
Diabetes is a condition in which the blood sugar level gets higher than normal, and therefore, a number of people believe that it is caused by consuming too much sugar. Although it is true that excess consumption of sugar can increase you risk of developing diabetes, sugar is just a piece of puzzle. There are a number of other factors that elevate your risk of getting diabetes, such as lifestyle, diet and genetics.
Read on to discover the role of sugar in developing diabetes and tips to prevent it.
What Is Diabetes?
When the body is unable to effectively regulate the blood glucose level in the body, it leads to diabetes. This happens when the pancreas do not produce enough glucose-regulating hormone, insulin, or the body becomes resistant to insulin or both. [1]
High blood sugar levels for a prolonged period of time can lead to a number of complications, including kidney damage, heart disease and nerve damage and therefore, it is important to keep blood glucose level in check.
Two major types of diabetes are:
• Type 1: When the pancreas are unable are produce insulin as the immune system destroys insulin-producing cells, it leads to type I diabetes. It is rather a rarer form of diabetes and is caused genetically.
• Type 2: It occurs when the pancreas do not produce enough insulin or the body develops resistance to the insulin synthesized or both. It is a lifestyle disease and is relatively more common in the population.
Metabolism of Sugar
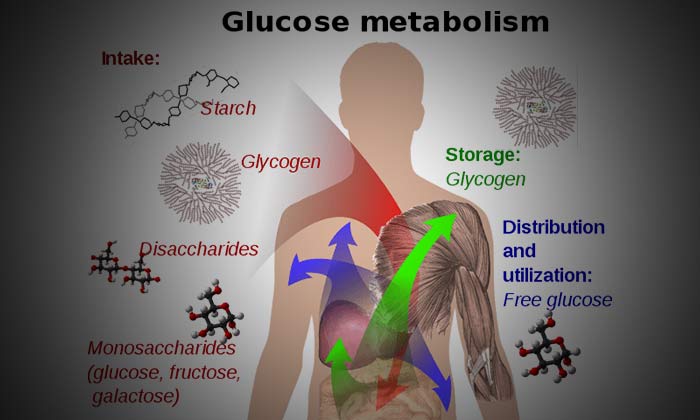
Our food contains complex sugars like sucrose and simple sugars like glucose and fructose. Complex sugars are broken down into simple sugars in the body. Glucose is the main source of energy in the body, and is absorbed from the bloodstream.
After the food gets digested, and the sugars have been broken down into simpler forms, they are absorbed into the blood and carried to different parts of the body. Absorption of glucose from the gut into the blood causes the blood glucose level to rise. This is where insulin comes into play and facilitates the uptake of glucose from the blood into the cells, thereby bringing down the blood sugar level. The glucose that is taken up by the cells is metabolized and used for producing energy for carrying out different life processes.
Another simple sugar is fructose, commonly found in sweet fruits. After being absorbed from the gut, a small fraction of it can be taken up by the cells and used for energy production. Majority of it is carried over to the liver and converted into either fat for storage or glucose for production of energy.
Since fructose can be stored in the body as fat after conversion, excess intake of foods rich in fructose is known to increase the levels of triglycerides, thereby increasing your chances of developing fatty liver and heart diseases.
When fructose is metabolized in the body, it can lead to increase in the levels of uric acid in the body which can settle in the joints and lead to gout.
If your consumption of sugar is more than what is required by your body, it gets accumulated in the form of body fat.
Does Sugar Increase Your Risk of Diabetes?

