
Overview and Facts
Lactose intolerance, also known as milk intolerance, is a digestive problem in which the body is not able to digest lactose which is a type of natural sugar found mainly in milk and dairy products. A person with lactose intolerance may feel sick after consuming lactose-containing foods. It should not be confused with food allergy to milk.
As lactose remains undigested while it moves through the large intestine or colon, it can lead to various symptoms like pain in the belly, gas and bloating. People with lactose intolerance are not able to digest any milk-based products. Nevertheless, there are a few people, who can eat or drink milk and milk-based products in small amounts without much issues.
In lactose intolerance, the small intestine is not able to produce enough lactase –an enzyme required for the breakdown of lactose. Research shows that about 75% of the global population becomes intolerant to lactose at some point of time. In the U.S., around 30 million adults are affected by this condition by the age of 20.
In some cases, infants are born intolerant to lactose. This occurs when there is mutation of the LCD gene – responsible for the production of lactase. This causes the small intestine of such babies to produce very little to no lactase; making it difficult to digest dairy products.
According to National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney disease (NIDDK), children inherit genes from parents that cause lactose intolerance.
Lactose intolerance is common among people of East Asian origin with over 90% of adults being affected by this condition. It is also common in people, who are of Jewish, Arab and Italian descent. People with milk intolerance may have different reactions after consuming dairy products. Some may experience intense symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal pain, while others may have only mild symptoms like gas. While the exact cause for such differences is not known, gut bacteria is supposed to be responsible for the same.
According to National Institutes of Health (NIH), symptoms of lactose intolerance may creep in as early as 30 minutes to two hours after the consumption of dairy products. One feels worse after consumption of milk and related products. Despite lactose intolerance, you may still consume certain types of cheese and yogurt without much hassles. Some types of cheese have trace amounts of lactose that make these easier to consume and digest by some people. According to NIDDK, research shows that adults, who have trouble absorbing lactose, can eat or drink at least 12 gm of it in one sitting with little to no problems.
If a lactose intolerant person cuts down on dairy and related products, he/she may end up lowering the normal calcium and vitamin D levels. Hence, the person may be required to consult a doctor about taking calcium and vitamin supplements, and increasing the intake of calcium-rich foods like lactose-free milk, broccoli and spinach. Also, in some cases, consumption of small amounts of milk may recondition the digestive system and build up your lactose tolerance some extent.
Types and Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
Types of Lactose Intolerance:
Basically, there are four types of lactose intolerance:
- Primary Lactose Intolerance: This is the most common form of lactose intolerance. In this type, the body stops producing lactase by about age 5 and in some cases (as in African Americans), the production stops by the age of 2. Thus, it gets more and more difficult to digest dairy products. People with primary lactose intolerance are able to produce very less lactase. It is more common in people of African and Asian origins. It has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, and is known as adult-type hypolactasia.
- Secondary Lactose Intolerance: This occurs due to some kind of injury or if a surgery has taken place. Illness, injury or surgery can affect small intestine and make a person to produce less lactase. Two most common intestinal diseases related to low lactase production are Celiac disease and Crohn’s disease. Secondary lactose intolerance occurs as a result of damage to intestinal mucosa that may occur due to bacterial gastroenteritis, chemotherapy or inflammatory bowel disease. This goes away as the intestinal mucosa begins to heal.
- Developmental Lactose Intolerance: It occurs in babies, who have premature birth. It goes away on its own and remains only for a short duration. The condition improves when the intestine matures.
- Congenital Lactose Intolerance: This is not very common, and occurrances when small intestine is not able to produce any lactase, right from the time of birth. It is a genetic disorder, and both the parents must pass the gene to the child.

Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance:
The symptoms of lactose intolerance may be mild or severe; depending on how much lactase is made by the body. If you have lactose intolerance, you may have the following symptoms:
- Bloating
- Cramps or pain in the lower belly, or abdominal cramps
- Gas
- Vomiting or throwing up
- Diarrhea or lose stools
- Gurgling sounds in the belly

Risk Factors of Lactose Intolerance
Factors that make you or your child more prone to lactose intolerance include:
- Age: Lactose intolerance generally appears in adulthood. It is rare in babies and young children and only developmental lactose intolerance occurs in babies.
- Ethnicity: It is more common in people of African, Asian, American Indian, and Hispanic descent.
- Premature Birth: Infants, who are born prematurely, have decreased level of lactase as small intestine is not able to produce enough of lactase.
- Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy: If you have received cancer treatments like radiation therapy in abdomen or intestinal chemotherapy then you have increased risk of lactose intolerance.
- Diseases Affecting Small Intestine: Small intestine issues can cause lactose intolerance like bacterial growth, Crohn’s disease and celiac disease.

