Tendon is a connective tissue that attaches muscle to other parts of the body, usually bones. These help in transmitting the mechanical force from muscles to the bones. Among the soft tissues of the body, tendons are known to possess the highest tensile strength. Hierarchical structure, tissue composition and parallel orientation of tendon fibers provides the strength to the tissue for withstanding the high stress generated through muscular contraction.
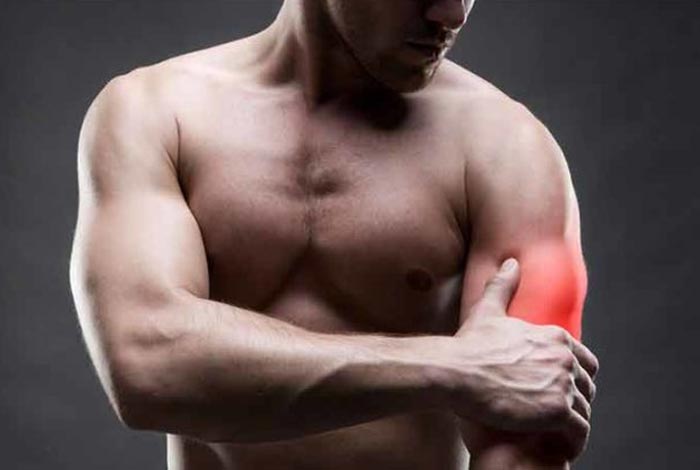
When inflammation or irritation occurs in a tendon, it gives rise to a condition called tendinopathy, commonly known as tendinitis or tendonitis.[1] It happens when a person injures or overuses a tendon during a strenuous activity. Often, it is an acute injury accompanied with inflammation, but can become chronic or recur in some people. While the condition can develop in any of the tendons, it is most commonly observed in the tendons around elbows, shoulders, knees, wrists and heels. Some of the commonly used names for tendinitis are:
- Tennis elbow
- Pitcher’s shoulder
- Swimmer’s shoulder
- Golfer’s s elbow
- Jumper’s knee
The pain experienced is quite severe in nature and is often sudden. The pain shares the characteristic of worsening with movement with the pain that occurs in arthritis. However, the pain is experienced in parts away from the joints, unlike arthritis.
Tendon injuries are quite commonly seen in recreational and professional athletes and in people involved in occupations that involve continuous repetitive work. [2] Tendinopathy is characterized by tenderness in the tendons, activity related pain and reduced strength and movement of the affected area.
As per the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, nearly 70,000 people miss their work each year due to tendinitis. [3]
Types and Symptoms of Tendinitis
I. Depending upon the type of injury being sustained by the tendon, tendonitis can be divided into following types:
1. Tendinitis with Damage
Damage to the tendon and surrounding connective tissue structure occurs due to overuse, repetitive strain or even normal use. Excessive load on the tendons can cause them to fray. Their structure can be further weakened by nutritional deficiencies. Micro damage occurs due to overuse of the tendons, due to sliding back and forth over different structures. The body responds to this damage by triggering an inflammatory response, which results in trapping the fluid in the area and releases the chemicals that enhances sensitivity to pain and makes the muscles tighter. This mechanism is called the downward spiral of the pain causing dynamic.
2. Tendinitis Without Damage
The muscles of the body become a little tighter and continue to stay tighter even when at rest due to over use or due to repetitive strain. Sometimes normal use and the natural pain causing dynamic also cause muscles to tighten up. This tightness in muscles puts tension on the tendons, surrounding connective tissue and attachment points. Since the muscles become tight and continue to remain tight for a long period of time, there is continuous tension in the muscles. This causes the connective tissue to shrink and compresses the muscle structures and signals the nervous system about the excessive load and potential damage of tendons.
