Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens and Its Most Common Drug List

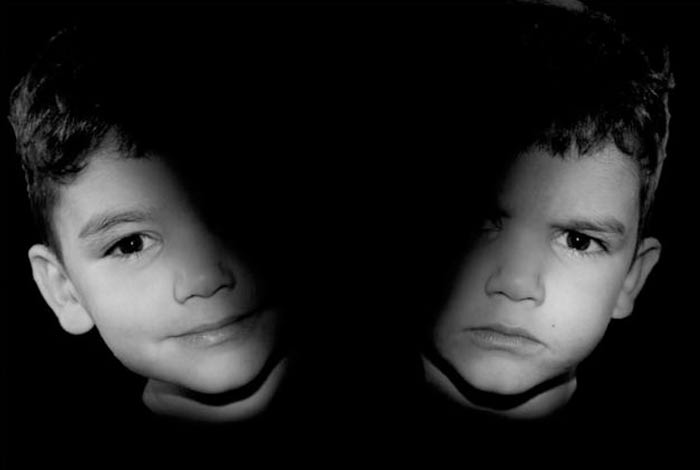
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive illness, is a serious mental health disorder. Generally, the typical onset of bipolar disorder is at 25 years of age. However, if it appears in early childhood or adolescence, it is referred to as “Early-onset form of mental illness”.
Bipolar disorder in children and teens is marked by drastic mood changes with periods of feeling extremely excited (known as manic episodes) and periods of feeling too low, hopeless and sad (known as depressive episodes). However, it should not be confused with normal mood swings seen in teens and children. If your child is experiencing such severe mood changes, along with changes in sleep pattern, thinking ability and energy level, then its most likely bipolar disorder.
Bipolar disorder poses a serious threat in children and teens, as compared to adults. This is for a simple reason that brains of children and teens are still immature. Gray matter of the brain, also called as thinking part of the brain, is still in its developing stage in children and teens. Similarly, frontal cortex, which is responsible for planning, reasoning, impulse control and judgment, is also immature in children and teens. Hence, an immature brain and severe mood changes can push the child towards suicidal tendencies and substance abuse. It may also induce tendencies of self-harm in teenagers. Therefore, recognizing bipolar disorder at an early stage is particularly significant in children and teens.
Although it is a dreadful condition, it is absolutely manageable. Medications and psychotherapy form the mainstay of treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens.
Symptoms
A child or a teen with bipolar disorder may have a manic episode, a depressive episode or a mixed episode. As per the National Institute of Mental Health, the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children and teens are as follows.[1]
A manic episode is characterized by the following symptoms.
- Unusually happy
- Short-tempered
- Talking extremely fast and abruptly changing topic while talking
- Inability to concentrate
- Thinking and talking about sex more often
- Risk-taking attitude
A depressive episode is marked by the following symptoms
- Feeling extremely sad
- Increased frequency of painful complaints, such as headache and stomach ache
- Sleeping too much or too little
- A feeling of guilt and worthlessness
- Eating too much or too little
- Reduced energy level and not finding pleasure in activities once enjoyed
- Suicidal thoughts
However, it must be noted that sometimes behavioral disorders and mood disorders can go hand-in-hand in children and teens. ADHD, substance abuse and anxiety disorders such as separation anxiety are some of the common conditions seen accompanying bipolar disorder in children and teens.
Treatment
There is no cure for bipolar disorder. Doctors treat bipolar disorder in children and teens, in the same way as they do in adults. Psychotherapy or talk therapy in combination with medications constitutes the chief treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy along with Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy are forms of psychotherapy, which play a vital role in treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens. These therapies help the children and teens in understanding themselves, adapting to stressful situations and augmenting their self-esteem.
However, medications are required to enhance the advantages of psychotherapy. Lithium carbonate, anti-psychotics, anti-depressants and anti-anxiety drugs are commonly advocated in the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens.
Other therapies, such as Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) may also prove effective.
The drugs used in the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens are described below.
1. Lithium Carbonate
It is a mood stabilizer and relieves manic episodes seen in bipolar disorder. However, the exact mechanism by which it works is not known and various theories have been formulated to decipher its acting mechanism.
