Chronic in nature, acne is a skin condition, which is characterized by pimples and spots on the face, chest, shoulders, neck, upper arm and back. It occurs when hair follicles on the skin get blocked by oil from sebaceous glands (oil-producing glands) or dead skin cells.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, hormones and stress are the two leading causes of acne in adults. When a person is chronically stressed, body produces more androgen hormones that trigger oil production and cause acne.
Nearly everyone at some point of life suffers from the problem of acne. Although acne is considered as a curse of adolescence, about 20% cases of acne are also found in adults. Usually, acne starts during puberty, in children aged 10 to 13 years, and it is found worst in people with oily skin. Teenage acne lasts for 5 to 10 years and ends up in the early 20s. It occurs in both boys as well as girls. However, boys usually have more severe acne than girls.
Types and Symptoms of Acne:
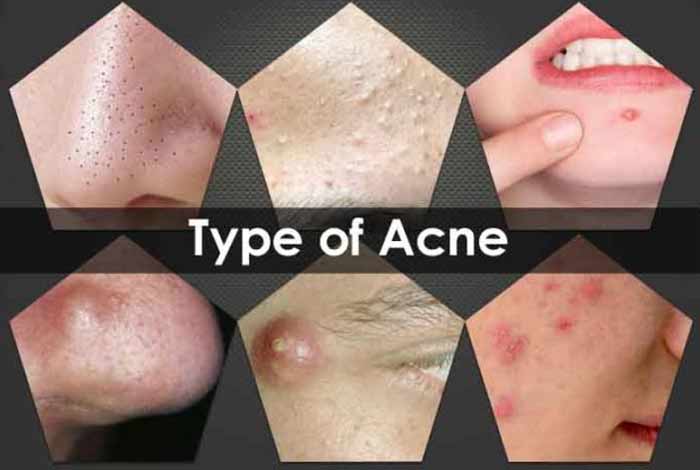
1.Types of Acne:
Acne may vary in terms of size, color level of its effect on the skin and pain. Below are the possible types of acne:
- Blackheads: These are black in color and appear on the upper layer of the skin. Blackheads are clearly visible.
- Whiteheads: These are smaller in size and remain under the skin.
- Pustules: These have a red base on the skin surface and pus in it.
- Papules: These are pink bumps that are clearly visible on the skin surface.
- Cysts: Filled with pus, these are small lumps on the surface of the skin and are painful too. Cysts can leave scars as well.
- Nobules: Deeply embedded in the skin, nobules are clearly visible on the skin. These are painful and large in size.
2. Symptoms of Acne:
The most common site of acne is face, but it can also occur on neck, back, chest, arms and shoulders. Moreover, you might not have acne everywhere, but only on the face. Acne spots may be inflamed or non-inflamed. Whiteheads and blackheads are non-inflamed, whereas inflamed spots are like lumps and red bumps or cysts filled with a yellow fluid. Skin may be greasy, so the spots may feel more delicate to touch. These symptoms may vary from person to person according to their skin type:
- Mild Acne: Non-inflamed spots.
- Moderate Acne: Inflamed spots, non-inflamed spots, or may be both, and there is a risk of scars as well.
- Severe Acne: A lot of inflamed spots and cysts, and at a higher risk of leaving scars.

Risk Factors of Acne:
The below-mentioned factors can lead to acne:
- Hormones: During puberty, the level of androgens increases in boys and girls. This enlarges sebaceous glands and produces more sebum. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and the use of contraceptives can also boost sebum production. Low level of androgens in the blood of women can worsen the condition of acne.
- Certain Medications: Some medicines, which include lithium, testosterone and corticosteroids can cause acne.
- Diet: Diets comprising fat- and carbohydrate-rich foods, such as chips, bread and bagels may worsen acne. Chocolates are also found worse for acne.
- Stress: Stress is one of the causes of acne.
- Family History: Genes play a crucial role in acne development. If parents had acne, children are more susceptible to have it.
- Oily Substances: If a person uses oily creams and lotions or works in greasy areas like kitchen, he/she is more likely to develop acne.
- Friction: Things such as helmets, cellphones, telephones, tight collars and backpacks can cause acne because such items may exert pressure on the skin.
Do I have Acne?
There exist other skin diseases, which has symptoms similar to those of acne. If you have blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, papules or pustules, it might be possible that you have acne, but possibilities are there that these might be indicative of other skin conditions.
Cysts are also formed in case of tumors, genetic conditions, defective skin cells, infections or chronic inflammatory conditions. On the other hand, papule is a skin lesion, which changes the color of the skin. It makes cluster on the skin and collectively form a rash. It can also be caused if you have dermatitis, eczema or chickenpox.
So, it is suggested to consult a dermatologist if you have a skin problem that you are ignoring for quite some time thinking it to be acne.
