Table of Content
- Overview and Statistical Facts
- Types of Tonsillitis
- Symptoms of Tonsillitis
- Risk Factors for Tonsillitis
- Do I Have It Tonsillitis?
- Causes and Prevention
- Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
- Treatment for Tonsillitis
- OTC or Self Management Methods
- Natural Ways to Cure
- Health Tip by experts
Overview and Statistical Facts
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils. Lumps of tissue at the back of the throat are known as tonsils. There are two of these, one present on each side. Tonsils are a component of lymphatic system along with adenoids. Lymphatic system helps in clearing infection and maintaining the balance of body fluids. Adenoids and tonsils trap the germs entering through the nose and mouth. At times, along with tonsillitis, adenoids also get swollen. Generally, it is caused due to a viral infection. Bacterial infections like strep throat can also cause tonsillitis.
It is common in children above the age of two. Every child in the U.S. gets it at least once in their life. Bacterial tonsillitis is common in children in the age range of 5-15. Viral tonsillitis is more prevalent in younger children. Adults too can get tonsillitis but it is not commonly seen. Tonsillitis in itself is not contagious but the bacteria and viruses that cause it can be spread. Frequent hand washing can prevent the spread of infections.
Tonsillitis generally affect children in the age range of 3-7 years. This is because at this time tonsils are most actively involved in fighting infections. As the child starts growing and tonsils start shrinking the incidence of the infection becomes less common. Tonsillitis aren’t really serious until there is development of tonsillar abscess. If this happens, the swelling could become serious to the extent that it can hamper the breathing of the child. At the same time, ear infections and adenoid issues that is swelling behind the nasal cavity above the tonsils can occur.
Types of Tonsillitis
The following are the types of tonsillitis [1] :
- Acute Tonsillitis [2] : This is caused either by a bacteria or virus
- Recurring Tonsillitis: This is said to occur when there are around seven culture proven episodes of throat infections or tonsillitis in a year, five in two years back to back, or three each in three consecutive years. In these cases, when antibiotics are stopped it leads to an episode of bacterial infections in few weeks causing it to occur again.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: It occurs when recurring tonsillitis cause chronic sore throat, tender cervical nodes and bad breath.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA) or Quinsy: It is a bacterial infection which develops in the region lateral to tonsillar region when an acute tonsillitis infection is left untreated. A swollen area or abscess with pus gets formed in the peritonsillar region. Generally, the pathogens are Streptococci, Staphylococci, Fusobacterium, and Haemophilus. There is no virus. Fever, foul breath, not being able to open the mouth, change in voice quality are some of the signs and symptoms.
- Tonsillar Hypertrophy or Hyperplasia: Enlargement of the palatal tonsils with symptoms like snoring, difficulty to speak and swallow.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
Some common symptoms are [3]:
- Sore Throat: This is usually accompanied by pain in throat
- Red, swollen, tender tonsils or lymph glands in the neck region or jaw with pus or white spots.
- Not being able to swallow or ingest anything
- Moderate to high rise in temperature of the body or fever more than 38.3 degree Celsius; rectally measured.
- Because of infection or sepsis on the tonsils the person may have fever with chills.
- Painful ulcers or blisters on the throat
- Pain in ears
- Headache, Body ache
- Cough
- Discomfort or malaise and lethargy
Adenoids and infected tonsils hamper the breathing of the person and drainage of the sinus. This disturbance in air passage can cause:
- Snoring in kids
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Bad or foul breath
- Pain in neck and ear

Risk Factors for Tonsillitis
The following are the risk factors for tonsillitis:
- Young Age: It is most prevalent in children in preschool and middle aged children
- Environment: The infection may spread due to pollution and improperly ventilated environment and excessive crowding
- Infected People: An infection may happen when a person breathes in bacteria or virus that someone else has sneezed or breathed out.
- Reduced Resistance of the Body: The chances of infection are more if the immunity is compromised. For example, someone on steroids for a long time or having an HIV infection will be at greater risk for getting the condition.
