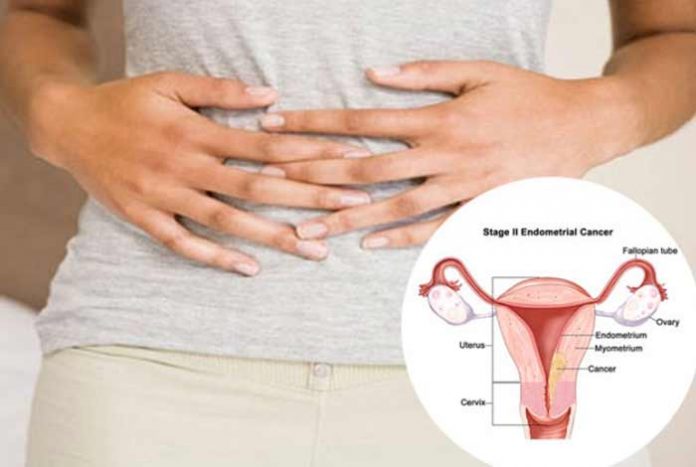
Overview and Facts
Ovarian cancer or cancer of the ovary is characterized by an abnormal and uncontrolled growth of ovarian cells. Ovaries are a pair of small glands that are located along the wall of the uterus. The ovaries are female reproductive part that produce female sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone and release eggs or ova. It is difficult to detect ovarian cancer at early stages. Also, it is one of the most common types of cancers in women. Ovarian cancer is more common in women who have attained menopause, a stage in women’s life when menstrual cycle stops permanently.
There are different stages of ovarian cancer:
Stage 1: The cancer is limited only to the ovaries and has not spread to other parts.
Stage 2: The cancer affects one or both the ovaries and other pelvic organs like bladder, uterus, fallopian tube, rectum.
Stage 3: The cancer affects one or both the ovaries and has spread to the abdomen or lymph nodes.
Stage 4: The cancer has spread to other body parts.
A few types of ovarian cancer like epithelial tumors, germ cell tumors and stromal tumors are not dangerous and do not spread outside the ovary. These tumors can be treated by removing either the ovary or part of the ovary containing the tumor.
The American Cancer Society has given the following estimates for ovarian cancer in the United States in 2017:
- Around 22,440 more women will go for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer
- Around 14,080 women will die from ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is one of the leading causes of deaths in women. It ranks fifth in cancer-related deaths in women. 1 out of 75 women is at risk of developing this cancer. A woman’s chance of dying from ovarian cancer is one percent. The cancer generally develops in aged females. It is found that 50% of women having ovarian cancer are above the age of 63. It is more common in white women than in African Americans. If the cancer is diagnosed in the early stages, there is 94% chance of surviving for 5 more years.
Types and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Types of Ovarian Cancer:
- Epithelial Tumor: This is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Most epithelial ovarian tumors are benign, i.e. they do not spread to other parts. Some epithelial ovarian cancers are malignant, i.e. they spread to other parts. Cancerous epithelial tumors are called as carcinomas. It is found that 85-90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Also, this type of cancer is more common in women who have crossed their menopause age.
- Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor: This type of tumor occurs in ovarian germ cells which produce ova or eggs. Most ovarian germ cell tumors do not spread. It is more common in women who are in their early 20s. There are several subtypes of germ cell tumors. These are teratomas, dysgerminomas, choriocarcinomas, endodermal sinus tumors. Teratomas are more common in women of reproductive age. It is also called as dermoid cyst as its lining is made up of the tissue also found in the dermis or skin.
Mature teratoma is benign in nature and the immature teratoma is malignant. Immature teratoma occurs in young girls below the age of 18. Dysgerminomas is a common ovarian germ cell cancer. Girls in their teens and twenties are generally affected by dysgerminomas. These are cancerous but do not spread quickly. - Endodermal Sinus Tumor and Choriocarcinoma: This type of cancer affects girls and young women. It spreads very quickly and is sensitive to chemotherapy.
- Ovarian Stromal Tumor: Around one percent of ovarian cancers are ovarian stromal cell tumors. They are more common in women above 50 years of age. The most common symptom of this cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. The excess bleeding occurs as these tumors produce female hormones like estrogen. These hormones cause vaginal bleeding even after menopause.
Sometimes, stromal tumors may produce male hormones which may halt menstrual periods. These male hormones may make facial and body hair grow. - Ovarian Cyst: It is a collection of fluid in the ovary. The cyst occurs normally as a part of the ovulation process. The cyst generally disappears after some time without treatment.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer:
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer are:
- Bloating of the abdomen
- Pain and pressure in the abdomen
- Feeling full after eating
- Difficulty in eating
- Frequent urination
- Urge to urinate
Some other symptoms may also appear, such as:
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Back pain
- Painful sex
- Fatigue
- Irregular periods
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Unexplained weight loss
Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
There are certain factors that increase the risk of ovarian cancer. These include:
- Age: The chances of developing ovarian cancer increases with age. It is less common in women under the age of 40. Most ovarian cancers start after menopause.