II. On the basis of the tendon that is affected tendinitis can be divided into following categories:
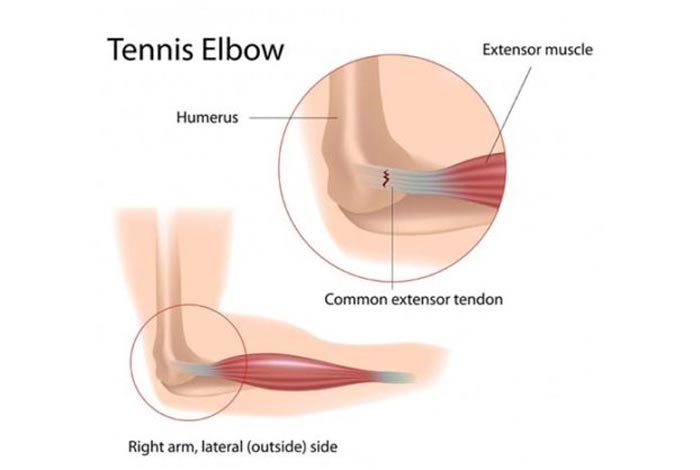
1. Elbow Tendinitis or Tennis Elbow
It is a type of tendinitis in which inflammation occurs in the tendons outside the elbow that connects the elbow bone to muscle which allows the finger and wrist to extend. As the name clearly signifies, this condition is commonly seen in tennis players. However, it is possible to have tennis elbow, even if the person has never picked up a tennis racket.
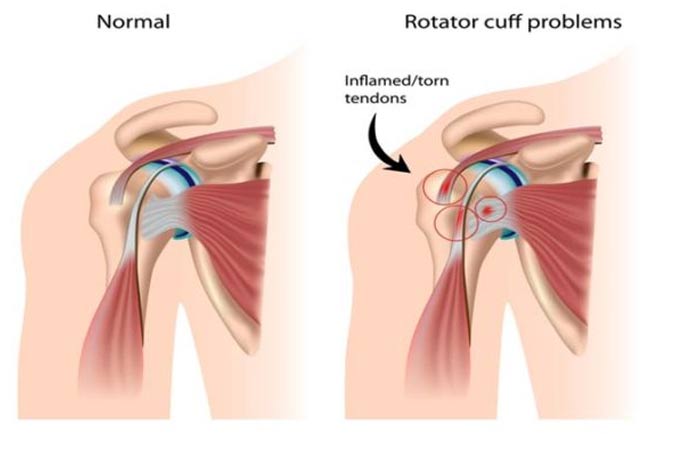
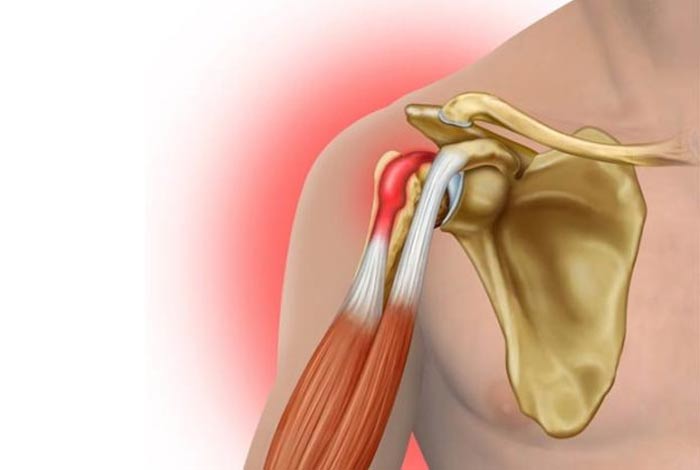
2. Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
In order to keep the bone in the shoulder socket, a group of muscles and tendons come into play, which form a tough sheath to support the arm at the shoulder joint. There are four tendons that help in the movement of shoulders and any of it can become swollen or injured, leading to rotator cuff tendinitis.
Such a situation can arise following a traumatic injury or due to repetitive motion as seen in professional baseball player who swings a bat, or a non-athlete person shoveling snow. It is also known as swimmer’s shoulder, pitcher’s shoulder or tennis shoulder.
