
Overview and Facts
The term arrhythmia is associated with any deviation from the actual sequence of electrical impulses generated by the heart’s electrical conduction system. This means that electrical impulses could happen too fast or too slow, or erratically. This causes the heart to beat faster or slower than normal. If the heart is not beating properly, it cannot pump enough blood to various organs. Because of this, the organs may not work adequately or may get damaged.
The heart is a strong, muscular pump, whose function is to continuously pump blood through the system. Every day the heart beats on an average around 100,000 times and pumps 2,000 gallons of blood through the body.
The heart has four chambers – two on right and two on left. The chambers on the upper side are known as atria and the two lower chambers are called ventricles. Also, there are four valves that allow the blood to flow in one direction – tricuspid valve present between the right atrium and right ventricle, pulmonic valve located between the pulmonary artery and right ventricle, mitral valve between left atrium and left ventricle and aortic valve situated between aorta and left ventricle.
Blood is pumped to the lungs by the heart and the body tissues also receive blood as the four chambers contracts. For the heart to beat properly, the four chambers must beat in an organized fashion. Heart beats when the electrical impulse moves through the sinoatrial node (SA). The SA node initiates the heartbeat and hence, called the body’s natural pacemaker.
The usual electrical signal initiates in the right atrium to the atrioventricular (AV) node. The electrical signals travel down to the ventricles through the AV node. As long as electrical impulses are transferred normally, the heart beats as well as pumps at a regular pace. Normally, the heart beats 60 to 100 times in a minute.
Electrocardiography (EEG) can help record the electrical activity of heart and detect arrhythmias. Arrhythmias are beats that are abnormal. It is associated with any deviation from the normal flow of electrical impulses leading to abnormal rhythms of heart.
Some arrhythmias are so brief that the overall heart rate is not greatly affected. But, if arrhythmias last for a longer duration, the heart rate may become too fast or too slow, or erratic. So, the blood is not pumped effectively.
Arrhythmia is a common heart condition. Around 2.2 million Americans live with atrial fibrillation. A recent research has revealed that nearly 25% of Americans above the age of 40 could develop irregular heartbeat.
Types and Symptoms of Arrhythmia
Types of Arrhythmia:
The following are the types of Arrhythmia:
- Tachycardia: A fast heart rhythm in which heart beats more than 100 beats per minute.
- Bradycardia: It is a slow heart rhythm in which heart beats lesser than 60 beats in a minute.
- Supraventricular Arrhythmias: These are arrhythmias that begin in the atria (upper chambers). Supra means above, ventricular refers to lower heart chambers or ventricles.
- Ventricular Arrhythmias: These are arrhythmias that begin in the lower chambers or ventricles.
- Bradyarrhythmias: Slow heart rhythms that may be caused due to fault in the conduction system of the heart like SA or AV node.
Types of Supraventricular Arrhythmias:
- Premature Atrial Contractions: These are extra irregular heartbeats that originate in the atria.
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT): It is a rapid and irregular heartbeat that comes from the atria. It begins and ends quickly.
- Accessory Pathway Tachycardias (Bypass Tract Tachycardias): It is a fast heart rhythm that results from abnormal connection between atria and ventricles. The electrical impulses move through the extra connecting pathways as well as through the usual route. So, this way, impulses travel through the heart very quickly, leading the heart to beat extraordinarily fast.
- AV Nodal Re-Entrant Tachycardia (AVNRT): It is a fast heart rhythm that happens because of presence of more than one pathway through the AV node.
- Atrial Tachycardia: A fast heart beat that originates in the atria.
- Atrial Fibrillation: It is a very common type of irregular heart rhythm. In this, several impulses start and spread through the atria, all competing for a chance to pass through the AV Node. As impulses start traveling down the atria in disorderly manner, there is loss of coordinated contraction of the atria.
- Atrial Flutter: It is also irregular heartbeat, but it is more organized than atrial fibrillation.
Types of Ventricular Arrhythmias:
- Premature Ventricular Contractions: As the name suggests, these originate in the ventricles. This is a common type of arrhythmia and happens due to too much stress, and caffeine or nicotine consumption. These can even be caused due to heart disease or imbalance in the electrolytes.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: It is an irregular fast heart beat that starts in the ventricles. In this, the heart is not able to pump sufficient blood through the body. It is a severe condition.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: It is an erratic firing of impulses from the ventricles. The ventricles are not able to create effective contraction, so blood does not get pumped properly. It is a condition of medical emergency and must be treated immediately.
- Long QT: On the ECG, QT interval denotes the time taken by heart muscles to contact and recover. When the interval of QT is longer than usual, the risk of ventricular tachycardia increases.
Types of Bradyarrhythmias:
- Sinus Node Dysfunction: Abnormal SA node functioning leading to slow heart rhythms.
- Heart Block: Blockage in the electrical impulse traveling from the sinus node to the ventricles. Heartbeat may go irregular or slow.
Symptoms of Arrhythmia:
Arrhythmia may be silent without causing any symptoms. Sometimes it may cause symptoms like:
- Palpitations: Pounding or fluttering of heart, skipping of heartbeats
- Pounding in the chest
- Discomfort in the chest
- Feeling tired or fatigued
- Breath Shortness
- Feeling light headed
- Sweating
- Fainting