Causes and Prevention of Acne:
1. Causes of Acne:
Acne starts with a greasy secretion from the oil glands present in the skin, known as sebaceous glands, that are connected with the small opening of hair follicles. If the opening of these follicles is small, then whiteheads – small, flesh-colored bumps on the skin – are formed, whereas if the pores are large, then blackheads – black spots with dark centers – are formed. Both kinds of pores can lead to pimples, inflammation or deeper lumps and sometimes, infection.
There are four main factors that cause acne:
- Excessively active hormones (androgens)
- Excessive oil production
- Bacteria
- Hair follicles congested by dead skin cells and oil.
Apart from these, there are several other factors that can trigger acne formation or may worsen the condition:
- Hormones: During puberty, a hormone, called androgen tends to increase in boys and girls, which causes the enlargement of sebaceous glands and thus, produce more oil. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or use of oral contraceptives can affect the production of sebum. Low level of androgens in the blood of women can worsen acne.
- Greasy Foods: Though greasy food has less impact on the skin, working in a greasy environment like a kitchen to fry something can cause acne. This is because oil used for frying can stick to the surface of the skin and may block the hair follicles to promote acne.
- Stress: Another cause of acne is stress. When a person is stressed, the stress hormone, cortisol – produced by adrenal gland – is released in the body to help the body deal with stress. Sadly, a bit of testosterone unnecessarily leaks out with the release of cortisol, which can boost this gland to produce more oil in the skin – a major cause of acne.
- Pollution: Air pollution forms a layer of dust particles on the surface of the skin, which clogs the pores and results in acne. It also discolors the skin, and dark patches start to appear on the skin surface.
- Use of Greasy Products: If a person has an oily or combination skin, he or she should choose skin-care products labeled as oil-free or water based. The product should not be greasy, since such products clog skin pores and cause acne.
- Frequent Cleaning of Face: Overwashing makes the skin dry, which can produce more oil to overcompensate the dryness. Hence, one should clean the face only twice in a day. More than this, could lead to acne.
- Medication Side Effects: Some drugs may trigger acne in some people; depending on the type of skin. People with sensitive skin are more prone to acne due to several drugs like isoniazid, progestins, lithium, seizure medications and even vitamin B. Sometimes, acne medication may also lead to acne as it begins the treatment through the development of acne first.
- Family History: Genetics play a prominent role in acne development. If your mother and your father had acne in their adulthood, you are more likely to get this condition. Treatments work no to little in this case.
- Pressure on the Skin: Friction on the skin may cause acne through stuffs like telephones, backpacks, tight collars, cellphones and helmets. Though it is quite rare, but extra rubbing on skin like wearing tight helmets, carrying backpacks for long may result in acne.
- Diet: Some diets that include foods rich in carbohydrates and skimmed milk may cause acne and even worsen the condition. Foods, such as chips, bread, bagels are not good for acne-prone skin.
- Sugar Intake: Sugar increases your insulin level, which increases the level of hormones responsible for oil production. Extra oil production in the skin can cause acne. It is better to cut down your sugar intake to prevent acne, and consume complex carb foods like whole grains that break down in the body and cause less effect of insulin in the body.

2. Prevention of Acne:
Several measures can be taken to prevent acne that are as follows:
- Wash your face, but not more than two times in a day using a mild soap and water.
- Do not scrub your face, especially the acne area as it may push the infection and can cause more redness and swelling.
- Avoid squeezing the pimples as this may leave scar marks.
- Do not touch the face frequently.
- Hold the telephone away from the face while talking as it may contain sebum and skin residue.
- Wash hands before applying creams or makeup.
- Clean eyeglasses before wearing as they contain sebum and skin residue.
- Avoid tight clothes as it may restrict the skin to breathe properly.
- Use oil-free cosmetics and skin-care products, and remove makeup before going to bed at night.
- Keep the hair clean as it contains sebum and skin residue. Avoid using oily products on hair.
- Try to keep dry and cool in humid and hot climates to prevent sweating.
- Avoid stress as it can increase the production of cortisol and adrenaline which can cause acne.
- Avoid excessive exposure to sun as it can produce more sebum, which is responsible for acne.
Diagnosis and Tests of Acne:
Dermatologists diagnose the problem by examining the affected area of the skin. The doctor may ask several problem-related questions and to check whether it is actual a problem of acne or other skin disorder. The questions may be related to:
- Areas of sensitive skin
- Any other medicine, which may reduce the effectiveness of medicine for acne.
- Previous drug allergy
- Use of steroids in case of bodybuilding
- Depression or other mental disorders
- Irregular menstrual cycle, use of contraceptives, breastfeeding or delivery.
