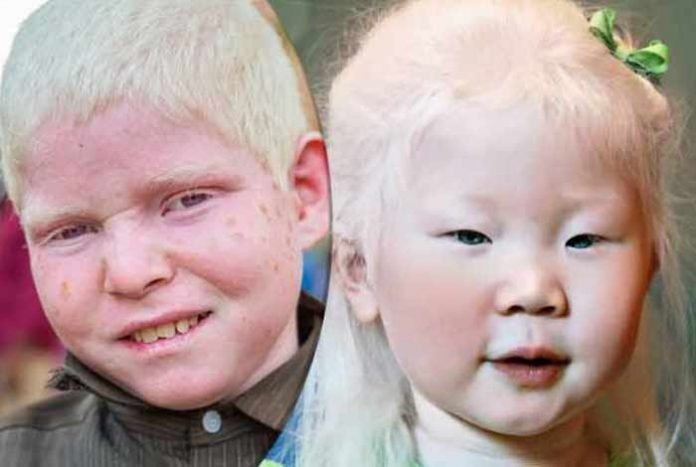
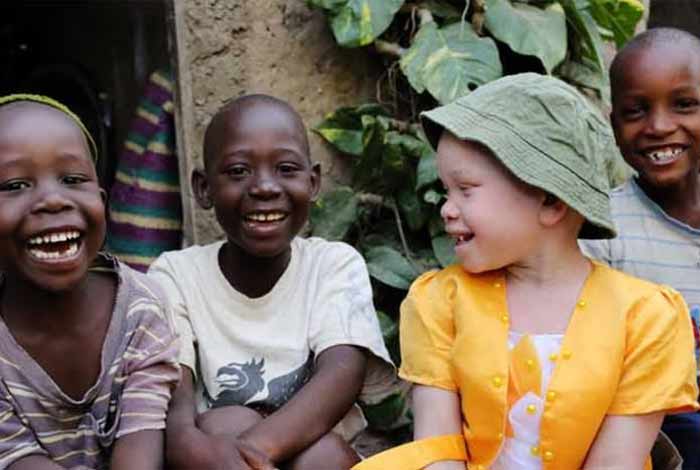
Albinism is a kind of genetic disorder, which results in lower melanin or no melanin production in the affected person. Thus, people with albinism have no color in their skin, hairs and eyes. This disorder can affect one or more than one members in the family. Apart from the abnormal skin pigmentation, people with albinism also experience vision dysfunction.
Incidentally, people with albinism are at a higher risk of skin cancer. Reason for higher risk of cancer is absence of melanin, which is protective agent against the harmful UV rays from the sun.
The symptoms of albinism include absence of color in hair and skin, and vision issues like photophobia, impaired vision and so on.
Genetic testing is the basic diagnostic approach for the diagnosis of albinism. Other methods used by doctors include utilization of electroretinogram technique.
Different treatment approaches are available for albinism. These treatments majorly focus on protecting the skin from UV damage.
Types and Symptoms of Albinism:
Types of Albinism:
Albinism is of different types depending on the type of mutation and type of gene. Different types of albinism include:
- Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA): When the mutation in one of the four genes, this results in the development of oculocutaneous albinism. This is further classified into several different types, depending on the type of mutation. Different types of OCA are type 1, type 2, type 3 and type 4. These different forms of OCA affect skin, hair and eyes differently.
- X-linked Ocular Albinism: Most common in males, this type of albinism is caused by the mutation in X-chromosome. Patients with X-linked ocular albinism have vision dysfunction, but they do not have skin, hair pigmentation problems.
- Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome: This is a rare form of albinism, and its symptoms are similar to oculocutaneous albinism. In this case, a patient develops health issues like lung, heart, bowel and kidney diseases, and may also develop bleeding disorders like hemophilia.
- Chédiak-Higashi Syndrome: This is also a rare type of albinism in which the mutation is caused in CHS1/LYST genes. Though its symptoms are similar to oculocutaneous albinism, the hair becomes silvery or gray in this type of albinism. Patients of this disease have defective white blood cells.
