Overview and Facts:
Back pain is quite common. According to Mayo Clinic, around 80% of Americans will have back pain once in their lifetime. Back pain may be uncomfortable, but it is not a serious condition. It can affect people belonging to any age group. However, it is more common in adults, aged 35 to 55. The lumbar spine or lower back is made up of interconnecting bones, joints, nerves and ligaments that work in conjunction with each other to provide support and strength to the body. The lower back provides support to the upper body and mobility for everyday functions like turning and bending. According to experts, back pain is related to the way the bones, ligaments and muscles are connected to each other. Pain in the upper back may be due to aorta disorders, chest tumors and inflammation of the spine. Acute low back pain might happen due to injury to the muscles, joints or ligaments. Low back pain is also called lumbago.
Back pain may be acute, subacute or chronic, depending on its duration. The pain feels like a burning sensation or as if something has been pierced, which may radiate into the arms and hands as well as legs. The pain originates from the muscles, bones, joints or the vertebral column in the spine. In the U.S., back pain is the fifth most common reasons for a visit to the doctor and remaining absent from work.
Types and Symptoms of Back Pain:
1. Types of Back Pain:
Back Pain is broadly classified into three categories on the basis of the duration of the back pain. Subacute pain lasts for a duration of 6-12 weeks, while acute pain lasts around 12 weeks. Chronic pain is said to have occurred when pain stays over a duration of 12 weeks.
Nonspecific back pain stems from muscles, ligaments and fascia, while radicular pain involves nervous tissues. Secondary back pain results from cancer or infection. About 98% of back pain cases have no serious pathology involved.
Back pain does not immediately require medical intervention. In majority of cases, back pain is non-progressive. Most of the back pain is due to inflammation

2. Symptoms of Back Pain:
The main symptom is ache or pain anywhere on the back, which might run all the way down to the buttocks and legs. Sometimes, back pain can cause pain in other parts of the body, depending on the affected nerves. While having back pain, stiffness or pain may persist along the spine. There may be a sharp pain in the neck, upper back or lower back. One may experience a chronic ache in the middle or lower back and is unable to stand straight without pain or muscle spasm. Doctor should be consulted if any of the following back pain symptoms persist:
- Loss of weight
- High body temperature (fever)
- Persistent back pain
- Swelling or inflammation on the back
- Urinary incontinence: Unable to control urine
- Urinating difficulty: Unable to pass urine
- Numbness around anus, thighs and genitals.