Risk Factors for Arrhythmia
The following conditions can increase the odds of one getting arrhythmia or abnormal heart rhythms:
- Cardiac Valvular Disease: Deposits in the cardiac valves involve the ventricles. If the valves are restricted, regular heart rate becomes difficult.
- Heart Failure: In this the heart cannot pump properly which causes collection of excess fluid in the legs and lungs.
- Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease): Coronary arteries surround the heart and carry oxygenated blood to the heart that pumps blood to the rest of the body. If a person has coronary artery disease, then he/she has greater chances of having arrhythmia.
- Conductive Tissue Disease: A few diseases can cause deposition of some substances like proteins and calcium in the bloodstream. These may accumulate in kidneys, connective tissues and specific conducting tissues present in the heart. Due to their deposition, conducting tissues become abnormal and affect heartbeat.
- Ingested Substances: Some substances like caffeine, tobacco, cocaine, alcohol, and certain OTC as well as prescribed medications may lead to arrhythmia.
- Physical Demands on Heart: Exercise and stress may also lead to irregular heartbeats.

Do I have Arrhythmia?
The symptoms of arrhythmia and panic attack may actually overlap. This makes it difficult to tell apart the conditions. If your heart starts racing, it may be panic attack, heart attack or arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia shares some symptoms with panic attack. A panic attack can last for some minutes to about an hour. Arrhythmia can make your heart pound 150-250 times in a minute. This can be mistaken for a panic attack. So, in order to rule out other possibilities, one must see a doctor or medical health professional.

Causes and Prevention of Arrhythmia
Causes of Arrhythmia:
Any disturbance to electrical impulses causing contractions of the heart may lead to arrhythmia. Arrhythmia may be caused by several factors that are listed below:
- Imbalance of electrolyte in blood (sodium or potassium)
- Changes in heart muscles
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Heart attack
- Alcohol and drug abuse
- Diabetes
- Drinking too much coffee
- Hypertension
- Stress
- Hyperthyroidism
- Smoking
- Some medications

Prevention of Arrhythmia (H3)
Arrhythmia can be prevented by taking care of the risk factors and by monitoring and treating heart problems:
- Exercising regularly, keeping a healthy weight, eating a low-fat diet, and more of vegetables and fruits assist one in living a life that is conducive to heart’s health.
- Do not smoke and absolutely avoid second hand smoke. Tobacco is the leading cause of almost all heart diseases.
- Cut down on caffeine, alcohol and other drugs.
- Don’t worry too much and refrain from negative emotions like anger, anxiety, fear, etc.
- Let your doctor know of your condition, so that a physical examination may be carried out on time.