Do I Have Tonsillitis?
The terms tonsillitis sore throat, and strep throat are often used interchangeably. However, they do not necessarily mean the same thing
- Tonsillitis refers to inflamed tonsils
- Strep Throat is an infection caused from a specific type of bacteria known as Streptococcus. In a strep throat the tonsils are generally very inflamed. This inflammation may even affect the surrounding areas of the throat.
- Other reasons for sore throat are viruses and cause inflammation around the tonsils and not on the tonsils itself.
Sore Throat
In infants, preschoolers and toddlers the cause of sore throats is a viral infection. When caused by a virus, no medicine is generally required and the child should get better over a seven to ten-day time span. Children having sore throats will also have cold with mild fever.
A specific virus called Coxsackie seen during summer and fall can cause the child to have higher fever, difficulty in swallowing, and feeling sicker. In coxsackie infection, blisters may be seen on throat, hands and feet. Infectious mononucleosis can lead to a sore throat with tonsillitis. However, most children infected with this virus may have few to no symptoms.
Strep Throat
It is caused by a bacterium known as Streptococcus pyogenes. The symptoms depend on the age of the child.
- Infants: Low fever with bloody or thick nasal discharge.
- Toddlers: They may also have low fever with thick discharge. These children get cranky, do not have an appetite, glands in the neck get swollen. They may even complain of tummy ache instead of sore throat
- Children above the age of three: They generally fall sicker and may have a very painful throat, fever more than 38.9 degree Celsius, pus on tonsils and swollen glands in the neck.
And it is important to distinguish sore throat from strep throat and tonsillitis as the treatment modalities may be different.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Since tonsils defend you from invaders of the world outside, they are themselves prone to getting infected. Tonsillitis is generally viral in nature but can be bacterial as well. Whether they are viral or bacterial, they can spread from one person to another. If the condition happens due to secondary illness like hay fever or sinusitis, it won’t be infectious.
Viral Causes
Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by viral infection. The common types of virus that infect the tonsils are:
- Adenovirus, which is responsible for sore throat and common cold
- Rhinovirus, which causes common cold
- Influenza, referred to as flu
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus, which causes acute respiratory tract infection
- Coronavirus, it has two subtypes which infect humans; one of it also leads to SARS.
Viral tonsillitis sometimes can be caused by:
- Epstein Barr virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Herpes Simplex virus
Bacterial Causes
A very common type of bacteria that infects the tonsils is Streptococcus pyogenes. Less commonly it can be caused by:
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Bordetella pertussis
- Chlamydia pneumonia
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Fusobacterium
Prevention of Tonsillitis
- Since tonsillitis is a contagious condition, so it is best that you stay away from people who have the condition. Make sure you wash your hands as often as possible. And this should be especially practiced when you come in contact with someone having sore throat or is coughing and sneezing. Maintaining good hygiene is the best prevention strategy. Washing is a way how you can keep germs away.
- Remain Hydrated: Drink a lot of fluids and keep yourself hydrated. It is the easiest way to prevent infection.
- Take Proper Rest. When you have tonsillitis, don’t exert yourself too much. This is because the body is weakened and cannot take too much of stress.
- Keep the room temperature in check. Stay in normal temperatures. Don’t sit in excessive cold or air conditioners.