Do I have Lactose Intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is not the same as dairy allergy. The two are often misunderstood and considered as the synonym of each other. If you have dairy allergy, you are allergic to some proteins in milk and dairy products. These reactions can be life threatening. On the other hand, lactose intolerance is less intense in nature and its symptoms are less severe than dairy allergy.
People with dairy allergy must avoid all foods and drinks related to milk and dairy items. However, if you are lactose intolerant, you may be able to consume small amounts of milk and related products. Moreover, reactions of lactose intolerance are never life threatening.
Chron’s disease and lactose intolerance have some symptoms in common. So, it is quite possible that a person may think he/she has one condition when actually the person may be having the other. Research shows that people with Chron’s disease have higher rates of lactose intolerance than the normal population.
Likewise, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) also have symptoms similar to those of lactose intolerance. Hence, it is best to consult a doctor to rule out the possibilities of other conditions.

Causes and Prevention of Lactose Intolerance
Causes of Lactose Intolerance:
Lactose Intolerance is caused by a basic deficiency in the lactase enzyme, which is normally found in the inner lining of the intestinal wall. It decomposes lactose into smaller molecules like glucose and galactose that are further absorbed by the intestinal lining.
Lactose intolerance can occur as a result of deficiency or complete absence of lactase enzyme. However, its complete absence is an extremely rare condition, where is caused by a defective gene. Generally, lactose intolerance is an acquired condition, not mainly present at birth. The intestinal wall may get damaged due to various conditions or factors like medications or infections, which can result in milk intolerance.
Some major causes of lactase deficiency include:
- Gastroenteritis by bacteria or virus
- Celiac disease
- Radiation therapy
- Crohn’s disease
- Diabetic enteropathy
- HIV enteropathy
Incidentally, the most common cause of lactose intolerance is the slow and gradual loss of lactase after childhood.
Prevention of Lactose Intolerance:
Prevention of the symptoms of lactose intolerance is more generally focused on avoiding dietary milk and milk-containing products. With proper dietary restrictions and use of supplements, lactose intolerance can be prevented.
- Limit the amount of food and drink that contains lactose. Most people can consume around 10 gm of lactose a day. Combining a solid food like cereal with a dairy product like milk may result in the reduction or elimination of the symptoms.
- Take lactose enzyme supplements to help the body digest lactose.
- Avoid soft cheese
- Take care of lactose fillers: It is a common filler in some kinds of medication as well as supplements. It is recommended to avoid such drugs.
It is important to know that lactose intolerance does not mean giving up on dairy products forever. Sometimes, the condition is only temporary and related to gastrointestinal issues like stomach flu or infection.