Several studies indicate that people, who consume sweetened beverages have nearly 25% more chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
As a matter of fact, consuming just one sugar-sweetened beverage everyday can increase your risk by 13%, irrespective of any weight gain due to it.
Additionally, it has been found that countries, where highest levels of sugar consumption is found show highest rates of type 2 diabetes and vice versa.
It has been discovered that the link between diabetes and sugar intake is true even when calorie intake, alcohol consumption, body weight as well as exercise are well controlled.
Although these studies do not show any direct link between sugar and diabetes, the link is strong. There are a number of scientists who believe that sugar plays a role in increasing the risk of diabetes, both directly as well as indirectly. This is because the impact fructose has on the liver.
Consuming large amounts of sugar can cause you to develop diabetes by increasing your weight and leading to obesity, which is another risk factor for diabetes.
Also, animal studies indicate that eating a lot of sugar might disrupt the signaling of a hormone, leptin, that is responsible for promoting the feelings of fullness, which leads to overeating and hence, weight gain.
Therefore, in order to decrease the harmful effects of high sugar consumption, WHO recommends that not more than 10% of your daily calories should come from added sugars.
Natural Sugars Do not Have the Same Effect
Natural sugars do not increase the risks for diabetes like the processed sugar. Sugars that are naturally found in fruits and vegetables and have not been added during processing and manufacturing are called natural sugars. Since these sugars are found in a matrix of water, fiber, antioxidants and other nutrients, they get digested easily and are absorbed slowly and have less chances of causing blood sugar spikes.
Vegetables and fruits have far less amounts of sugar by weight than most processed foods, and hence, it is easier to keep your consumption in check.
What About Fruit Juice?

Researchers have a mixed opinion whether consuming 100% fruit juice can increase diabetes risk or not.
There are a number of studies that have discovered a link between fruit juice consumption and diabetes as fruit juices have high sugar and low fiber content.
What About Natural Sweeteners?

Although natural sweeteners maple syrup, honey and agave are made from plant sources, they are still extremely refined; almost like table sugar or sucrose.
They are rich in sucrose and fructose and therefore, are considered just like added sugar when used in food preparation.
Do Artificial Sweeteners Increase Diabetes Risk?

Artificial sweeteners are sweet tasting substances that are manufactured artificially and cannot be metabolized by humans for energy. In simple terms they can be said to provide just the sweetness without any energy.
Even though, artificial sweeteners are not known to spike blood sugar levels, they are still thought to play some role in developing type II diabetes.
It is not clear why and how artificial sweeteners increase the risk of diabetes. However, there are a number of theories. One such theory believes that artificially sweetened products induce cravings for sweet-tasting foods, which causes higher consumption of sugar consumption and hence, weight gain, which ultimately increases the risk for diabetes.
Another theory is that artificial sweeteners disrupt the ability of the body to compensate for calories that are consumed from sugar as the brain relates the sweet taste with zero calories.
Artificial sweeteners are also thought to alter the type and number of bacteria found in the gut, thereby contributing to glucose intolerance, weight gain and hence, diabetes.
Other Risk Factors for Diabetes

Some of the other risk factors for diabetes are as follows:
• Obesity
• lack of regular exercise
• Smoking
• Sleep apnea
• Hereditary
How to Eat to Lower Your Risk of Diabetes
Along with putting an end on the consumption of sugar, here are some of the ways by which you can reduce your risks of developing diabetes:
• Follow a whole-foods diet: Diets rich in fruits, nuts, vegetables and whole grains help in decreasing the risks of diabetes.
• Drink coffee: Consuming coffee on a regular basis can decrease your risks for diabetes by up to 7%.
• Eat green leafy vegetables: Make sure you fill your plate with green leafy vegetables as they bring down your diabetes risk by 14%.
• Drink alcohol in moderation: Moderate consumption of alcohol has been roughly linked to bringing down the risk of diabetes by 30%. this figure is in comparison with completely abstaining or drinking heavily.
If it feels overwhelming to completely reduce the consumption of added sugar in your diet, you can start with a small step and decrease your in take of sugar-sweetened beverages.
Carefully read the nutrition labels of all your packaged materials as there are more than 50 different names for sugars that are added in the food products.
The Bottom Line
Excess consumption of added sugars can be linked to increasing the risk for type 2 diabetes, mainly due to harmful effects on the liver and an increased risk for obesity.
Natural sugars that are found in vegetables and fruits are not linked to diabetes risk, whereas processed and artificial sweeteners are.
Along with keeping a check on the consumption of sugar, it is equally important to keep normal body weight, maintain diet quality and exercise regularly. Eat a diet that is rich nuts, fruits, vegetables, fruits, vegetables and coffee. Take alcohol in moderation and exercise regularly to keep yourself healthy and away from type II diabetes.