- Obesity: It has been found that obese women are at higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Pregnancy: Women who became pregnant before the age of 26 have lesser chances of developing ovarian cancer. For women, who have their pregnancy after the age of 35, are at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Family History of Ovarian Cancer: The chances of developing ovarian cancer is more if any family member has had the disease.
- Genetic Mutation: Ovarian cancer may occur with the mutation of genes like BRCA1 or BRCA2. When these genes are normal, they prevent the cancer by making proteins that protect cells from abnormal growth. But, if a person has inherited the mutation from his or parents, the chances of developing ovarian cancer increases.
- Personal History of Breast, Uterine or Colon Cancer: A woman who has had breast, uterine or colon cancer, are at a higher risk developing ovarian cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy or Fertility Drugs: Use of fertility drugs or hormone replacement therapy increases the chances of ovarian cancer.
- Endometriosis: It is a condition in which tissues that cover inner part of the uterus grow outside.

Do I Have Ovarian Cancer?
Many ovarian cancer symptoms cannot be detected at early stages and can be easily mistaken for other health conditions. For example, bloating, pain and abdominal distention occur in both ovarian cancer and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It can also be wrongly diagnosed as diverticulosis, gallbladder problems, urinary infections and hernia. There is a difference between symptoms of IBS and ovarian cancer. IBS is a long-term problem whose symptoms occur periodically. These symptoms produce mixed emotions in the affected person. In case of ovarian cancer, the symptoms remain for a long time and become worse with time.

Causes and Prevention of Ovarian Cancer
Causes of Ovarian Cancer:
There are many theories related to ovarian cancer, but the actual causes of ovarian cancer are not yet known. Scientists have not yet found a single chemical in the environment or food that can be linked to ovarian cancer. Some genetic factors and unhealthy lifestyle can increase the chances of you getting ovarian cancer.
Some of the ovarian cancers are associated with mutations in the genes responsible for breast cancer. These genes are BRCA1 and BRCA2, i.e. breast cancer gene 1 and breast cancer gene 2. Further, if you belong to an Eastern European country or are of Jewish origin, your chances of having one BRCA mutations are higher. Your risk of having ovarian cancer increases manifolds if you have a family history of breast cancer, uterine cancer, rectal cancer and colon cancer.
Prevention of Ovarian Cancer:
There are certain ways to prevent ovarian cancer. These are:
- Oral Contraceptives: Using birth control pills decreases the risk of developing ovarian cancer. According to a study, women who have used oral contraceptives for 5 years or more had a very little risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Gynecologic Surgery: Tubal ligation and hysterectomy can reduce the chances of developing ovarian cancer. If you have a long family history of ovarian or breast cancer or if you are going to have hysterectomy for some reason, then you may consider getting both the ovaries and fallopian tubes removed.
- Genetic Counseling and Testing: Your personal and family medical history is reviewed during genetic counseling. This will also help you know whether you have a gene mutation associated with increased risk of ovarian cancer.
Diagnosis and Tests of Ovarian Cancer
- Physical Examination: If the symptoms of ovarian cancer persist, your doctor may suggest some physical tests for you. The doctor may examine if the ovaries are have enlarged or if the abdomen is filled with fluid. If the examination of pelvic region or reveals that you have ovarian cancer, you will need a surgeon who is expert at treating women with this type of cancer. A gynecologic oncologist treating you would mean that you get the best type of surgery for your ailment.
- Medical Imaging: Imaging tests like CT scans, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound can confirm the presence of mass in the pelvic region. It may not be cancer, but these tests could reveal whether the mass is metastasizing or spreading to other tissues.
- Laparoscopy: In this procedure, the doctor uses a thin tube to examine the ovaries. It provides a view of the ovaries that can help in surgery and other treatments. This test can also confirm the stage of ovarian cancer.
- Colonoscopy: It is a procedure to examine the organs of the abdomen. Before carrying out the test, the colon and rectum must be cleared of any stool. A patient is given sedative before starting the test.
- Biopsy: In Ovarian cancer biopsy, the tumor or part of the tumor is removed for diagnosis. In some cases, ovarian cancer biopsy can be done through laparoscopy or by placing needles in the tumor through abdomen wall. The entry of needle is guided by computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are performed to make sure the normal count of RBCs, WBCs and platelets. Tests will also be conducted to measure kidney and liver function. The doctor may also suggest CA-125 test.
- Genetic Counseling and Testing: A person diagnosed with ovarian cancer is recommended to go for genetic counseling. It helps the person to decide if he or she should be tested for inherited mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Treatment and Care of Ovarian Cancer
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer:
After diagnostic and tests, your health care provider will recommend you some treatment options. The recommended treatments for ovarian cancer are:
- Surgery
- Hormone therapy
- Targeted therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
The treatment options depend on the type ovarian cancer and the stage of cancer. The treatments are:
- Surgery: It is generally the first step in the treatment of ovarian cancer. It is performed by taking out a piece of the mass to examine if it is cancer. This is called biopsy. In some cases, the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes need to be removed. If the cancer is in its early stages and you want to have children, your doctor may not remove all your reproductive organs.