Treatment and Care of Acne:
The treatment of acne depends on the severity of the acne. A treatment should be chosen keeping in mind the sensitivity of the skin. Treatments are better if it is under the supervision of a dermatologist. Below are some of the medicines that your dermatologist may prescribe you:
- Antibiotics: It may be applied in the form of creams, gels, solutions and lotions on the surface of the skin or may be taken orally. It fights against acne bacteria and reduces inflammation. Topical antibiotics have a limited ability to penetrate the skin and clear deeply embedded acne. Some topical antibiotics like clindamycin and erythromycin are also anti-inflammatory drugs. Oral acne-treating antibiotics include doxycycline, minocycline, and tetracycline that fight against acne and help to unclog skin pores.
- Retinoids and Similar Drugs: These drugs are available in both the forms, i.e., topical as and oral. Topical retinoids clear acne; whether it is a moderate or severe one, and further, restore the skin. There are also some minor side effects of this class of drugs, such as dryness, redness and itchy skin. Isotretinoin is used as a drug to treat severe cystic acne. Oral form of retinoids is not recommended for pregnant women as it may lead to severe birth defects in the child.
- Azelaic Acid: Another acne drug is azelaic acid, which is available for topical use as well as oral. It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It may be helpful in mild acne.
- Dapsone: It is available in the form of topical gel, which has antibacterial as well as anti-inflammatory properties and can fight against acne.
- Spironolactone: It is an oral drug, which blocks the activity of hormones that boost the function of oil-producing glands. This medication is not FDA approved, but highly effective on acne, which worsens at the time of menstruation.
- Triamcinolone: It is a type of corticosteroid, which is directly injected in acne nodules to treat the same.
- Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills contain female hormones and prevent acne by neutralizing the effect of male hormone – testosterone – on acne. It shows its effects in three to four months. Nevertheless, there are some side effects of these medicines, such as nausea, spotting, breast tenderness, weight gain and blood clots.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Acne
1. OTC Medications for Acne:
Gentle cleansing of the face twice a day may prevent acne. However, it does not work on acne scars. One should wash the face with gentle soap and water when back to home from outside. Cleansers should contain ingredients like salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, retinol and glycolic acid that fight against acne problems:
- Salicylic Acid: Basically, a beta-hydroxy acid, salicylic acid works in exfoliating unclog pores. Use it gently on the face as it also helps to treat spots.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: It kills the acne bacteria and exfoliates pores at the same time. It is not gentle in nature and makes the skin dry if used too much. In fact, it is more beneficial for spot treatment.
- Sulfur: It extracts the oil out of the skin and gives a drying effect, which helps prevent acne formation. It is also good for spot treatment.
- Glycolic Acid: It is an alpha hydroxy acid and acts as an exfoliating ingredient, which helps in preventing acne. It also works on wrinkles, and improves skin texture and reduces fine lines.
- Retinol: Topical retinoids are highly effective for can, and works well as and anti-aging agent, because of its ability to boost collagen production. However, they are harsh and can leave the skin dry.
- Alcohol and Acetone: While alcohol has anti-bacterial properties, acetone removes oil from the surface of the skin. A combination of the two may effectively work against acne, but can dry out the skin.

2. Self-Management Methods for Acne:
One can follow the below-given tips to prevent and manage acne on their owm:
- Wash your face twice a day to keep it clean and remove extra oil
- from the skin
- Always use moisturizers that minimize the dryness and lessen
- skin peeling
- If you wear makeup, do wash it at the end of the day.
- Avoid applying oils or gels in the hair. If such hair comes onto your face, they can block the pores, which may lead to acne.
- Be specific about the choice of soap or face wash. Avoid using soaps containing harsh chemicals. Use medicated or herbal soap if you have acne.
- Use only a soft and clean towel for face. Avoid harsh rubbing as it may harm your skin. A dirty towel may bring bacteria on top your face that can worsen the condition of acne.
Natural Ways to Treat Acne:
There are a handful natural stuffs, most of which are usually available at homes, that can help treat acne without any side effects:
- Apple Cider Vinegar: It has antibacterial and antiviral properties. It is also known to wipe off extra oil from the skin.
- Honey and Cinnamon: These are excellent sources of antioxidants, fight against bacteria and reduce inflammation that triggers acne. Make a paste of two tablespoon of honey with one teaspoon of vinegar. Apply it on the face and leave in for 10-15 minutes. Rinse off the mask completely. It makes the skin acne free.
- Tea Tree Oil: It fights against bacteria and reduces inflammation. Mix one part of tea tree oil with 9 parts of water. Dip a cotton ball into it and apply on the affected area. Repeat this process 1-2 times a day. It helps reduce acne scars and makes the skin acne free.
- Aloe Vera: It helps in the healing of burns and wounds, and fights against inflammation. Take a gel from the Aloe Vera plant and apply directly on to the skin as a moisturizer. One can repeat the process once or twice a day.
Health Tip by Expert:
Products containing salicylic acid are beneficial in acne. Separating treatments, such as using salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide in the morning and a retinol-based product at night, might be helpful if a person has sensitive skin.