
Overview and Facts
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located inside the abdominal cavity, right below the rib cage, with each being on either side of the spine. Each kidney is attached to a tube-like structure called ureter, which carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Kidney is responsible for the purification of blood. Kidneys receive blood from renal arteries and pass out the purified blood from renal veins. Purification inside the kidney is done by nephrons – the structural and functional units of kidney. When blood has high concentration of stone-forming minerals like calcium, uric acid and oxalate, nephrons are unable to filter them, which leads to the formation of kidney stones.
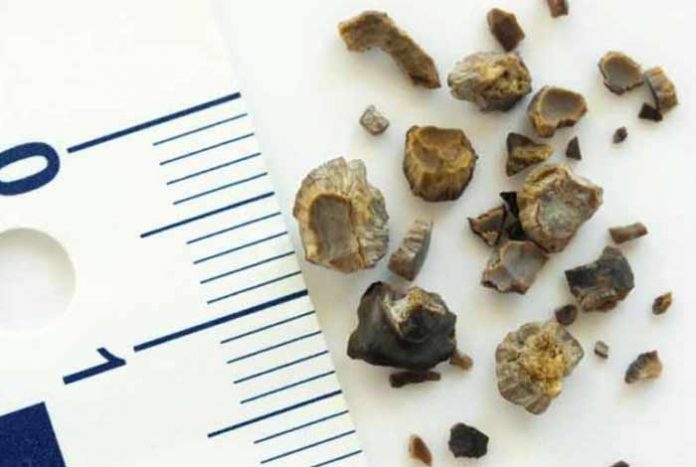
A kidney stone is a hard, crystalline, pebble-like deposit inside the kidney or urinary tract. It can happen in one or both the kidneys and can often cause bloody urine with severe pain. Kidney stones are also known as nephrolithiasis. Urolithiasis is having a kidney stone in the urinary tract, while the term “ureterolithiasis” signifies stone in the ureter.
Kidney stones are of varying shapes and their size may vary between less than 1 centimeter to a few inches. The largest kidney stone till date was 1.36 kilograms in weight and the smallest was microscopic, around 0.1mg in diameter. Small kidney stones are often passed out during urination and do not show any prominent symptom.
Kidney stones rarely do any permanent damage if treated by a medical professional. Calcium stones are the most common type of kidney stones and are found in more than 200 varieties, like calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate etc.
Various studies have found that men are more susceptible to kidney stones than women. Around 10% of men and only 6% of women are likely to develop kidney stone at least once in their lifetime. [Source]
Types and Symptoms of Kidney Stone
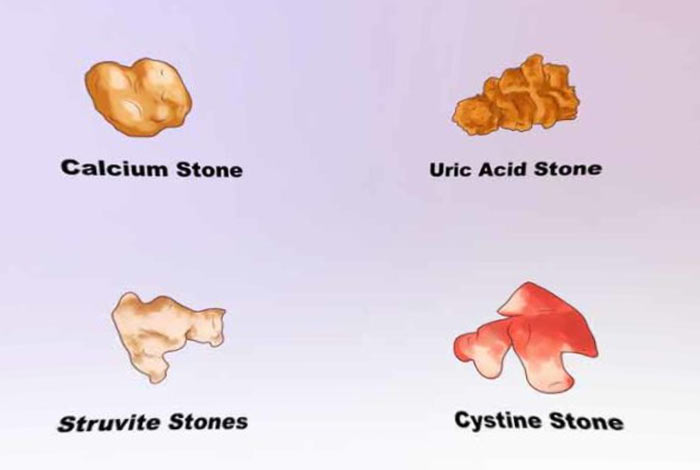
Types of Kidney Stone:
Determining the type of kidney stone is crucial as specific treatments are available best on the type of kidney stone one develops.
There are four major types of kidney stone:
- Calcium Stones: It is the most common type of kidney stone and accounts for nearly 80% of kidney stone cases. Mostly, calcium deposits in the kidney in the form of calcium oxalate. Oxalate can be found in various food substances and is also produced by liver on a daily basis.
Higher concentrations of Vitamin-D, metabolic disorders and intestinal bypass surgery can enhance the concentration of oxalate or calcium in the urine.
Calcium stones can also be found in the form of calcium phosphate. Metabolic conditions like renal tubular acidosis is a major reason for the formation of calcium phosphates. However, certain medications and migraine headaches can also lead to calcium phosphate stones. - Struvite Stones: This type of stone is mostly found in women and responsible for around 10% of kidney stone cases. Infections like urinary tract infection (UTI) leads to struvite stone formation. Also known as “staghorn calculi,” these stones have a high growth rate.