Some researchers believe that it affects the ionic reflexes of the brain by replacing the sodium ions present in the body. Another theory suggests that it rectifies the chemical imbalance seen in bipolar disorder by blocking the release of certain brain chemicals (medically known as neurotransmitters), namely Noradrenaline and Dopamine. But, some researchers argue that lithium carbonate specifically targets the hyperactive neurons by cutting down the supply of a chemical, known as inositol.
Basically, lithium carbonate normalizes the brain functioning by altering the brain chemicals and signal transduction of the brain.
Available as: Oral preparations
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: lithium carbonate
Brand name: Lithium Carbonate tablet
Side-effects: Nausea, vomiting, thinning or drying of hair, hand tremors, skin itching, lack of coordination.
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely indicated as it can cause cardiac abnormalities in fetus, like Ebstein’s anomaly
Alcohol Content: Absent
2. Typical Antipsychotics
These constitute the earlier developed antipsychotic dugs and are also called as first-generation antipsychotics.
Research has shown that bipolar disorder is strongly associated with dopamine imbalance. Dopamine is a brain chemical that regulates various body functions, such as attention, sleep, learning and motivation. These actions of dopamine are mediated through a specific receptor present in brain, known as D2 receptor. Typical antipsychotics block the D2 receptor and thus normalize the imbalance of dopamine. Hence, they alleviate mood changes, specifically the manic episodes, seen in bipolar disorder in children and teens.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
I. Phenothiazines
A. Chlorpromazine
US-FDA Status: Unapproved for Bipolar Disorder
Generic name: chlorpromazine hydrochloride (oral)
Brand name: Thorazine
Side-effects: Weight gain, dizziness, skin rash, dry mouth, extrapyramidal side effects, such as tardive dyskinesia (involuntary movements, like eye blinking, lip smacking, etc.), dystonia (abnormal posture and movements)
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely needed as evidence shows prolonged labor, fetal abnormalities and even fetal death on administration of drug in pregnancy
Alcohol Content: Absent
B. Trifluoperazine
Trifluoperazine Oral
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: trifluoperazine hydrochloride
Brand name: Trifluoperazine Hydrochloride
Side-effects: Extrapyrimidal side-effects (as already mentioned), dry mouth, muscle weakness, skin rash, anorexia, blurred vision, dizziness
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely needed as evidence shows prolonged labor, fetal abnormalities and even fetal death on administration of drug in pregnancy
Alcohol Content: Absent
Trifluoperazine Injection
US-FDA Status: Unapproved for Bipolar Disorder
Generic name: trifluoperazine hydrochloride
Brand name: Stelazine
Side-effects: Same as observed with Oral Trifluoperazine
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely indicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
C. Fluphenazine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: fluphenazine hydrochloride (oral), fluphenazine decanoate (injection)
Brand name: Fluphenazine Hydrochloride (oral), Fluphenazine Decanoate (injection)
Side-effects: Extrapyramidal side-effects (already described above), depression, blurred vision, drowsiness, cataract
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only if benefits outweigh risk to the fetus as it can disrupt the skeletal and cerebral development of fetus
Alcohol Content: Absent
II. Butyrophenones
A. Haloperidol Oral and Injection
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: haloperidol (oral), haloperidol decanoate (injection)
Brand name: Haloperidol (oral), haldol (injection)
Side-effects: Extrapyramidal side-effects (already described above), constipation, dry mouth, blurred vision, weight gain
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only if benefits outweigh risk to the fetus as it can disrupt the skeletal and cerebral development of fetus
Alcohol Content: Absent
3. Atypical Antipsychotics
These are newly developed antipsychotic drugs, which are also known as second-generation antipsychotic drugs.
Similar to typical antipsychotics, these drugs also alter the brain chemicals and affect the chemical transduction of brain. However, unlike typical antipsychotics, these drugs have a weak D2 receptor inhibiting action and they strongly block other brain receptors, namely alpha-adrenergic receptors and serotonin receptors. Hence, atypical antipsychotics can effectively manage mood changes seen in bipolar disorder.