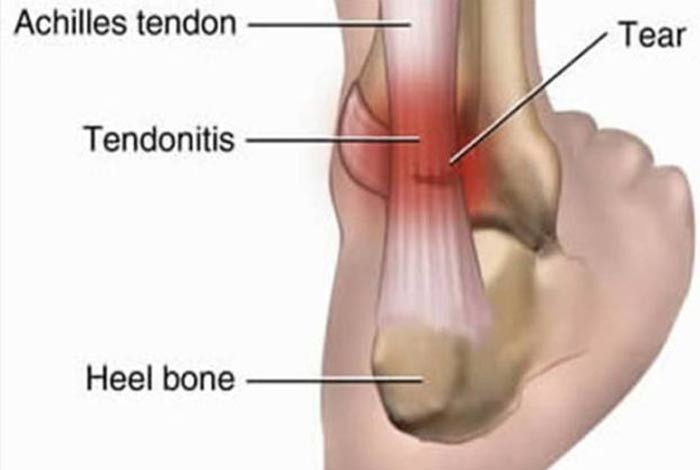
3. Achilles Tendinitis
When the tendon connecting the lower calf muscles to the heel bone becomes inflamed in elderly people, especially those who exercise semi regularly, it is called Achilles tendinitis. It is commonly seen in runners and jumpers. It can be easily managed through ice and rest. However, it is one of the most stubborn, recurring type of tendinitis, especially among athletes who do not give their tendons rest and time to heal.
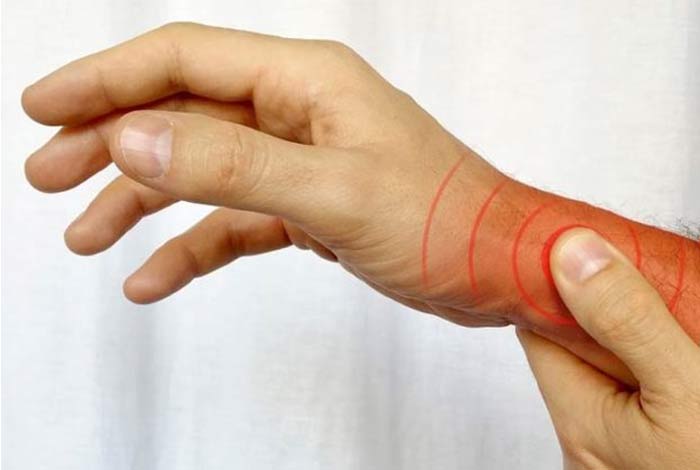
4. de Quervain’s Tendinitis
Swelling in the tendons found on the thumb side of the wrist in which discomfort or pain is experienced while trying to make a fist or grip something. This condition has been named after a Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain who is famous for his work on thyroid ailments.
In this condition, pain can be felt from the base of the thumb to the lower arm. It is commonly seen in people who are athletes, use keyboards for typing and suffer injury to the outer part of the hand. In the recent times, when the use of smart phones has become so extensive, de Quervain’s tendinitis is also called Blackberry thumb or texting thumb as it is increasingly becoming common due to the style most people use for typing on their smart phones.
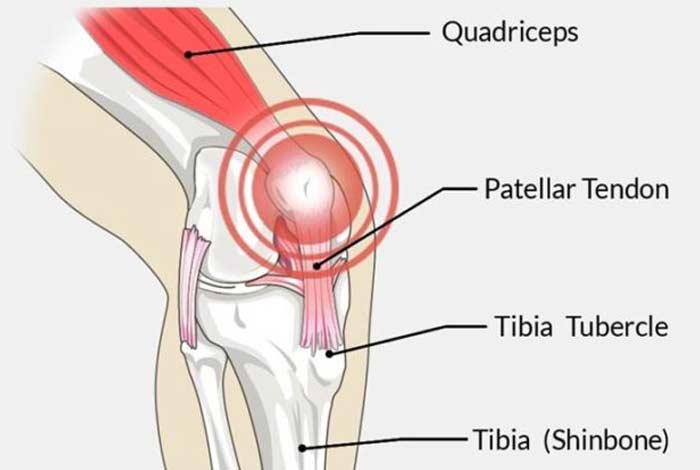
5. Patellar Tendinitis
Patellar tendon connects the shin bone (tibia) to the patella or the knee cap. When this tendon gets inflamed due to frequent jumping as seen in basketball and volleyball, patellar tendinitis or jumper’s knee arises.
