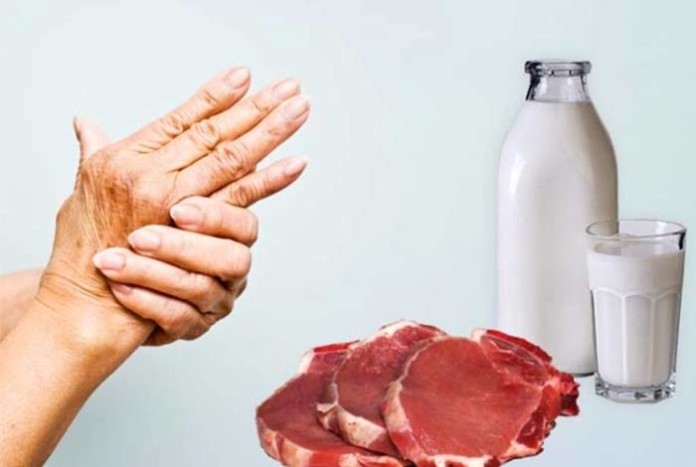
In a recent study conducted by a team of researchers from the University of Central Florida (UCF) College of Medicine, the researchers discovered a link between Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP), a bacteria generally found in milk, and rheumatoid arthritis. The bacterial strain is generally found in a large number of cows in the US. It can spread to humans after they consume beef or milk from the infected cow.[Source]
This link between rheumatoid arthritis and MAP is highlighted for the first time, and the findings of the research has been published in journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. The researchers had earlier discovered a relation between MAP and Crohn’s disease. They are currently working on phase-III clinical trial approved by the FDA, to treat Crohn’s disease with antibiotics.
Generally, both rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease are caused due to genetic errors. Also, both of these conditions can be treated by immunosuppressive drugs. This relation between the two diseases led researchers to investigate if MAP is also responsible for causing rheumatoid arthritis. The researchers collected clinical samples from hundreds of patients that volunteered for the trial. In about 78% patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, a genetic mutation in PTPN2/22 gene was traced. A similar genetic error is traced in the patients with Crohn’s disease. Also, about 40% of the total number of patients werRheumatoid arthritise found to have MAP their body.
However, the researchers are conducting further studies to confirm their findings. They are also planning to study participants from different ethnical and geographical backgrounds.