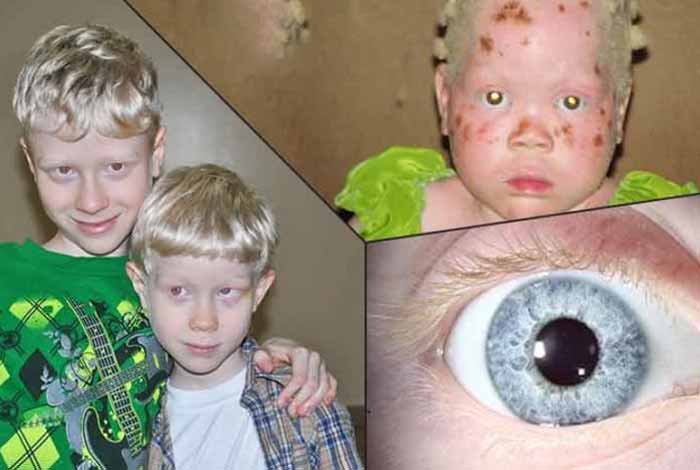
Symptoms of Albinism:
While symptoms of albinism are usually visible on the skin, hair and eye of the patients, it has been reported that patients of albinism experience vision dysfunction as well. Symptoms of albinism can be seen at the time of birth of a child.
Common symptoms for albinism are listed below:
- Changes in the color of skin is the most common symptom of albinism. As a result, the hair becomes white and skin gets pinkish white color. Even in some cases, there is no change in the color of skin, because of normal melanin production. When people with albino skin are exposed to sunlight, they experience freckles, moles, lentigines and tanning.
- Variation in hair color can be easily observed. The color of hair varies from white to brown, which may vary in African or Asian people. The hair color of Asian or African people tend to be yellow, reddish or brown.
- Eye color change can vary from light blue to brown. Reduction in the amount of pigment in the iris may make them appear a bit translucent. Sensitivity to light in albino people is due to lack of pigments in the iris that prevents compete blockage of sunlight.
- Albinism affects vision and eye functions. Common symptoms include back and forth, uncontrollable movements of eyes. Other eye-related symptoms are photophobia, and extreme nearsightedness and farsightedness.
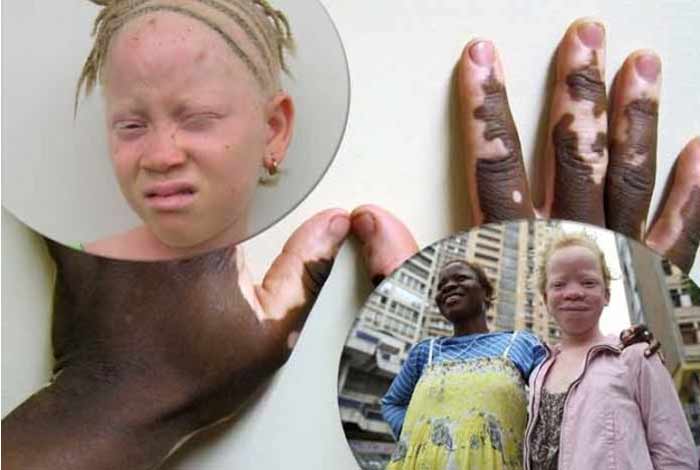
Risk Factors of Albinism
Since albinism is a genetic disorder the only risk is hereditary. If there is a family history of albinism, then the child is more prone to acquire the condition.
Do I have Albinism?
If you observe that the color of your hair and skin changes to white from normal pigmentation, then there are chances that you have albinism. Other symptoms for albinism are change in the color of eyes, growth of moles and freckles on the skin, skin get rashes when exposed to sunlight, etc.
But this is not a confirmatory diagnosis for albinism as these symptoms are related to some other types of skin issues like in eczema the person may have light color patches on the skin. Similarly, in case of vitiligo person may develop pigmentation in the skin as well as in the hair.
Thus, it is better to consult a doctor before reaching on to a conclusion of having any specific disease.
Diagnosis and Tests of Albinism
Diagnosis of albinism is done by following methods:
- Physical or visual examination
- Examination of eyes by an expert using special equipment like electroretinogram
- Genetic testing to detect defective genes
Causes and Prevention of Albinism
1. Causes of Albinism:
Albinism is caused by mutation in one of the several types of genes. These genes are responsible for the production of melanin in the skin and eyes. Mutation alters the enzyme tyrosinase, which eventually affects melanin production in the body. The production of melanin may completely stop or slows down due to mutation. With this problem of pigmentation, visual dysfunction is always associated.
