drinking water can also lead to bladder cancer.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: Past radiation exposure may lead to the cancer of bladder.
- Chronic bladder infections: Irritation in the lining of the bladder may lead to bladder cancer.
- Genes: If there is a family history of bladder cancer, then the chances of developing the condition is more. There may be bladder defects from birth.
2. Prevention of Bladder Cancer:
Adopt the following measures to prevent bladder cancer:
- Don’t Smoke: If you won’t smoke, then cancer causing chemicals in smoke will not accumulate in your bladder. Don’t start smoking if you haven’t smoked yet. If you smoke, consult your doctor. Medications and support groups could help you quit smoking.
- Be Cautious with Chemicals: Follow safety instructions while working with chemicals. This helps you reduce exposure to chemical hazards.
- Choose Food Rich in Antioxidants: Consume diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which reduces the risk of bladder cancer.
Diagnosis and Tests of Bladder Cancer:
Cystoscopy and imaging tests can be used to diagnose a bladder cancer. A doctor can examine the inside of the urethra and bladder using a cystoscope, which is a narrow tube containing a camera and lighting system that gets inside the bladder through urethra. It is carried it out under the influence of local anesthesia. To detect a bladder cancer, following imaging tests are used:
- Pyelogram: This includes injecting a contrast dye in the bladder to make tumors more visible on X-rays.
- Computerized Tomography (CT): Specialized X-rays can help in the determination of shape, size and position of tumors.
- Ultrasound: It can be used to find out if the tumor has spread to other organs.
- Urine Cytology: Presence of cancerous cells can be detected with urine samples.
- Urine Culture: This helps analyze signs of bacterial growth when the urine sample is placed in a growth medium.
- Biopsy: It helps examine the invasiveness and grade of cancer.
- Staging: To detect stages of cancer using additional tests like CT scans, chest X-Ray, bone scans and MRI.
Treatment and Care of Bladder Cancer:
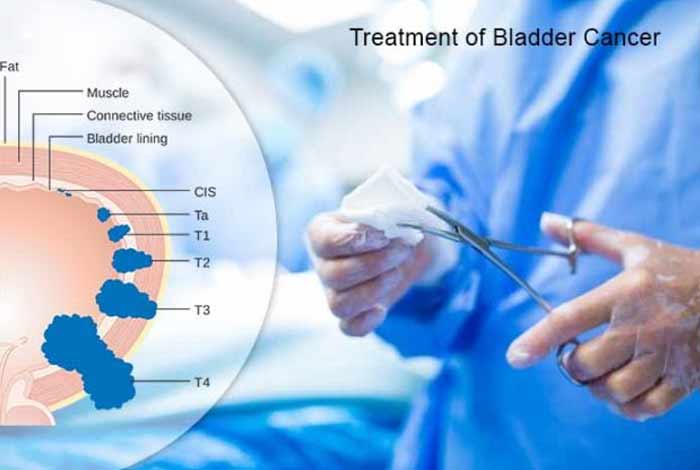
1. Treatment of Bladder Cancer:
Bladder cancer treatment depends on various factors like type of cancer, stage of cancer and grade of cancer. Bladder cancer treatment may include the following:
- Surgery: This helps in the removal of cancerous cells or tissues.
- Bladder Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy treat tumors confined to the lining of bladder, and are at a risk of progression to advanced stages.
- Reconstruction: Creating a new way to expel urine after bladder removal.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy helps destroy cancerous cells.
- Immunotherapy: It is used to activate the immune system to fight cancer cells in the bladder.
i. Bladder Cancer Surgery:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor: This procedure is used to remove bladder cancers present in the inner layers of the bladder, which are not yet muscle invasive. During this procedure, surgeon passes a wire loop through a cystoscope into the bladder. The loop of the wire burns away cancer cells with the help of electric current. As part of this procedure, doctor injects a cancer-killing medicine in the bladder to destroy the remaining cancer cells.
ii. Cystectomy:
It is a surgery to remove all or part of a bladder. During partial cystectomy, surgeons remove a portion of the bladder that contains cancerous cells. Radial cystectomy is a procedure to remove the bladder completely.
