Overview and Facts
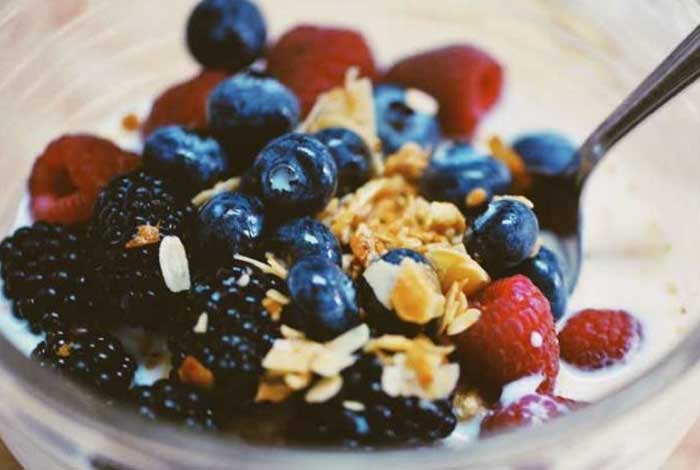
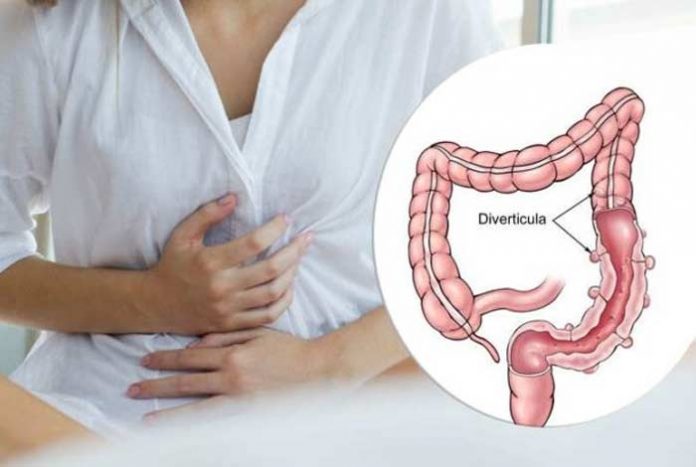
Diverticulitis is a disease of the digestive system. In this disease, pouches in the wall of the colon or within large bowel wall become inflamed. It is a very common problem in the West. It results from the development of diverticula or small sacs in the walls of the colon (large intestine). Thus, diverticulitis is inflammation or infection in diverticula, which are bulging protrusions that occur when large intestine comes out through the outer muscular layer. It can lead to many complications.
Simple diverticulitis can be treated with antibiotics. When infection is left untreated or does not resolve on its own, pus starts to collect in the colon. This is known as abscess, which further spreads and causes infection in the healthy colon tissues. If the hole is large, then pus will leak out and reach the abdominal cavity. This can lead to cause the inflammation of peritoneum. This condition requires medical intervention with immediate effect as it can be fatal.
Sometimes, diverticulitis is referred to as diverticulosis, but there is a lot of difference between these two conditions. In medical terms, they both are the stages of diverticular disease. Diverticulosis develops when many diverticula get formed inside the colon. Diverticulitis is a more severe stage or phase of diverticular disease. It happens when pouches become entangled with fecal or waste matter and bacteria, and becomes inflamed due to strain and pressure. Diverticulosis has no symptoms and often there is no pain. On the other hand, diverticulitis symptoms are stark and cause uneasiness. It is often accompanied by pain.
The third type or stage of diverticular disease is diverticular bleeding. This happens as blood vessels around diverticulum ruptures or bursts. In this case, one experiences stool that is full of blood and blood appears as dark red clots. It is not painful but must be checked by a doctor for immediate relief.
It is common in people above the age of 45. In the U.S., around 30% of people above the age of 45 and 70%, and people over the age of 85 have this condition. These days, younger people are also getting diagnosed with this condition, particularly those, who are obese. Around 10-25% of the people with diverticulosis suffer from diverticulitis.
Around 25% of the people with diverticulitis develop complications. We have already discussed about the abscess, which happens as pus gets collected in the pouch. Further, there may be a blockage in the colon or small intestine. Other complications include development of abnormal passageway between bowel sections.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
Common symptoms of diverticulitis are as given below:
- Pain which stays for several days. Pain is generally experienced in the left side of the
- lower abdomen. In people of Asian descent, the pain may even be felt on the right side.