6. Wrist Tendinitis
It is a common problem that can manifest as swelling and pain around the wrist joint due to inflammation of tendons. Often, there is accumulation of fluid in the tendon sheath, which is a layer of the connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the tendon. The sheath is responsible for producing a fluid for keeping the tendons lubricated.
One of the major aspects of treating a wrist tendinitis is to identify the tendon or tendons that are causing trouble for a more effective treatment. It can be of different types, depending upon the wrist bone affected such as:
- Exterior carpi ulnaris tendinopathy, involving the exterior carpi ulnaris
- de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, involving the abductor pollicis longus and exterior pollicis brevis
- Intersection Syndrome
- Flexor caarpi radialis tendinitis
- Flexor carpi ulnaris tendinitis
7. Biceps Tendinitis
Biceps tendons connect the muscles at the front of the arm, i.e. biceps brachii, to the bone in the shoulder. Overuse and repetitive shoulder movement can result in irritation of these tendons and cause biceps tendinitis or bicipetal tendinitis. This condition might accompany rotator cuff tendinitis.
8. Medial epicondylitis
Also known as golfer’s or baseball elbow, medial epicondylitis is caused due to inflammation of the tendons that bend the wrist towards the palm. In this, the patient experiences pain from the elbow to the wrist on the palm-side of the forearm.
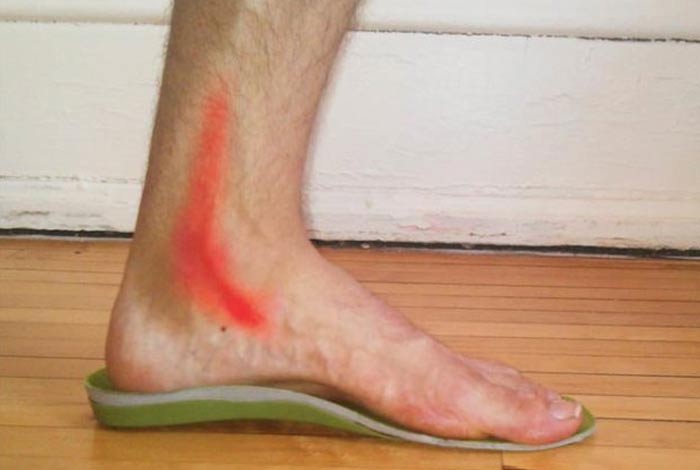
9. Posterior Tibial Tendinitis
When the posterior tibial tendon becomes torn or inflamed, the tendon is unable to provide support and stability to the arch of the foot, resulting in flatfoot. This condition is called posterior tibial tendinitis. It can occur when an acute injury like a fall tears the tendon or causes inflammation. Repetitive use in high-impact sports like tennis, basketball or soccer often causes tears in the tendons, resulting in tendinitis. Once there is inflammation or tearing in the tendons, the arch of the foot slowly collapses with time.
It is commonly observed in women and in people belonging to the age group of 40 years and above. Risk factors include diabetes, hypertension and obesity.
10. Peroneal Tendinitis
This is a common form of ankle tendinitis in which micro-tears are observed in the peroneal tendon, resulting in gait alterations due to pain and swelling in ankle and foot. It often results from ankle sprains and overuse or tightness of the calf muscles.
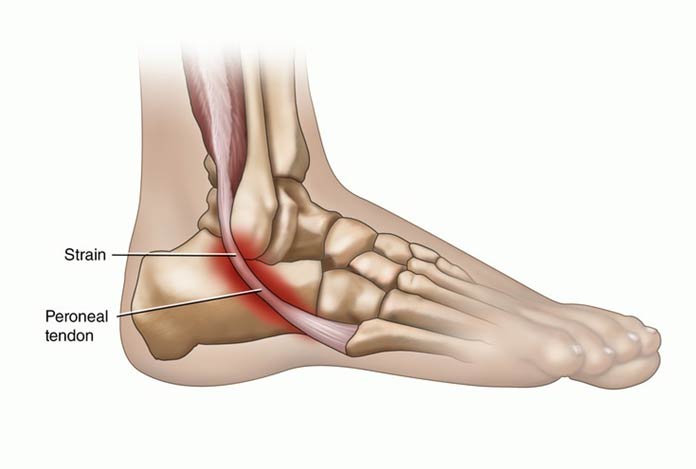 Symptoms of Tendinitis
Symptoms of Tendinitis
Following symptoms are observed in tendinitis:
- Pain in the tendon on movement
- Swelling due to fluid accumulation and inflammation
- Tenderness
- Loss of motion in the shoulder, referred to as ‘adhesive capsulitis’ or frozen shoulder
Risk Factors of Tendinitis
Risk factors for developing tendinitis include age, working in particular jobs or participating in certain sports.