Risk Factors:
Back pain can happen to anyone. But, there are some risk factors that put you at a greater risk developing back pain. Some of these factors are listed below:
- Age: Back pain is more commonly observed in individuals in their late 40s and early 30s. As you age, you would find yourself complaining more about back pain.
- Little to No Exercise: Muscles that are less utilized tends to become weak, and complete lack of exercise promotes back pain. This condition predominantly exists in people, who lead a sedentary lifestyle involving very less or no body movement.
- Being Obese: If you are carrying extra weight around your abdomen, you would put more strain or stress on your lower back, which may cause back pain.
- Diseases: Prevalence of diseases like arthritis and cancer contribute to back pain.
- Improper Lifting: Improperly lifting heavy weights with the support of your back can lead to back pain.
- Psychological Illness: People with psychological disorders like depression and anxiety are at a higher risk of developing back pain.
Do I have Back Pain?
Kidney pain and back pain are difficult to distinguish. Kidney pain is usually a pain that happens deeper and higher in the back located under the ribs. On the other hand, back pain is something that occurs in the muscles of the back, and generally affects the lower section of the back.
There are also different causes of back pain and kidney pain. Kidney pain may be caused due to infections in the urinary tract and stones in the kidney. Whereas, Back pain is caused by strain in the back or structural problems like rupturing of the discs.
Causes and Prevention of Back Pain:
1. Causes of Back Pain:
Back pain develops often without a specific cause, which can be identified with a test or imaging study. Commonly known conditions that result in back pain are discussed below:
- Strain: The most common cause of back pain is strained muscles, strained ligaments or muscle spasm. Incidences that could lead to strain include lifting heavy objects improperly. Repeatedly lifting heavy weights or sudden awkward movement may strain muscles of the back and ligaments. Constant strain on the back may lead to spasm of muscles.
- Structural Problems Like Rupturing of Disks: Disks cushion each vertebra of our spine. There will be more pressure on nerve if disk ruptures. This may result in back pain. Bulging disks can also increase pressure on the nerve.
- Sciatica: Bulging or herniated disk that presses nerve may result in intense pain that could extend down to the back of the leg through the buttock.
- Arthritis: Patients with osteoarthritis have problems with lower back, knees and joints of the hip. Spinal stenosis develops in some cases when space around the spinal cord narrows.
- Curvature of Spine: If spine curves abnormally, then the person has greater chances of having back pain. Scoliosis is a condition in which spine curves.
- Osteoporosis: Vertebra of the spine and bones become brittle leading to pain in the back.
2. Some other causes of back pain are listed below:
- Cancer of the Spine: Tumor on the spine may press against a nerve leading to pain in the back.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: Cauda Equina is a bunch of spinal nerve roots arising from lower end of the spinal cord. During this syndrome, there is pain in upper buttocks and lower back, and numbness in the thigh region.
- Sleep Disorders: People with sleep disorders are more prone to back pain.
- Shingles: An infection, which affects the nerves and may cause back pain.
- Bad Mattress: If the mattress does not support the spine enough to keep it straight, it may result in back pain.
- Poor Posture: Lifting or carrying something heavy or bending awkwardly may result in back pain.
3. Prevention of Back Pain:
- Exercise Regularly: Core strengthening exercises that strengthen the abdominal and back muscles for protecting the back are recommended. Exercises that improve flexibility of spine, hips, legs can prevent back pain.
- Prohibit Smoking: Back pain is significantly higher in smokers than in nonsmokers. Thus, one must refrain from smoking to avoid back pain.
- Regulate Body Weight: Maintaining body weight is a great way of avoiding back pain. People, who are obese and the ones, who carry weight in the abdominal area as against the hip area, are at a higher risk of developing back pain.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Make sure you maintain a proper posture while sitting and standing. For example, when you are standing let your back straight and balance your weight evenly on both the legs. Good seat should have good support for back and armrests. Keep your feet flat on the floor.
- Cautious While Lifting Things: If something is particularly heavy, see if you can lift it with someone’s support. While you are lifting things, look straight ahead, so that the back of your neck is in line with your spine. When you move things, push them using your legs, and refrain from lifting them up.
Diagnosis and Tests of Back Pain:
Most of the time, back pain can be diagnosed by carrying out a physical examination of the patient. In majority of the cases, imaging tests may not be required. Tests are conducted if some injury is suspected on the back. If pain persists for a longer duration of time, further tests may be recommended.
- Imaging Techniques: X-rays or imaging scans like CT Scan or MRI may be used. X-Rays procedure shows whether a patient has broken bones or arthritis. MRI or CT Scans may be used to detect herniated disks or problems with tissues, muscles, bones and ligaments.
- Bone Scans: Bone scans may be used for identifying bone tumors or fractures caused by brittle bones. A radioactive substance is injected into the vein, which helps identify problems in bones with a special camera.
- EMG or Electromyography: This helps in measuring electrical impulses produced by nerves responding to muscles.

Treatment and Care of Back Pain:
1. Treatment of Back Pain:
Pain can be dealt with by using over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers or prescription drugs. To relieve pain, hot compress or an ice pack may be applied to the affected area. Resting may help, but not for a long duration as this may lead to weakening of muscles. If home treatments are unable to produce the desired effect, the following treatments may be used:
- Medication: If back pain does not respond to OTC painkillers, prescription-based nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) is recommended. Codeine or hydrocodone may be prescribed for short periods. Some tricyclic antidepressants have been known to alleviate symptoms of back pain.
- Physical Therapy: Application of heat, ice, electrical stimulation, and some muscle release techniques may be used to alleviate back pain. As the pain lessens, therapists may prescribe flexibility and strength exercises for abdominal and back muscles.
- Cortisone Injections: If the above-stated therapies are not effective, cortisone injections may be given in the space around the spinal cord, known as epidural space.
- Botox: It could also be used to reduce pain as Botox paralyzes sprained muscles.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Patients can be trained to perceive less pain. CBT uses relaxation therapies to maintain a positive attitude. This technique helps manage chronic back pain.