Diagnosis and Tests of Lactose Intolerance
You may be asked to keep a check on the consequences of various foods you eat to see if stopping some foods causes the symptoms to go away or eating some types of food causes the symptoms to come back.
To diagnose whether you are lactose intolerant or not, your doctor may look at your symptoms and ask you to check whether avoiding dairy product for 2 weeks improves the symptoms. To confirm the presence of lactose intolerance, following tests may be performed:
- Hydrogen Breath Test: Generally, people have little hydrogen in their breath. If your body is unable to digest lactose, hydrogen builds up in the intestines and after some time it is present in the breath. To perform this test, you may be asked to consume a lactose loaded drink and then, the levels of hydrogen are measured after some time in your breath. If the level is high enough after 3-4 hours of consumption, then it indicates that that you can’t digest lactose quite well.
- Lactose Tolerance Test: When lactose is broken down in the body, sugar is released in the blood. This can be used to test how much sugar is present in the blood. Blood test is carried out after fasting. Then, the person is asked to drink or eat a food rich in lactose. This should cause the blood sugar level to rise if he/she is not intolerant to lactose. Next, another blood sample is taken 2 hours after the lactose consumption. If the person is lactose intolerant, his/her blood sugar level will not rise, or there will be a very small rise in the blood sugar level.
Treatment and Care of Lactose Intolerance
Treatment of Lactose Intolerance:
While there is no cure for lactose intolerance, dietary adjustments is the main form of therapy for patients with lactose intolerance. However, some treatments may help you safely consume milk products in small to moderate quantities.
Dietary supplement tablets can help eliminate lactose intolerance symptoms if the lactose consumption is up to 20 gm at a time. Pills are not very effective for larger amounts of lactose.
Another treatment for lactose intolerance is drinking hydrolyzed milk or lactose-reduced milk. This is produced by adding lactase to the milk hours before the consumption of milk.
It may also be effective to consume probiotics, and yogurt containing lactobacillus and other good bacteria. Commercially available lactase enzyme preparations is effective in reducing the symptoms. Supplemental calcium is also recommended. According to a study, 70% of people with lactose intolerance, who took probiotics for about 35 days had reduction in abdominal pain caused by milk consumption.
Caring for People with Lactose Intolerance:
Care takers must talk with a health care provider or a dietitian about having a diet plan for people with milk intolerance. A diet plan will help manage the symptoms of lactose intolerance and simultaneously, make sure the sufferer gets enough nutrients.
Milk and milk products may be gradually introduced, so that the digestive system may be able to adapt itself with fewer symptoms. Cereals along with milk can be given to lactose intolerant persons. Hard cheese like Swiss or cheddar are well tolerated as compared to a glass of milk. Lactose-free foods can be freely given to such persons.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Lactose Intolerance
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs for Lactose Intolerance:
Over-the-counter pills or drops containing lactase can be taken before meals to reduce or eliminate the symptoms. For example, Lactose pills or lactose-free milk allows people to process dairy products without difficulty. Below are the medicines (enzyme supplements) to treat or reduce the symptoms of milk intolerance:
| Medicine | Type |
| Lactaid Oral | OTC |
| Lactase Enzyme Oral | OTC |
| Dairy Digestive Oral | OTC |
| Dairy Aid Oral | OTC |
| Lactase Fast Acting Oral | OTC |
Taking these over-the-counter drugs 30 minutes before consuming dairy products can control most symptoms associated with lactose intolerance.
Self-Management Methods for Lactose Intolerance:
- Drink low-fat milk or fat-free milk. You can take it with other foods like breakfast cereal instead of having it on empty stomach.
- Eat dairy products different from milk, such as hard cheese, cottage cheese and yogurt.
- Use over-the-counter pills or other enzyme supplements containing lactase.

Natural Ways to Cure Lactose Intolerance
- Ginger: It deals with digestive problems and helps in relieving the symptoms of lactose intolerance. It reduces abdominal gas by relieving gastrointestinal issues and conditions of indigestion.
- Saffron: It is helpful in getting rid of gas formation in the intestine and, relieving stomach pain.
- Peppermint: Lactose intolerance can cause diarrhea, which can be prevented with peppermint extracts. Peppermint can also relieve stomach spasms and pain due to lactose intolerance.
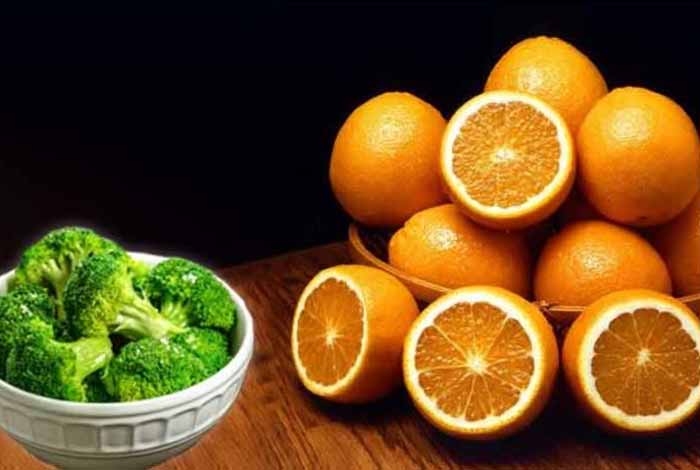
- Broccoli: It is known to fight lactose intolerance and boost the immunity by removing free radicals in the body due to the presence of vitamin C.
- Orange: Since orange has high in vitamin C concentration, it is beneficial for people with lactose intolerance.

Health Tip by Expert
Many people with lactose intolerance can handle varying levels of lactose in their diet. Some dairy products should still be kept in the diet like cheese and yogurt that contain less lactose.





