Glutathione is a peptide that is naturally produced in the human liver and has several functions in human body. It acts as an important antioxidant in plants, animal fungi, bacteria and archaea. Besides neutralizing free radicals, it also prevents damages caused by peroxides, lipid peroxides and heavy metals those are harmful to health. Chemically, it is very active in nature and breakdowns easily, that’s why it has limited application in supplementary foods.
Moreover, natural glutathione is a super antioxidant that is placed in the cells and useful for each and every cell of the body. It conjugates drugs to make them soluble for excretion.
Structure and composition of glutathione:
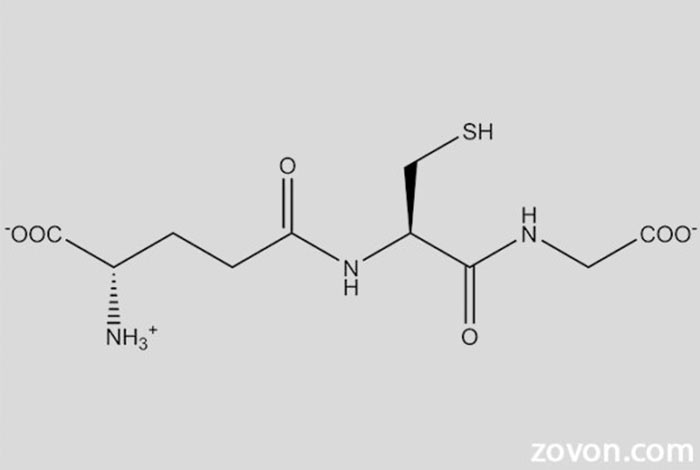
Glutathione is a tripeptide and comprised of three amino acids namely, cysteine, glutamic acid and glycine. Its chemical composition is C10H17N3O6S. The sulfur molecule of glutathione reacts with some harmful species such as halides, epoxides and of course free radicals and forms harmless molecules in the end. Glutathione is involved in the formation and maintenance of disulfide bonds in proteins and helps in transferring amino acids throughout body cells. The internal structure of the glutathione is shown in the figure below:
Sources of glutathione:
Glutathione has three types of sources; natural food and vegetable source, foods those stimulate glutathione production in the liver and synthetic glutathione. Some micronutrients such as selenium, chromium stimulates glutathione in the liver. Foods, those stimulate glutathione in livers are very important as they enhance liver activity.
Natural source:
- Avocado and asparagus are the highest natural sources of glutathione; 27 and 28 mg per 100gm.
Other sources include:

- Spinach (11mg/100 gm)
- Okra (11 mg/100 gm)
- Broccoli (9 mg/100 gm)
- Cantaloupe (9 mg/100 gm)
- Tomato (9 mg/100 gm)
- Carrot (8 mg/100 gm)
- Grapefruit (8 mg/100 gm)
- Orange (7.5 mg/100 gm)
- Strawberry (7 mg/100 gm)
- Watermelon (6.5 mg/100 gm)
- Papaya (6 mg/100 gm)
- Red and green bell peppers (5.5 and 3.5 mg/100 gm, respectively)
- Peach (5 mg/100 gm)
- Lemon (4.8 mg/100 gm)
- Mango (4.3 mg/100 gm)
- Banana (4.1 mg/100 gm)
- Cauliflower (4 mg/100 gm)
- Walnuts (3.7 mg/100 gm)
- Cucumber (3.5 mg/100 gm)
- Apple (3.3 mg/100 gm)
- Grapes (2.7 mg/100 gm)
Foods those stimulate glutathione in liver:
Some organic chemicals those contribute production of glutathione in the liver are present in some natural foods. Once these foods metabolize and reach the liver, glutathione is produced. This category includes vegetables and spices. These type of glutathione sources include broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, garlic, parsley, spinach, beets, turmeric, cinnamon, cardamom, black cumin etc.
Synthetic source of Glutathione:
Chemically synthesized glutathione is a series of organic molecules, coupled by peptide bond to the alpha-NH2 group of Glu. Glutathione is manufactured through the fermentation process. This type of glutathione is used in dietary supplements as a food additive.
Benefits/Applications of Glutathione:
Among all antioxidants, glutathione is the super-antioxidant with multiple-benefits. It can be either taken orally or injected. It can also be sometimes inhaled. Glutathione, taken orally has a low impact on glutathione level as it first gets absorbed by the intestines cells and not by the liver cells. Cooking also reduces glutathione activity, only raw uncooked fruits, vegetables, unpasteurized milk, raw meats are rich in glutathione. It has dozens of health benefits and applications in everyday life. It could be a good dietary element if belongs to regular dietary chart. Some applications of glutathione as a medication are listed below:
1. Glutathione consumed orally:
- Detoxifier that prevents glaucoma and cataract.