Diagnosis and Tests for arrhythmia
Some tests that may be done for confirming arrhythmia are given below:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): It shows a picture of the electrical impulse traveling through the heart muscle. Electrodes are used to map the ECG on a graph paper. Electrodes are fixed on the skin of the chest, arms and legs.
Ambulatory Monitors:
- Holter Monitor: It is connect to the electrodes on the chest, and continuously measures the rhythm of heart.
- Transtelephonic Monitor: A small monitor is attached to electrode leads, generally on a finger or wrist. Through this device, rhythm of heart gets transferred over the phone.
- Transtelephonic Monitor with a Memory Loop: A portable recorder is attached for some time, which records information about the heart rhythms. The rhythms are recorded, saved and transmitted over phone.
Stress Test: This test is used to record arrhythmias that get triggered due to exercise. It can also help determine if there is some other heart disease or not.
Echocardiogram: It is used to see if a heart muscle or valve disease may be causing arrhythmia.
Cardiac Catheterization: In this, a catheter is put in a blood vessel and taken to the heart using an X-ray. Contrast dye is injected through the catheter to study the X -ray of coronary arteries, and heart valves and chambers.
Electrophysiology Study (EPS): Catheters are inserted in the heart for recording electrical activity. It determines the underlying cause of arrhythmia and helps suggest the right treatment.
Tilt Table Test: This records blood pressure and heart rate.
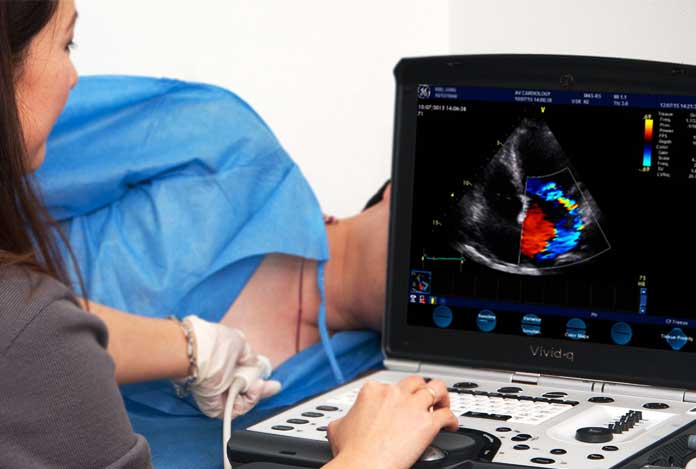
Treatment and Care of Arrhythmia
Discussed below are different treatment methods to manage the condition:
1). Medications:
Prescription drugs available to treat arrhythmia are classified as:
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: These drugs include beta blockers that regulate heartbeat.
- Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy: These include blood thinners like warfarin and aspirin. Dabigatran has also been approved lately for preventing stroke in people having atrial fibrillation.
If irregular heart rate cannot be controlled by drugs, cardioversion may be required. In this method, first an anesthesia is administered, post which, an electric shock is given to the chest.
2). Pacemaker:
If needed, a pacemaker can also be implanted. It is a device that sends out electrical impulses to the heart muscles for maintaining normal heartbeat. These prevent the heart from beating slowly. There is a pulse generator in the pacemaker, which sends impulses to the heart muscles.
3). Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD):
This device is used to treat arrhythmia. It constantly regulates the heart rhythm. When the heart beats very fast, a sequence of electrical impulses may be sent to the heart muscle to restore normal heart rate and rhythm. To bring back the normal rhythm of the heart, ICDs can be used in several ways:
- Anti-Tachycardia Pacing (ATP): When heart is beating at dangerously high levels, higher energy shock may need to be given for restoring normal rhythm.
- Cardioversion: A low-energy shock might be given when the heart continues to beat to restore the usual rhythm.
- Defibrillation: When the heart begins to beat at alarmingly fast or in an irregular manner, a higher-energy shock might be given to cardiac muscles to bring back the normal rhythm.
- Anti-Bradycardia Pacing: If the heart rhythm is too slow, ICDs can give backup pacing to restore the normal rhythm.
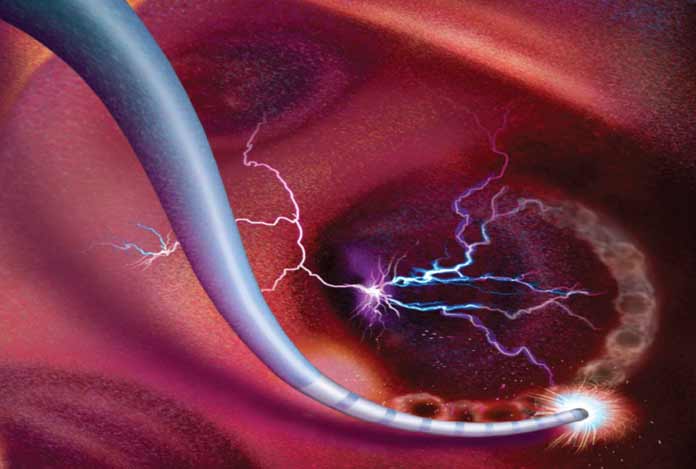
4). Catheter Ablation:
During ablation, electrical energy is sent via a catheter to a small area of tissue inside the heart that is responsible for the abnormal rhythm of the heart. What this electrical energy does is it disconnects the passage of the abnormal rhythm. This is used in the treatment of many other conditions like atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. For achieving correct treatment, ablation may be combined with other procedures.
5). Heart Surgery:
Sometimes, heart surgery may be required to rectify heart disease that is causing arrhythmia. A type of surgery, known as Maze procedure is used for correcting atrial fibrillation. In this, a series of incisions are done in the right or left atria to keep electrical impulses travel through defined pathways. A pacemaker may be required after this procedure.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Arrhythmia
There are many medications available for arrhythmia, but almost all of them are prescription based. This is because, the condition is related to heart and so, it becomes important to get it treated under medical supervision to avoid any complication.
However, many people with irregular heartbeats have less than normal amounts of magnesium in their body. Thus, one can consider taking magnesium supplements. Coenzyme Q10 supplements are also known to be beneficial in managing arrhythmia symptoms.
If you are not consuming fish, you can take fish oil supplements that have high content of omega-3 fatty acids, which is good for heart.