- Vomiting and nausea
- Tenderness in the abdominal region
- Fever
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea
- Strained bowel movements
- Painful cramps

Risk Factors of Diverticulitis
Several risk factors associated with this disease are as follows:
- Increasing Age: As age increases the likelihood of having diverticulitis also increases.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the chances of developing diverticulitis. Furthermore, invasive treatments may be required for diverticulitis.
- Smoking: People who are smokers are more likely to get diverticulitis than those who do not smoke.
- Sedentary Lifestyle/Lack of Exercise: If one regularly exercises one may cut his odds of developing diverticulitis.
- Animal-Fat Rich Diet: If one consumes a diet that is high on animal fats and low on fiber, then one is more likely to develop diverticulitis.
- Several Types of Medications: There are many drugs known to increase the risk of diverticulitis. These include steroids, NSAIDs (nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs) and opiates.
- Lack of Vitamin D: A study has revealed that people with diverticulitis have less amounts of vitamin D in their body. The exact reason for this observation has not been cited.
Do I have diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis has symptoms similar to other conditions like:
- Inflammation of appendix (Appendicitis)
- Obstruction in bowel
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Ulcerative colitis
However, it must be noted that in diverticulitis, there is an intense and severe pain in the lower left side of the abdomen. Other signs are fever, vomiting, nausea, and alternating constipation and diarrhea. In order to correctly identify the condition, one must consult a doctor, who is the right person to tell apart diverticulitis from other similar conditions.
Causes and Prevention of Diverticulitis
Causes of Diverticulitis:
The exact cause of diverticulitis is still not known. Bacteria grow in diverticula or pouches, and this further leads to inflammation or infection. Pressure results in tearing of the wall of the intestine. The reason why diverticula develop in the colon is not completely known. However, it is believed that diverticula are formed when high pressure in the colon pushes the weak spots in the wall of the colon. The main cause is fecal matter that blocks the opening of diverticula, which results in inflammation and infection. The reasons for blockage are different from person to person.
With aging, the outer layer of the intestinal wall gradually thickens. The open spaces in the intestine start to become narrower and subsequently, stool puts more pressure on the opening as it moves through the colon. A diet, which is low on fiber produces hard stools, which is difficult to move through the colon putting even more pressure. This persistent strained bowel movement increases pressure and forms diverticula.

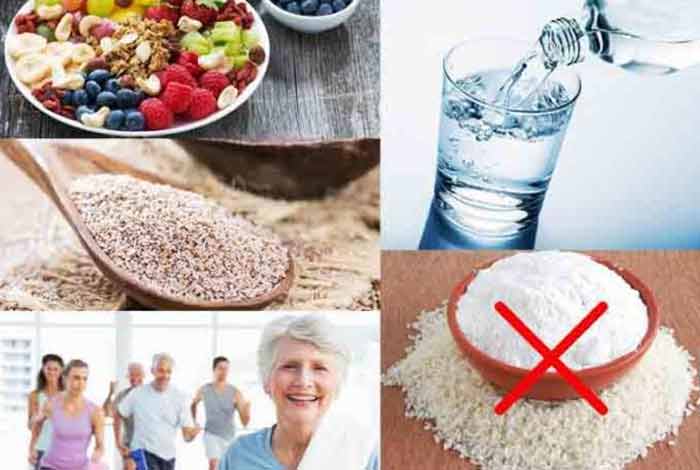
Prevention of Diverticulitis:
The best prevention method is modification of lifestyle and diet. Some tips are discussed below:
- Increased Intake of Fiber: Eat more of oatmeal, cereals, fibrous fruits and vegetables. Do it gradually as suddenly switching over to a high-fiber diet can lead to gas and bloating.
- Add Psyllium to the Diet: It is extracted from Plantago psyllium. Make a mixture of 1 tablespoon psyllium seed with cold liquid and consume within a few minutes of preparation.
- Drink Lot of Fluids: It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of water every day; particularly if one increases the intake of fiber.
- Avoid Refined Foods: Refined foods like white rice and white flour must be strictly avoided.