- Uric Acid Stones: Uric acid is a waste product that is generally passed out during urination. Alcoholism, dehydration, higher concentration of protein in diet and gout are some of the causes of uric acid stones that account for about 5% of kidney stone cases. These stones are formed when acidity level of urine increases beyond a certain level. Uric acid stones are more common in women than men.
- Cystine Stones: Rarest of all, it is responsible for only 1 % of kidney stone cases. Cystine stones develop due to hereditary disorder that can increase the excretion of some amino acids (cystinuria) through kidney.
Symptoms of Kidney Stone:
The common symptoms of kidney stone are discussed below:
- Pain in Back, Belly or Sides: Kidney stone pain, also called renal colic is excruciating. The pain occurs when pressure builds up due to the blockage of ureter. This stimulates the nerve endings, which sends pain signals to the brain. The intensity and location of the stone keeps on changing as the stone grows or moves. Stone pain is usually sudden and occurs in waves. Even though large stones can be more painful than smaller ones, pain intensity isn’t necessarily related to the size of the stone.
- Pain or Burning Sensation: Burning sensation is felt once the stone reaches the bladder. This can be easily misunderstood as urinary tract infection.
- Urgent Urination: Once the stone moves to the lower part of urinary tract, urgent as well as frequent urination occur.
- Bloody Urine: Scratching of inner linings of urinary tract can lead to bloody urine. Urine can be pink, red or brown, depending on the concentrations of blood in the urine.
- Cloudiness or Urine: Cloudy urine is a sign of puss in urine. Puss can be found in urine because of bacterial infections due to stones.
- Foul-Smelling Urine: This can be a sign of kidney stone or urinary tract infection. Foul smell can also be there due to highly concentrated urine, which is a sign of kidney stone.
- Reduced Urination: Reduced or no urination can occur due to the blockage of urinary tract by a kidney stone. No urination is considered as a medical emergency.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea or vomiting is a common sign of kidney stone. These occur due to a common nerve sharing between gastrointestinal (GI) tract and kidneys.
- Chills and Fever: Besides kidney stone, chills and fever may also be the signs of urinary tract infection or a more serious complication.

Risk Factors of Kidney Stone
Factors that can increase the risk of Kidney stones are as follows:
- Family or Personal History: People having family or personal history of kidney stones are at a higher risk of developing kidney stone in future.
- Dehydration: Low level of water intake can increase the risk of kidney stone. People, who sweat too much are at an increased risk of developing kidney stones due to increased loss of fluids from their body.
- Diet: Diet rich in protein, sugar and sodium salt can increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing a kidney stone.
- Surgery or Digestive Diseases: Chronic diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease or gastric bypass surgery can alter the digestive process, affecting the absorption of water and calcium. This increases the level of stone-forming substance, such as calcium in the urine.
- Medical Conditions: Urinary tract infection, cystinuria and renal tubular acidosis are some of the medical conditions that are known to increases the risk of kidney stone.

Do I have Kidney Stone?
Major symptoms of kidney stone are abdominal pain, bloody urine, frequent urination and sometimes, fever. However, these symptoms can also be a sign of some other medical conditions, such as:
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Appendicitis
- Cholecystitis
- Diverticulitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Hernias
- Constipation
- Ovarian cyst
- Prostatitis
So, if you are experiencing any symptom of kidney stone, especially pain with high fever, it is highly recommended to consult a doctor to rule out the possibility of any other condition.
Causes and Prevention of Kidney Stone
Causes of Kidney Stone:
Kidney stones are formed when there is an increase in stone-forming substances (such as calcium) in the blood or a decrease in fluid intake.
Dehydration, metabolic abnormalities and urinary tract infection substantially increase the risk of developing a kidney stone.
Some medical conditions that can cause kidney stones are:
- Gout: It can cause kidney stone by increasing the formation of uric acid.
- Hypercalciuria: It is the underlying cause in around 50% of the kidney stone cases. In this, the concentration of calcium in urine increases significantly.
- Chronic Disorders: Chronic diseases, such as diabetes and high blood pressure can also cause kidney stone.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: People with inflammatory bowel disease are more likely to develop kidney stone.
- Medications: Certain medicines like diuretics, protease inhibitors and calcium-containing antacids can also increase the risk of developing a kidney stone.
- Hyperoxaluria: This is an inherited condition, which increases the levels of oxalates in the urine.
Prevention of Kidney Stone:
It is always said that prevention is better than cure and is true for kidney stone too. Some preventive measures that can reduce the risk of developing a kidney stone are as follows:
Be Hydrated: Being hydrated is always a good idea. Drinking a lot of water throughout the day can subside a lot of problems, including kidney stone. People having a history of kidney stone are advised to drink enough water to pass out approximately 2.5 liters of urine a day.