Natural Ways to Cure Arrhythmia
Following are some easy natural methods that help in managing arrhythmia:
- Breathe Slowly and Deeply: When you are having an irregular heartbeat, what best you can do is just sit with your feet elevated from the surface and practice slow and deep breathing. If you take deep long breaths, you will notice that your heart beat will come back to the normal.
- Drink Cold Water: Being hydrated is important to stay healthy and even more important when you have arrhythmia.
- Increasing Magnesium Content: Lack of magnesium is a primary cause of arrhythmia. So, one can treat the condition by taking a magnesium supplement each day. This will bring about a stability in the heart’s electrical impulses.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: It works by removing toxins that may be leading to arrhythmias. Further, it has minerals like magnesium and calcium that regulate heart rate.
- Cayenne: It helps in the stimulation of blood through the body. It further improves the overall heart function.
- Acupuncture: A recent study revealed that 87% of people, who participated in the study, showed normal functioning of heart after acupuncture.

Health Tip by Expert
It is important to take care of the diet as what you eat controls to a large extent how your heart beats. Thus, making smart food choices is important for health of the heart and managing symptoms of arrhythmia. Reducing consumption of salt controls blood pressure and keep heart rate in check. Eat fish and seafood as these have omega-3 fatty acids which help manage arrhythmias. Potassium-rich foods like bananas and yogurt are also known to cut down the risk of arrhythmia.