- Prevent Constipation with Laxatives: Constipation can be prevented by over-the-counter (OTC) stool softeners. Laxatives, before use, must be checked with a doctor. Prunes, psyllium seed and prune juice are natural laxatives. Whatever one uses to fight constipation, the same must be used according to directions as inappropriate use can lead to complications.
Note: Avoid senna, which is an herbal laxative and can lead to addiction. Prescription drugs like lubiprostone are available for long-term constipation. - Regular Exercise: Exercise on a regular basis help maintain healthy bowel movements. Never stop the urge to move bowels.
- Avoid Red Meat: Do not consume red meat.
- Avoid Unhealthy Fats: Avoid foods that have unhealthy fats as it may block the intestine and aggravate the symptoms of diverticulitis.
- Give Up on Smoking: Smokers have more risk of having diverticulitis.
- Avoid NSAIDs: Taking NSAIDs is associated with diverticular bleeding, so these must be avoided.
- Decrease the Amount of Caffeine: If it is thought that drinking caffeine will make it easier to pass stools, then it is a mistake. Caffeine makes one lose water, thus making stools harder.

Diagnosis and Tests for Diverticulitis
Doctor will examine the abdomen for any tenderness. Women can have a pelvic examination test to rule out the possibility of pelvic inflammatory disease.
The doctor may also recommend to recommended to undergo:
- Blood and urine test to look out for infection signs
- Pregnancy test for women to rule out pregnancy as a reason for abdominal pain
- Liver function test (LFT) to rule out possibilities of other causes of pain in the abdomen
- Stool test to rule out infection in people with diarrhea
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan for confirming the diagnosis of diverticulitis
The following tests may also be performed:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This may let the doctor know if one has very less red blood cells (RBCs) in the blood because of bleeding in the colon
- Urinalysis: It will show whether there is infection in the urinary tract.
- Abdominal X-Ray: It tells about what causes the abdominal pain.
- Digital Rectal Exam: It looks for tenderness in the lower pelvic area
- Fecal Occult Blood Test: To looks out for stool in the blood.
Other tests are as follows:
- CT Scan: This test may be done when symptoms suggest that there might be an infection or abscess in the abdomen, or if a pouch has ruptured. Other possible causes may also come to fore with this test.
- Barium Enema X-Ray: It is done to show diverticula or other symptoms. It must not be done while one is having an attack of diverticulitis as there is risk of barium getting spilled in the peritoneum if there is a perforation.
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy and Colonoscopy: This is done when the main symptom is bleeding from the intestine. Again, it should not be done while one is having an attack of diverticulitis as the scope may tear the lining of colon. When this happens, an infection could spread into the peritoneum. This is a more severe condition.
- Ultrasound and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): These can also be used for the diagnosis of diverticulitis, but are less commonly used due to their high cost.
Treatment and Care of Diverticulitis
Treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms. If the pain is not so intense, one can easily drink liquids and there is hardly any complication, then treatment may include:
- Antibiotic medicines and pain relievers
- Introducing changes in diet, beginning with a clear diet low in fiber content, and gradually increasing the levels of fiber
If the pain is not mild and one finds it difficult to drink liquids, then the following line of treatment may be recommended:
- Antibiotics given through intravenous injection (IV). Some common antibiotics are metronidazole or amoxicillin.
- Giving intravenous fluids and nutrition for about a week to allow rest to the bowel.
- A tube may be passed down from the nose through the throat to the stomach to suck out the content. This is known as NG tube.
- Performing surgery for complicated cases of diverticulitis. Less than 6% of people with diverticulitis need surgery.
- In some of the cases, diverticulitis may reach complicated stages like abscess, perforation and bowel obstruction. In these cases, surgery is required to remove the affected part of the intestine. If you have seen two or more diverticulitis attacks, and are below the age of 40 and the immune system is impaired, then in such cases, nonurgent (elective) surgery may be done.
For severe cases, there are two types of surgery:
- Primary Bowel Resection: In this surgery, the surgeon or doctor removes the part of the intestine that has become diseased and connects the healthy segments. This will help one have easy and normal movements of bowel. Depending on the degree and extent of inflammation, one may have to undergo surgery or have a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure.
- Resection of Bowel with Colostomy: If the inflammation is to such an extent that it is not possible to rejoin the colon and rectum, then colostomy may have to be performed. Opening in abdominal wall is connected to the healthy colon. Waste moves from the opening into the bag. Once inflammation eases away, colostomy can be reversed.

OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Diverticulitis
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications for Diverticulitis:
If the inflammation is not severe, then one may use some over-the-counter drugs to treat the condition. OTC pain relievers for relieving the symptoms of diverticulitis include acetaminophen. Stronger pain medications are not recommended as these may increase the pressure on the colon. Usage of OTC in less severe cases may clear up symptoms in 2-3 days. Nevertheless, it is a general recommendation to

Self-Management Methods for Diverticulitis:
Discussed below are several self-management methods that can be employed by a person to relieve the symptoms of Diverticulitis:
- Avoid Foods that Irritate the Gut: There are some food allergens that are associated with causing diverticulitis like soy, nuts, gluten, corn and seeds. One must avoid them.
- Reduce Stress: Stress is directly associated with the inflammation of gut and has a bad effect on the immune system, which can cause flare-ups related to diverticulitis. So, it is advised to take measures that control stress like exercising and meditation that could help reduce the level of cortisol in the bloodstream.
- Eat a Diet Rich in Fiber: Fibrous foods like carrots and apples contain enzymes that boost digestion. Fruits like apple and prune also contain fibers that can be used as a substitute of laxatives that can be harmful.
- Keep Oneself Optimally Hydrated: Instead of tea and coffee, rely more on purified water. Water helps in effective waste elimination. Consume more water and your digestive system will thank you.
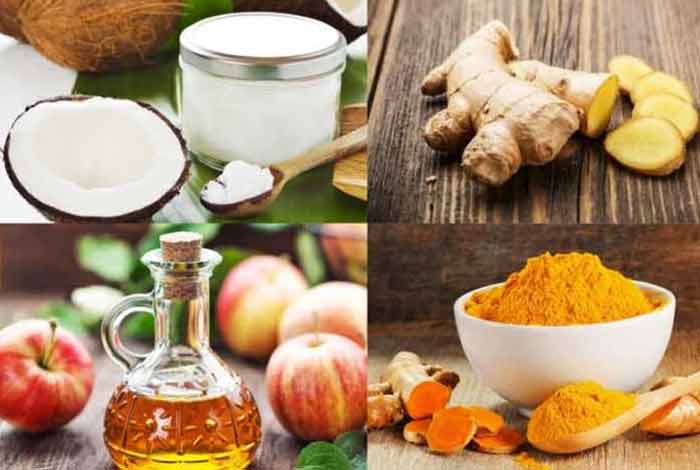
Natural Ways to Cure Diverticulitis
Following natural remedies can be used that are known to be very effective in Diverticulitis:
- Coconut Oil: This gets broken down in the body in an antibacterial compound, known as monolaurin. This compound relieves indigestion and constipation. It further helps reduce inflammation.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: With high content of acetic acid, apple cider vinegar has antimicrobial properties that curb the growth of bad bacteria in the colon and thus, helps remove waste from the body.
- Ginger: It is quite surprising, but ginger contains more than 100 different chemicals that soothe the lining of the stomach and hence, helps in cleaning the digestive tract.
- Turmeric: To relieve the symptoms of diverticulitis, one can treat him/herself with anti-inflammatory ingredient like turmeric. Turmeric reduces inflammation of bowel and has a healing effect on damaged tissues across the digestive tract.
Some Gut-Healing supplements are discussed below:
- Betaine HCL: As we grow older, the production of HCL in the stomach decreases. This is the reason why many cases of diverticulitis come up after the age of 40. Supplementation with Betaine HCL stimulates digestive enzyme, so that foods can be broken down easily and digestion can be improved.
- Probiotics: When probiotics are consumed regularly, these can reduce the symptoms associated with diverticulitis like bloating, constipation, gas and diarrhea.
- Digestive Enzymes: These help in optimal functioning of the gut. Individuals with diverticulitis can improve digestive functions using these enzymes.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera is known to boost healthy gut function. It prevents bacteria in intestines, which ensures bowel movements are regular and easy.

Health tip by Expert
Women below the age of 51 should consume at least 25 grams of fiber daily as it helps reduce pressure on the digestive tract. Studies have shown eating fiber-rich foods can help control the symptoms of diverticulitis.