Also, atypical antipsychotics are preferred over atypical antipsychotics due to their relatively less side-effects.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
I. Olanzapine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: olanzapine (oral), olanzapine pamoate (injection)
Brand name: Olanzapine (oral), Zyprexa Relprevv (injection)
Side-effects: Extrapyramidal symptoms, weight gain,drowsiness, weakness, dry mouth
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually not given in third trimester as it may cause hypotonia, hypertonia, tremors, agitation, distress and feeding disorders in infants
Alcohol Content: Absent
II. Risperidone
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: risperidone
Brand name: Risperidone (oral), Risperdal Consta (injection)
Side-effects: Anxiety, aggression, agitation, skin rash, increase amount of urine, itching, memory problems
Indicated in Pregnancy: Evidence of stillbirths have been reported, hence it is given in pregnancy only when absolutely indicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
III. Aripiprazole
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: aripiprazole
Brand name: Abilify (oral), abilify maintena kit (injection)
Side-effects: Muscle trembling, loss of balance control, limbs stiffness, drooling, speech difficulty, drooling
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely needed, as it may cause fetal developmental defects
Alcohol Content: Absent
IV. Quetiapine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: quetiapine fumarate (oral)
Brand name: Seroquel XR
Side-effects: Muscle trembling, loss of balance control, limbs stiffness, drooling, speech difficulty, drooling
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely needed, as it may cause fetal developmental defects
Alcohol Content: Absent
V. Ziprasidone
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: ziprasidone hydrochloride (oral), ziprasidone mesylate (injection)
Brand name: Geodon (oral and injection)
Side-effects: Loss og balance control, fever, cough, drooling
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely needed, as it may cause fetal developmental defects
Alcohol Content: Absent
VI. Lurasidone
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: lurasidone hydrochloride (oral)
Brand name: Latuda
Side-effects: Difficulty with swallowing, drooling, inability to sit still, muscle discomfort
Indicated in Pregnancy: It can cause tremors, agitation, hypotonia, somnolence and respiratory disorder in fetus, if administered in third trimester
Alcohol Content: Absent
VII. Asenapine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: asenapine maleate (oral)
Brand name: Saphris
Side-effects: Inability to move eyes, trouble with swallowing, breathing, or speaking, lip smacking or puckering, abnormal or reduced touch sensation
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated, particularly in third trimester
Alcohol Content: Absent
4. Selective Serotonin Re-Uptake Inhibitor (SSRI) Anti-depressants
SSRIs are newly developed anti-depressants, which are used to relieve the depressive episodes of bipolar disorder. It inhibits a particular transporter situated on the nerve cell membrane, known as Serotonin Transporter (SERT). SERT plays an important role in re-uptake or reabsorption of a brain chemical, serotonin back in the nerve cell. Thus, by blocking SERT, these anti-depressants prolong the stay of serotonin in the blood. Potentiated action of serotonin elevates the mood and helps in managing moos changes in bipolar disorder.
However, it may aggravate manic episodes in bipolar disorder. Also, it may take weeks to show desirable results.
Available as: Oral preparations
I. Fluoxetine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: fluoxetine hydrochloride (oral)
Brand name: Sarafem
Side-effects: Inability to sit sill, restlessness, itching, hives, skin rash
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely indicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
II. Paroxetine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: paroxetin mesylate (oral)
Brand name: Brisdelle
Side-effects: Chills, cold sweats, chest pain, agitation, chest congestion, agitation
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely indicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
III. Sertraline
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: sertraline hydrochloride (oral)
Brand name: Zoloft
Side-effects: Reduced sex drive, Failure to ejaculate (in men)
Indicated in Pregnancy: Only when absolutely indicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
IV. Citalopram
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: citalopram hydrobromide (oral)
Brand name: Celexa
Side-effects: Fever, loss of memory, blurred vision, confusion, agitation
Indicated in Pregnancy: Absolutely contraindicated in third trimester and is used only when absolutely needed
Alcohol Content: Absent
V. Escitalopram
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: escitalopram oxalate (oral)
Brand name: Lexapro
Side-effects: Dizziness, muscle cramps, confusion, coma, convulsions
Indicated in Pregnancy: Absolutely contraindicated in third trimester and is used only when absolutely needed
Alcohol Content: Absent
5. Anti-epileptic or Anti-convulsant Drugs
This group of drug forms the chief medications in epilepsy (commonly known as fits). Anti-epileptic drugs used in the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens are as follows.
I. Aliphatic Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Action potential or brain signals are generated when certain ions flow across the voltage-gated channels present on the nerve membrane.
These anti-epileptic drugs inactivate the voltage-gated sodium ion channels and decrease the calcium ion influx across the nerve membrane. These also increase the release of a particular brain chemical, known as GABA (gamma-Amino butyric acid).