Check your Oxalate Intake: If you are susceptible to develop calcium stone, then you should keep a check on your oxalate intake. High levels of oxalate can catalyze the process of stone formation. Some of the food that are rich in oxalate and should be avoided are:
- Sweet potatoes
- Swiss chards
- Spinach
- Okra
- Beets
- Rhubarb
- Black pepper
- Chocolate
- Tea
- Soy products
Limit your Salt and Animal Protein Intake: If you are susceptible to kidney stone, you should reduce your salt intake and avoid animal protein.
Be Cautious with Calcium Supplements: Calcium in food doesn’t increase the risk of kidney stones. However, calcium supplements have been linked to increased risk of calcium stone formation.

Diagnosis and Tests for Kidney Stone
If a kidney stone is suspected, one or more of the following diagnostic tests can be suggested by the doctor or nephrologist.
- Blood Test: Higher levels of calcium, phosphorus and uric acid in the blood can be detected by a blood test. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) can be suggested to check the functioning of kidney. Blood test tells a lot about the health of a person and in this case, the health of the kidneys. BUN may also highlight the possibility of other medical complications.
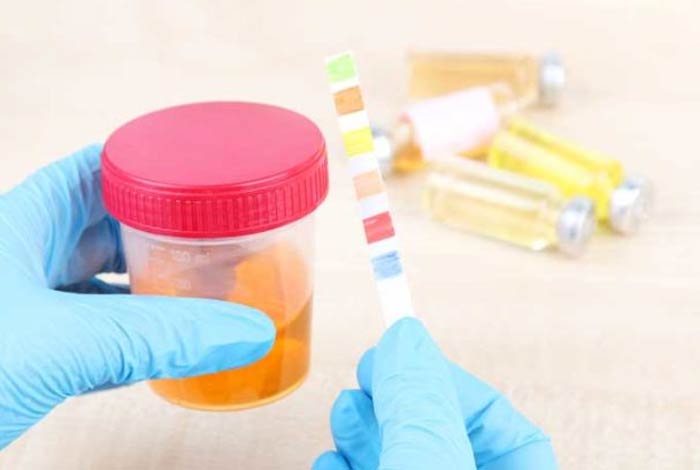
- Urine Test: Urine test can be done to detect if you are urinating a higher amount of stone-forming minerals or a lower amount of stone-preventing minerals. In this, doctor may advice you to collect two urine sample in two consecutive days.
- Imaging: Imaging techniques such as computerized tomography (CT) scan, MRI and X-rays can detect kidney stones. Some less common imaging tests that can be used to detect kidney stone are ultrasound, intravenous urography (it involves taking X-ray after injecting a dye in the vein).
- Analysis of Passed Stones: Patients may be asked to urinate through strainer in order to catch any stone if they pass. Proper analysis of passed stone can reveal almost everything about the type of stone the patient’s kidney has accumulated.
Treatment and Care for Kidney Stone
Treatment of Kidney Stone:
Kidney stones that are smaller in size do not require an invasive treatment. They can be passed out by:
- Drinking Water: Drinking a lot of water can help dissolving and disintegrating small stones, and the patient may be able to pass it through urine.
- Medicines: Some medications like alpha blockers can help by relaxing ureter muscles. A patient may then be able to pass small stones without much pain.
Kidney stones that can’t be passed through urine require different treatment approach. Some of the treatments to cure kidney stone are as follows: - Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): In this technique, kidney stones are broken down into pieces by using shock waves. This allows them to easily travel down through urinary tract and pass out from the body. The procedure lasts for around 50 minutes and can cause pain.
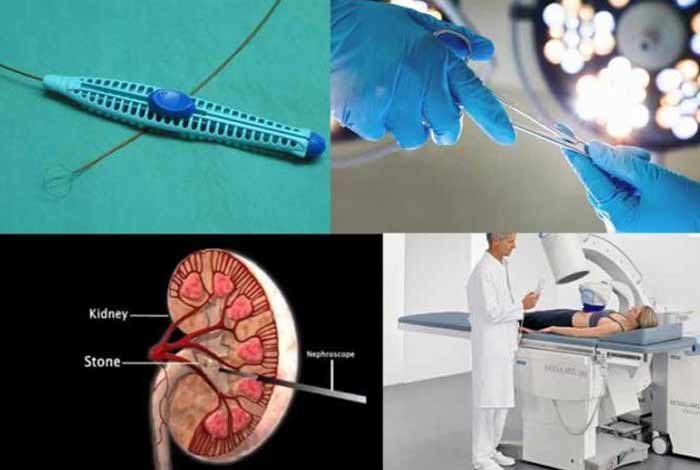
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: It is a procedure in which kidney stone is removed surgically. Patients are given general anesthesia during survey and are discharged from the hospital after two to three days.