Other Approaches:
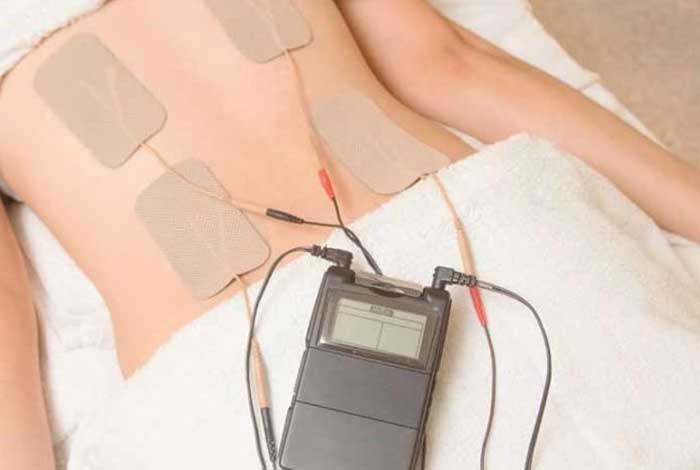
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): This approach involves giving small electrical impulses in the body through electrodes placed under the skin. This technique produces endorphins and blocks sensation of pain. Pregnant women, epilepsy patients, heart patients should not use TENS.
Surgery for Back Pain:
Surgery for back pain is rare and employed in cases of herniated disks. Examples of surgeries are:
- Fusion: Two vertebrae are joined together with metal plates and grafting a bone between the two. There are greater chances of developing arthritis in these vertebrae.
- Artificial Disk: Artificial disk replaces the cushions between the two vertebrae.
- Diskectomy: If a disk is pressing against a nerve, it may be removed.
- Vertebrae Removal: Vertebra may be removed if it is pressing against the spinal cord or nerves.
Caring for Someone with Back Pain:
The following care tips can be applied to deal with the condition of back pain:
- Use an Ergonomic Chair or Back Support: This will help in maintaining right posture if the chair is aligned. Also, make sure that peripheral items are easily accessible. Environmental factors like position of the computer impact the health of the spine. Monitor screen that is lower than the level of the eye could help prevent slouching or arching of the back.
- It is Best to Avoid Movement on Stairs: If you are located at a place that requires a lot of moving up and down, then it may lead to back pain. So, it is best to avoid stairs.
- Minimize Driving: Driving with back pain is difficult as this requires getting in and out of the car, constantly looking over one’s shoulders and other motions involved in diving. It is suggested to minimize trips.
- Consuming Medicines on Time: Remember to take your medicines and don’t just sit at one place for too long. Get up from your seat, and move around whenever possible.
OTC Medications Methods for Back Pain:
1. OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Back Pain:
a. Ibuprofen: Advil or Motrin, which is available over the counter, is an excellent medication for short-term treatment of back pain. The usage has some side effects like ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding; so, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Acetaminophen like Tylenol can also be used to relieve pain.
Topical agents like deep heating rubs can be used.
2. Self-Management Methods for Back Pain:
a. Complementary Therapies:
- A Short Period of Rest: One can take rest for one or two days in which strenuous activity must be minimized and not much pressure should be borne on the spine. It is best to use recliner or sit in a position such that there is no stress on the lower back.
- Application of Ice: Application of cold pack to lower back can decrease inflammation. Ice is recommended within the first 2 days of the start of the pain. To avoid ice burn, ice should not be applied directly to the skin.
- Application of Heat: This will help ease muscle tension, relieve muscle spasms and increase flow of oxygenated blood to facilitate healing.
- Maintaining Adjustments to Posture: Don’t engage in daily activities that put pressure on the spine. For example, move carefully and take short walks periodically to reduce stiffness and increase flow of blood.

Natural Ways to Treat Back Pain:
- Chiropractic: This therapy involves diagnosis by touching and visual inspection. This technique focuses on adjusting the spinal cord. Chiropractors also use urine sample and blood tests to come to any conclusion.
- Osteopathic Approach: This approach involves slow and rhythmic stretching and indirect techniques like applying pressure on joints and muscles.
- Shiatsu: This is a type of massage in which pressure is applied along the energy lines in the body. A practitioner applies the pressure with the help of fingers and thumbs.
- Acupuncture: This involves inserting fine needles and activating specific points in the body. Acupuncture results in releasing natural painkillers, called endorphins which helps in alleviating pain.
- Yoga: It involves specific poses, movements and breathing exercises which strengthen back muscles and help in improvement of posture.
- Strength Training: Strengthen your back and core as building strength in these areas may prevent and relieve back pain.
- Physical Therapy: Doing physical activity within two weeks from the start of back pain is associated with less need for having medical care and also settles the back pain easily.
- Comfrey Root: Application of an ointment that contains this plant-based extract reduces the intensity of lower back pain.
- Aquatic Therapy: Sedentary adults, who undergo aquatic therapy, i.e., physical therapy in the pool, see reduction in pain and improvement in their quality of life.
- The Alexander Technique: Practitioners of the Alexander technique teach patients how to adjust posture during everyday activities to reduce muscular stress and pain.
- Massage: People, who receive regular massage for a duration of at least 10 weeks, reported less back pain than those, who did not.
- Tai Chi: This Chinese martial art is an effective treatment for back pain. Research shows the practice of Tai Chi reduces intensity of pain to a great extent.
Health Tip by Expert:
“While you sleep, place a pillow between your knees to keep your spine in a neutral position and relieve strain on your back.”