By all these actions, these anti-epileptic drugs affect the transmission of brain signals and counteract the mood changes and manic episodes seen in bipolar disorder.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
A. Valproic Acid (Sodium Valproate)
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: valproic acid (oral), valproate sodium (injection)
Brand name: Depakene (oral), Depacon (injection)
Side-effects: Black tarry stools, blood in stool or urine, confusion, bloating, bleeding gums, hoarseness, cough
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
B. Divalproex (Semisodium Valproate)
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: divalproex (oral)
Brand name: Depakote
Side-effects: Black tarry stools, blood in stool or urine, confusion, bloating, bleeding gums, hoarseness, cough
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
II. Iminostilbene
Similar to aliphatic anti-epileptic drugs, these drugs also inactivate the voltage-gated sodium ion channels and relieves the mood changes and manic episodes in bipolar disorder. However, they are used as an alternative to another mood stabilizer, i.e., lithium carbonate.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
A. Carbamazepine
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: carbamazepine
Brand name: Tegretol (oral), Carnevix (injection)
Side-effects: Continuous back and forth eye movement, blurred vision, double vision
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
III. Phenyltriazine
This group of drugs inactivates the voltage-gated sodium channels and also impart stability to nerve cell membrane, thus blocking the release of specific brain chemicals i.e., aspartate and glutamate.
By doing so, these normalize the brain activity and are used as mood stabilizers and anti-manic drugs in bipolar disorder.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
A. Lamotrigene
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: lamotrigine (oral)
Brand name: Lamictal
Side-effects: Unsteadiness, blurred vision, skin rash, poor coordination
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
IV. Benzodiazepines
GABA (gamma-Amino butyric acid) is a brain chemical that decreases the excitability of nerve cell. BZDs potentiate the action of GABA and thus, produce an anti-anxiety effect.
However, it must be remembered that BZDs only relieve the anxiety associated with bipolar disorder and are thus, used only on a short-term basis.
Available as: Oral preparations and Injectable preparations
A. Diazepam
Diazepam Oral
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: diazepam (oral)
Brand name: Valium
Side-effects: Problem with muscle coordination or control, unsteady walk, trembling
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
Diazepam Injection
US-FDA Status: Unapproved for Bipolar Disorder
Generic name: diazepam (injection)
Brand name: Valium
Side-effects: Same as observed with oral diazepam
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
B. Alprazolam
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: alprazolam (oral)
Brand name: Xanax
Side-effects: Speech alteration, forgetfulness, unsteadiness, irritability, drowsiness
Indicated in Pregnancy: Not indicated in first trimester as it may cause congenital malformation in fetus
Alcohol Content: Absent
C. Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide Oral
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride (oral)
Brand name: Librium
Side-effects: Mood changes, difficulty in muscle coordination, fainting, unsteadiness
Indicated in Pregnancy: Not indicated in first trimester as it may cause congenital malformation in fetus
Alcohol Content: Absent
Chlordiazepoxide Injection
US-FDA Status: Unapproved for Bipolar Disorder
Generic name: chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride (injection)
Brand name: Librium
Side-effects: Same as observed with oral chlordiazepoxide
Indicated in Pregnancy: Not indicated in first trimester as it may cause congenital malformation in fetus
Alcohol Content: Absent
D. Lorazepam
US-FDA Status: Approved for Bipolar Disorder
Availability: Prescription only
Generic name: lorazepam (oral and inejction)
Brand name: Ativan (oral), lorazepam (injection)
Side-effects: Drowsiness, abdominal pain, agitation
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated, due to its potential to cause neonatal flaccidity, feeding and respiratory difficulties.
Alcohol Content: Absent
E. Oxazepam
US-FDA Status: Unapproved for Bipolar Disorder
Generic name: oxazepam (oral)
Brand name: Oxazepam
Side-effects: Black tarry stools, dark urine, chest pains, fainting, abdominal pain
Indicated in Pregnancy: Usually contraindicated
Alcohol Content: Absent
OTC
The medications used in the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and teens act on the nervous system and can produce major side-effects. Hence, all these drugs are available on prescription only.
It must be remembered that doctor’s consultation should not be neglected in such mental health disorders. Self-medication is not recommended.