- Using a Scope: To remove smaller stones from kidney or ureter, doctor can insert a thin tube called ureteroscope through urethra. Once the location of the stone is identified, it is then broken down into pieces by using special tools. Patients are given general or local anesthesia before undergoing the procedure.
- Parathyroid Gland Surgery: Sometimes, stones, especially calcium phosphate stones, are formed due to hyperactive parathyroid glands. Hence, treating this underlying cause becomes important in such a case. Hyperthyroidism sometimes occur because of the formation of tumor in one of the four parathyroid glands.
Doctors may also prescribe certain drugs, depending on the type of stone:
- Calcium Stones: Phosphate-containing drugs like thiazide, orthophosphate and potassium citrate can be prescribed if a person has or is susceptible to calcium kidney stone.
- Uric Acid Stone: Drugs like allopurinol, potassium citrate, sodium bicarbonate can be prescribed in case of uric acid stone.
- Cystine Stone: Drugs like penicillamine, tipronin and potassium citrate can be prescribed in case of cystine stones.
- Struvite Stones: Struvite stones are generally formed due to kidney infections. Mostly antibiotics are prescribed in this case.
Care for People with Kidney Stone:
Some of the measures to take care of the patient are:
- Increase fluid intake
- Reduce the intake of sodium salts
- Do not use calcium supplements
- Reduce oxalate intake
OTC and Self-Management Methods for Kidney Stone
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications for Kidney Stone:
There is no such OTC drug available for the treatment of kidney stone because different medicines work for different types of kidney stone. However, some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen can help relieve the pain.
Self-Management Methods for Kidney Stone:
A few self-management tips to prevent or treat kidney stone are listed below:
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Limit your sodium intake; below 2400 milligrams per day.
- Restrict your calcium intake from natural sources only
- Restrict the intake of vitamin C
- Switch to Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet
Natural Ways to Cure Kidney Stone
Some natural remedies found to be effective in curing kidney stone are as follows:
- Lemon Juice: Lemons are rich in citrate, which helps by breaking down calcium deposits. Two glasses of lemon juice are advisable. One in the morning, empty stomach, and another a few hours before dinner.
- Basil: Basil is rich in compounds that help in stabilizing uric acid levels. Optimum uric acid levels check the formation of kidney stones. One teaspoon of pure basil juice can help treat and prevent kidney stones.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: This is again a rich source of citric acid and can help dissolve calcium deposits. Approximately 7 ounce of water mixed with 2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar can help reduce the development of kidney stone.
- Wheatgrass Juice: Wheat glass increases urine production, which helps in passing out of kidney stones. It also contains antioxidants that help remove excess of minerals and salts from the urinary tract. For best results, two to eight ounces of pure juice should be consumed.
- Celery Juice or Seed: Celery juice and seeds are rich in antioxidants and thus, reduces the risk of developing kidney stone. It could be consumed daily to treat symptoms of kidney stone.
- Uva Ursi: Uva ursi is an herb that helps clean urinary tract with its solvent and disinfectant properties. People with kidney stones are advised to have 500 milligrams of uva ursi thrice a day.
- Kidney Bean Broth: Kidney stones are a rich source of magnesium, which is very helpful in reducing kidney stones.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: It is a thick oil and may help reduce the pain by lubricating the urinary tract. It should be consumed twice a day.
- Tribulus terrestris: Tribulus terrestris is an herb, which can be added to various drinks. It helps reduce phosphate levels in the urine. It also promotes the formation of urine and help dissolve various mineral deposits.
- Pomegranate Juice: Pomegranate has antioxidants and astringent properties that limit the formation of kidney stones.
- Dandelion Extract, Tea or Juice: It increases the production of bile juice and urine.
- Yoga: Various yoga asanas, such as ustrasana, uttanpadasana, pawanmuktasana, bala-asana and bhujangasana help treat kidney stone.
- Acupressure and Acupuncture: These alternative medicine techniques are known to be effective in kidney stones.

Health Tip by Expert
Kidney stone is generally not a serious condition and can be prevented easily with dietary changes, medicines or surgery. However, symptoms should not be ignored, especially if followed by fever.
Switching to a better lifestyle and increasing the intake of water can help reduce the chances of developing kidney stone. Yoga can be a natural yet effective way to prevent as well cure kidney stone.