2. Caring for someone with Bladder Cancer:
If someone you care for has been diagnosed with bladder cancer, you will have some grave long-term issues to manage the condition. If the cancer has been detected early and the treatment is minimally invasive, it is best to keep track of the symptoms and coordinate with the doctors periodically. If the cancer has spread to the point, where the only option left is to remove the bladder and surgery has to be performed, then the affected person may need help with maintaining and changing the urostomy bag, which is used to collect the urine.
As a person, who is caring for the person with bladder cancer, you may be required to help the person deal with the side effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Patients may also need psychological support to cope up with the effects or cancer and various surgeries that he/she has undergone. As there are chances of bladder cancer to return, it is required to help the person keep meeting the doctor, so that there should no delay in the treatments whenever required.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Bladder Cancer:
Medicines may be used to control the growth of bladder cancer cells and ease away the symptoms. These medications may be injected into a vein, may be taken orally by mouth or given directly to the bladder using a catheter. Factually, there is no over-the-counter drug available for bladder cancer. In fact, the medicines must be only prescribed after proper diagnosis of the condition by a surgeon or cancer expert.

Self-Management Methods for Bladder Cancer:
Supportive care will help meet physical and emotional challenges faced by a bladder cancer patient. It is an important part of cancer care. Recovery from bladder cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the type of treatment.
Bladder cancer and its treatment can affect self-esteem and body image. Counselling and emotional support will help cope up with the changes in the body. There are several ways to cope with the aftereffects of bladder cancer treatment, including protective products, diet changes, exercises and medicines.
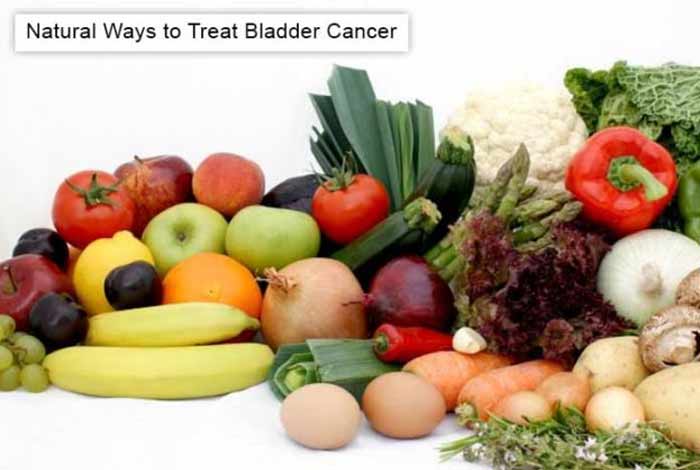
Natural Ways to Treat Bladder Cancer:
Intake of healthy food may reduce the risk of bladder cancer:
1. Grape Fruit or Orange Juice: Research shows that citrus fruits like oranges and grapes contain a compound, called limonene, which blocks the growth of tumor. Hence, it is advised to consume fruits or their juices regularly.
2. Mistletoe: Regular consumption of mistletoe after surgery to remove the tumor prevents recurrence of bladder cancer.
3. Spinach: Spinach contains good amount of vitamin E, which is present in the form of alpha tocopherol and gamma tocopherol. Regular consumption of spinach reduces the risk of bladder cancer by up to 42%.
4. Tomato: Lycopene found in tomato is an antioxidant that offers a protective effect against different types of cancers. Its regular consumption reduces the risk of bladder cancer.
5. Parsley: It is a commonly used herb containing flavonoids and polyacetylenes that are effective against cancer and bear cancer-delaying properties. In general, daily intake of 30 gm of parsley provide a range of health benefits.
6. Baking Soda: Cancer cells flourish in acidic environment, so what is important in treating cancer is to adjust the pH of the body. Baking soda can influence pH and can be helpful in the treatment of cancer.
7. Lemon: Lemon contains a lot of vitamin C, which is quite effective in treating cancers. Drinking lemon water every day or adding lemon juice to the dishes you consume is an easy and effective method to reap benefits of antioxidants, and make the treatment of bladder cancer more effective.
Some other easily available natural foods are red wine, green tea, water, almonds and other nuts, beans and whole grains also reduce the risk of bladder cancer and are known to be beneficial in the treatment of bladder cancer.
Health Tip by Expert:
“Bladder cancer cannot be prevented, but you may be able to reduce some of your risks of getting it by avoiding smoking, exposure to industrial chemicals and eating healthy foods.”