- Effective anti-aging element.
- Improves liver and pancreas functions.
- Prevents shock induced behavior such as depression, trauma, anxiety, stress.
- Protects nerve cells, DNA by detoxifying reactive oxygen species in the brain.
- Declines infections by enhancing microbial killing activity.
- Glutathione has a major impact on declining activity of carcinogenic cells.It decreases the risk of oral and throat cancer. It also has the potential to repair damage caused by cancer drugs and chemotherapy.
- Reduces the intensity of OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder) by reducing free radicals in the brain cells.
- Effective in the detoxification of alcohol and other drugs.
- Protects heart, cardiovascular, pulmonary organs and prevents these from infection and disorders.
- Strengthens bones and muscles and prevents osteoarthritis.
- Supports body immunity system and prevents AIDS.
- Helpful to fight chronic fatigue syndrome and viral infections.
2.Glutathione Inhaled:
- Treats lung diseases and infections.
3.Glutathione taken intravenously:
- Controls inflammation
- Prevents infections
- Effects positively in treating male-fertility
- Prevents Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease
- Effectively prevents anemia caused by medication for kidney disorders
- Prevents complications associated with diabetes
Other than above-mentioned medications, glutathione is also beneficial for
- Reducing abnormal cell death
- Improving sleep apnea i.e., sudden breathlessness during sleeping
- Helpful against acne
- Glutathione intake is good for pregnant women and unborn child. Glutathione deficiency might cause impaired brain development in the unborn child. Breast milk is the primary source of glutathione among newborns.
- It is effective for treating cystic fibrosis
Industrial application of glutathione:
Glutathione has industrial application in wine and cosmetic production. Glutathione is the first raw form of wine that determines the caramelizing effect during the production of white wine.
In the cosmetic industry, it has numerous applications in skin care as it effectively prevents oxidative damages. Some researches have proved that it has lightning and brightening effects over skin by inhibiting melanin synthesis.
Side-effects of glutathione:
An appropriate dose of glutathione prescribed by an expert could be beneficial, sometimes, in treating some diseases practitioner prescribed over-dose of glutathione for short period. But overdose and very long-term use without expert’s advice could be adverse. Inhaling glutathione in asthma could be adverse and increase problems. Supplements have not been reported as harmful though they are not thoroughly researched. Pregnant, breastfeeding women and children need to ask practitioner before taking it. Though results say, it is beneficial for pregnant and breastfeeding women as well as for unborn and newborn babies. People who are already under some conventional medication are also advised to consult doctors before glutathione consumption.
FAQs: What people normally want to know about Glutathione?
1. How important is glutathione?
It is one of the most important antioxidants that are responsible for lots of wellness keys of the human body. It is essential for body immunity function and anti-inflammatory. It has several uses in medical applications and is extremely beneficial for human health. It not only protects body but also helps in treatment.
2. What is the role of glutathione in the body?
Glutathione is also called body’s super-antioxidant and is capable of providing relief from body pain and inflammation. It reduces cell death and helps in lightening skin color. It improves liver and pancreas activity and supports metabolism by helping in excretion of toxic substances.
3. What foods are high in glutathione?
Avocado and asparagus are the ultimate natural sources of glutathione. Apple, grape, peach, berries, grapefruit, tomato, carrot are some other important green sources of it. Human liver produces glutathione in body with the help of broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, garlic, parsley, spinach etc. Some glutathione supplements are also available in the market.
4. How does glutathione help liver?
Liver is the primary detox organ of body and glutathione is a good detoxifier. It is found throughout the body but produced in the liver only. This is the molecule generated by liver enzymes which are capable to flush the wastage from the body. This is hoy glutathione helps the liver in metabolism as well as excretion.
5. What is glutathione injection?
Since glutathione is highly recommended by experts in healthcare and wellness treatment. it is injected into the blood of kidney patients to help their anemia. It helps patients of hemodialysis, other kidney disorders, bypass surgery to improve blood flow and reduce blood clotting.
6. Is glutathione safe?
Glutathione is more than safe, it is beneficial. According to some expert’s opinion, it is good for pregnant and breastfeeding women and also for unborn and newborn babies. But, it is important to consult a doctor before taking glutathione supplements during pregnancy and breastfeeding condition and also for children and aged people.