- Hormone Therapy: Your doctor may suggest hormones or hormone-blocking medications. This therapy is used for treatment of ovarian stromal tumors and not ovarian epithelial cancers.
- Chemotherapy: After surgery, there may be cancerous cells still present in the body. You may require chemotherapy to get rid of these cells. These medications are received by the body through intravenous injections. These injections work better in case of ovarian cancer if they are injected into the abdomen.
- Targeted Therapy: The medications in targeted therapy are taken orally or given as intravenous injections. These stop the growth of cancer cells. They attack cancer cells without causing much damage to the nearby or surrounding cells.
- Radiation: These are high-energy beams of X-rays. These can kill cancer cells in the pelvic area. Radiation is given just like normal X-rays.A number studies are being conducted to find new treatment methods. Several clinical trials also have been conducted to find effective treatment process.
Care for People with Ovarian Cancer:
- A woman having ovarian cancer need proper care for fast recovery: Proper care can be taken in the following ways:
- Offer support to your friend or family member having ovarian cancer. Know about their available resources. Seek suggestions from your health care provider. Stay in touch with the local support groups.
- Accompany your close friends or family members having ovarian cancer, to the doctor for treatment and appointments. This would provide emotional support to the patient, especially during chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- Provide an emotional support to the patient.
- Provide them practical help like doing chores and gathering information.
- Tell the healthcare provider about the symptoms your loved one is having and the intensity of the symptoms. Make sure that the healthcare provider is aware of all medications, supplements, vitamins, herbal medicines or any therapy that your dear one is taking.
- Learning new skills like changing or dressing or giving an injection to your loved one can be distressing at first. But, over time, it may become easier for you.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Ovarian Cancer
Over-the-Counter Medications for Ovarian Cancer:
There are no OTC medications available for ovarian cancer. Some of the medications for chemotherapy of ovarian cancer are:
- Carboplatin
- Cisplatin
- Docetaxel
- Paclitaxel
- Oxaliplatin
- Doxorubicin
Further, treatment of ovarian cancer with chemotherapy may result in nausea and vomiting. Both IP and IV chemotherapy can lead to serious side effects like nerve pain, belly pain, kidney or liver problems.
For dry skin, which is a side effect of ovarian cancer treatment, you may go for OTC creams like ammonium lactate or anesthetic creams like hydrocortisone.
Self-Management Methods for Ovarian Cancer:
There are several ways to self-manage ovarian cancer. These are as follows:
- Do regular exercise
- Walk as much as you can. Instead of driving to the nearby grocery, walk to the store.
- While watching television, raise your legs and move your arms. You can even dance to your favorite music.
- There are many cancer centers that offer exercises like tai chi, yoga, etc. It is better to consider those instructors who have had experience of working with people who have had surgery and have undergone chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy-related hair loss can affect scalp and body. Ask your doctor how likely it is that a particular drug can cause hair loss. Accordingly, think about the options to protect your hair.
- For dry and irritated skin that happens during chemotherapy, you can use creams and ointments and moisturizer. If your skin becomes very dry, you can consult your doctor for ammonium lactate cream. Apply sunscreens often and use anesthetic medications.

Natural Ways to Cure Ovarian Cancer
Inclusion of several food items in our daily diets can help prevent and manage the symptoms of ovarian cancer:
- Shiitake Mushrooms: Shiitake mushroom contains beta glucan, also known as lentinan, has been found effective in stopping the growth of cancerous ovarian cells.
- Soy Products: If you are suffering from ovarian cancer, consuming soy products can reverse the symptoms and control the disease. Isoflavones is an important ingredient is found in soy products. This ingredient prevents the transmission of cancerous cells decreasing the growth of cancer and tumor.
- Peppermint Tea: It reduces stomach pain which is a common symptom of ovarian cancer. It also contains antioxidants, which boosts the immune system and leads to a faster recovery.
- Hydration: The major side effects of ovarian cancer are diarrhea and constipation. Drinking enough water makes sure that you are hydrated. This also helps in digestion and reduces constipation.
- Sunshine: According to studies, vitamin D helps fight against cancer. It has been significantly related to preventing ovarian cancer. Women in northern latitudes have greater chances of developing ovarian cancer as these are colder areas and receive less sunlight.
- Gingko Biloba: It can protect against ovarian cancer. Gingko Biloba prevents mutation of ovarian epithelial cells leading to ovarian cancer.
- Green Tea: It has anti-oxidants that makes it one of the best beverages to treat cancer. If you are at risk of developing ovarian cancer, add green tea to your diet and protect yourself from developing the disease.
- Fish: It is a source of omega 3 fatty acids, which are beneficial in preventing the cancer, as they have anti-angiogenic properties.

Health Tip by Experts
Regular exercise and proper diet can help in preventing ovarian cancer. Early diagnosis of the disease helps in managing the disease. An infected woman should regularly consult doctor for treatment. Extra awareness about the disease can protect you from developing ovarian cancer.