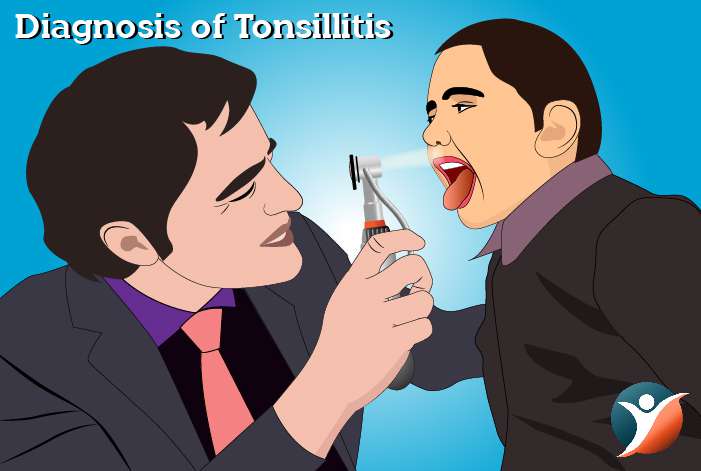
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
The doctor will do a physical exam which includes:
- Using an instrument to look a t the throat and also his or her ears or nose which are possible infection sites.
- Checking for a scar called as scarlatina which is related to strep throat.
- Gently palpating the neck to feel any swollen glands
- Listening to the patient’s breathing using a stethoscope.
- Checking for spleen enlargement as in case of mononucleosis that inflames the tonsils.
Throat Swab
In this simple test, the doctor runs a sterile swab on the back of the child’s throat to get secretion sample, which will be analyzed in the clinic or in lab and see if there is presence of streptococcal bacteria.
Some of the labs can provide you the results in minutes. But the second test which is more reliable is sent to a lab which will give results in 1 to 2 days.
If the results of the tests done in clinic come positive, it is certainly a case of a bacterial infection. In case of negative test results, it could be a viral infection. But it is better to wait for the out of clinic test to know the exact cause of infection.
Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC)
You may be required to go for CBC with a small blood sample. This test which can be done in a clinic tells you the count of different types of blood cells. Blood profile indicating whether the levels are high, low or normal tells us whether the infection is viral or bacterial. CBC may not be needed for the diagnosis of strep throat. If the lab test for strep throat is negative, CBC might be required to ascertain the exact cause of tonsillitis.

Treatment for Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis treatment will depend on the cause. For determining the cause, doctor may perform a throat swab culture or rapid strep test. If tests point to bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to cure the infection. Antibiotics can be taken in a single shot or over a span of 10 days by mouth. The results of the treatment may be seen in as less as two days but you should not stop the medication and must continue taking it for the period it is directed. A second course of antibiotics may be suggested in some cases.
If virus is known to cause tonsillitis, antibiotics won’t be helpful and the body will have to fight the infection on its own. You may do some things to feel better like get some rest, drink warm fluids to do away with throat pain. Eat smooth foods like applesauce, ice cream. Gargle with warm water by adding salt to it. Take OTC pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen
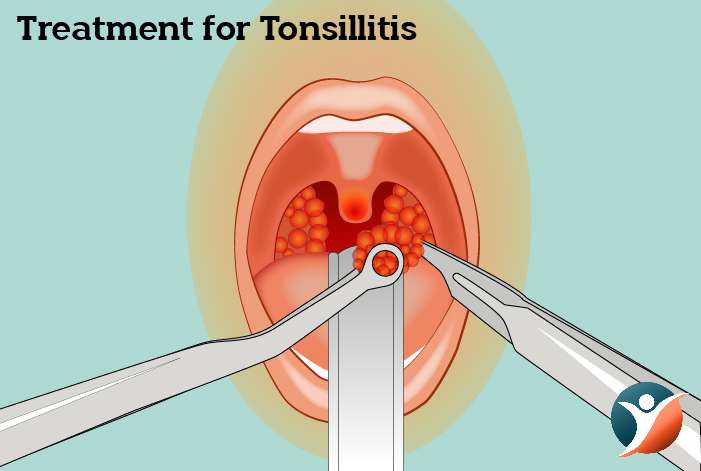
When Is Tonsillectomy Needed?