2. Prevention for Albinism:
Taking preventive measures for albinism help patients to get relief from the symptoms. These include:
- Wear sunglasses in order to protect eyes from UV radiation.
- Put on some sunscreen and cover the skin with clothes to avoid UV damage.
- Must consult an ophthalmologist for vision problems related to the disease.
- Correction of vision by surgical methods to treat eye muscles.
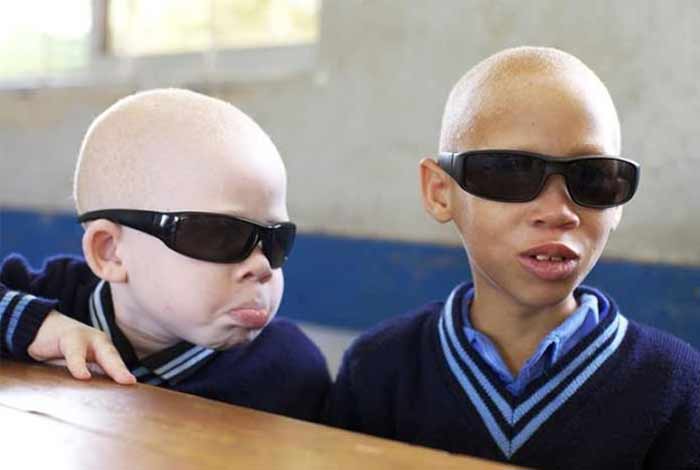

Treatment and Care of Albinism
1.Treatment of Albinism:
Since albinism is a genetic disorder, there are not many treatment options available. One way to avoid the symptoms is to take certain preventive measures. Nitisinone has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating tyrosinemia type 1. It increases the levels of plasma tyrosine that further enhances pigmentation of the hair and eye. It could soon be used in the treatment of people with ocular albinism.
Albino patients with an eye condition, known as strabismus tend to lack depth perception and binocularity after receiving surgery due to the absence of neuronal connections.
2. Care for People with Albinism
- Low Vision Aids: Young children may need glasses and older people may need bifocals. Telescopic lenses can be used for close-up work and distance vision. Using Braille is not required as children are able to read dots.
- Tinted Glasses: These can be used for reducing photophobia. In case, one does not like wearing tinted glasses, they may wear cap or visor when in the sun or outdoors.
- For treating strabismus, eye patching can be done in infants, who are 6 months old. Cases of strabismus can be corrected with the use of glasses.
- Many people with albinism have problems adjusting to impairments of vision. The affected person may tilt the head to one side while reading and hold the book close to the eyes. This may improve vision.
- You can also help your child affected with albinism by asking their teachers to adjust the classroom environment like allowing them to seat in the front row of the classroom, giving them some extra time to complete tests and assignments, and providing them a tablet computer to enhance learning.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Albinism
Albinism is a genetic disorder and its treatment is quite complex. No over-the-counter drug is available in the market that can help relieve a person from its symptoms.
There are some ways of handling the albinism by oneself. The following self-care methods can be used:
- Apply Sunscreens: Use Sunscreens with sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 that helps protect against both UVA and UVB.
- Avoid Exposure to Sun: Don’t go outside, particularly during the day time or sunny days, and at high altitudes.
- Wear Clothes that Shield You Completely: Wear long pants, full-sleeve shirts and it is best to cover your head as well with a scarf.
- Eyes should be protected by wearing sunglasses and transition lenses that become dark in bright light.
Natural Ways to Treat Albinism
In albinism, the skin and eyes become highly sensitive. In this condition, natural remedies are known to be very effective. Some of the natural treatments for albinism are:
- Massaging the skin with red raspberry oil can prevent it from harmful effects of sunrays.
- Mixture of herbal oils like myrrh, geranium, lavender, thyme, clove and olive oils helps prevent the skin from sun burns and irritation.
- Applying natural sunscreens, prepared using aloe vera gel, vitamin E and lavender essential oil, soothe skin.
- Carrot seed oil treats skin burns caused by solar radiation.
Health Tip by Expert
If you have albinism and want to enjoy outdoors, you can do so by limiting sun exposure, wearing appropriate clothing and applying sunscreens.