Tonsils are an essential part of the immune system. So, you should not get them removed. But if tonsillitis occurs frequently and is persistent or if enlarged tonsils cause hindrance to the upper airway and difficulty is experienced while eating, in such cases tonsillectomy or surgical removal of tonsils is required. In tonsillectomy, a conventional scalpel is used to remove the tonsils. But there are many alternatives to this. Of late medical practitioners have been using technologies like lasers, ultrasonic energy, radio waves, electrocautery for cutting, burning and evaporating enlarged tonsils. Just like all surgeries, these too have plus and minuses. When you are looking forward to getting a surgery done, speak to your doctor to find out the best option available out there.
Expectations After Surgery
Tonsillectomy is an outpatient surgery done under general anesthesia and lasts for somewhere between 30 minutes to 45 minutes. It is generally done in children. They go back after about 4 hours of surgery and need 7-10 days for recovery. Patients will generally have throat pain post-surgery. Some will experience ear pain [4] , some report pain in jaw and neck. The medicine suggested would be based on the case. During the stage of recovery, rest is important. Also ensure that the patient gets plenty of fluids although for the first one or two days, you must not give milk to your child. Throat pain will lead to difficulty in swallowing food but the earlier the child starts eating, the sooner the child will recover.
For a few days after the treatment, the child may have low fever and there may be small specks of blood from saliva or nose. If the fever is more than 102 Fahrenheit and there is appearance of dark red blood specks, then you must quickly call the child’s doctor as immediate medical attention may be needed.
Any OTC or Self-Management Methods Available
In most cases, sore throats will not require treatment and will automatically resolve. OTC medicines which can help relieve symptoms are aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen. Patients having problems related to stomach or kidney should not take ibuprofen or aspirin.
Self-Management Methods Available:
- Hot drinks and foods may irritate the throat
- Cool soft foods and cool drinks may relieve the symptoms
- Warm drinks (not hot) may be helpful
- Smoke will be an irritant to the throat
- Sucking ice cubes can help relieve symptoms
- Gargle with mouthwash as it will help reduce swelling and alleviate pain
- Salted warm water is a great option.

Treating children with honey is a good alternative to cough medicines. But honey should not be given to kids below the age of 1 year. Antibiotics is used generally when the throat infection is severe or if the immune system of patients is weak. Patients who get repeated bacterial throat infections may be given antibiotics.
Natural Ways to Cure Tonsillitis
There are a number of home remedies or natural ways that can help treat or reduce the symptoms of tonsillitis:
- Salt Water Gargling: Gargling with warm water can help treat a sore throat and sooth the pain caused by tonsillitis. It can reduce inflammation and help treat infections. Mix around half teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water. Stir till the salt gets dissolved. Swish it through the mouth for some time and then spit it out. Rinse it with regular water.
- Licorice Lozenges: Lozenges containing licorice have strong anti-inflammatory benefits and sooth swelling and discomfort in throat. These should not be given to young children as there is risk of choking. For children of this age, throat sprays are a better option. If you don’t know what to do, call their pediatrician.
- Warm tea with raw honey: Warm drinking items like tea can help reduce problems due to tonsillitis. Raw honey has strong anti-bacterial properties and can help treat the infections. Don’t drink hot tea. Make it warm and stir it till all the honey gets dissolved. Ginger tea and fennel tea are strong anti-inflammatory beverages which can help reduce discomfort and inflammation.
- Popsicles and Ice Chips: These can be very effective in treating pain, swelling, inflammation that accompanies tonsillitis. Frozen foods and frozen drinks are useful for children who can’t use other home remedies. Adults and older people can suck on ice chips.
- Humidifiers: These can help relieve sore throat if you are experiencing dry mouth because of tonsillitis. The throat may become irritated due to dry air so humidifiers can sooth discomfort by putting moisture back in the air. The most beneficial ones are cool mist moisturizer when virus cause the tonsillitis. If you don’t have a humidifier, sit in a steam filled room which can help reduce the symptoms.

Health Tip by Experts
If your child has repeated and frequent bouts of tonsillitis, they are probably a candidate for tonsillectomy. So, do not wait and if the symptoms become severe, without delay, seek medical help.