1. Age
With age, tendons lose their flexibility and therefore, their susceptibility to injury increases.
2. Occupation
Tendinitis is commonly seen in people whose jobs require
- Repetitive motions
- Difficult positions
- Frequent overhead reaching
- Forceful exertion of the tendons and the muscles.
3. Sports
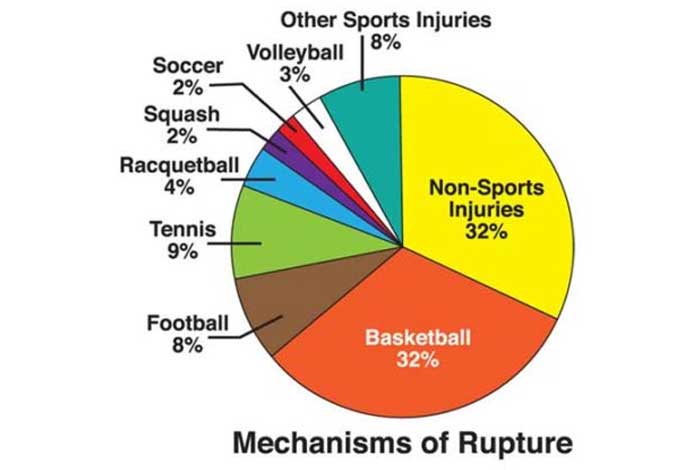
Participating in certain sports activities can increase the chances of developing tendinitis, especially if it involves having repetitive motions. Such a situation might arise in the following games:
- Baseball
- Basketball
- Bowling
- Golf
- Running
- Swimming
- Tennis
Do I Have Tendinitis?
There are a number of areas of the body that are red flagged for developing tendinitis, like base of thumb, hip, knee, elbow, shoulder and heel. If on waking up in the morning you feel that an isolated part of your body is feeling extremely stiff, there is a high chance you have tendinitis. If you observe that you are having a hard time moving a specific joint or experience weakness in a particular area, along with redness, heat and swelling and you find quite a visible lump in the affected area, there is a a high probability that you might have tendinitis. If you observe any of these symptoms, do not panic. Follow R.I.C.E. therapy (rest, ice, compression and elevation) for immediate relief. Consult a doctor as soon as possible. There is also a possibility these might be a sign of bursitis or any other soft tissue injury. In order to get a proper diagnosis, visit a doctor soon.
Causes and Prevention of Tendinitis
Causes of Tendinitis
Overexertion, repetitive movements, strain, injury and sudden or unaccustomed movements often result in tendinitis. However, it can also be caused due to the following reasons:
- Improper posture or walking habits
- Stress on soft tissues from an abnormal or poorly positioned joint or bone (such as leg length differences or joint deformities)
- Arthritis and related conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout
- Metabolic conditions like diabetes
- Side effects from certain medicines like ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin and levofloxacin
As the pain is often experienced near the joints, these conditions are commonly misdiagnosed for arthritis. Middle aged people and seniors are more susceptible to tendinitis than people belonging to younger age groups as their tendons have low flexibility and already have sustained a large number of microscopic tears as a part of normal wear and tear process throughout their lifetime.
Those people who have gout, uric acid crystals get deposited in the inner layer of the tendons which can cause friction and the consequent tearing. People with high cholesterol and triglyceride levels are also at a risk of developing tendinitis. They cause low levels of inflammation in the tendons and damage in its structure. [4]
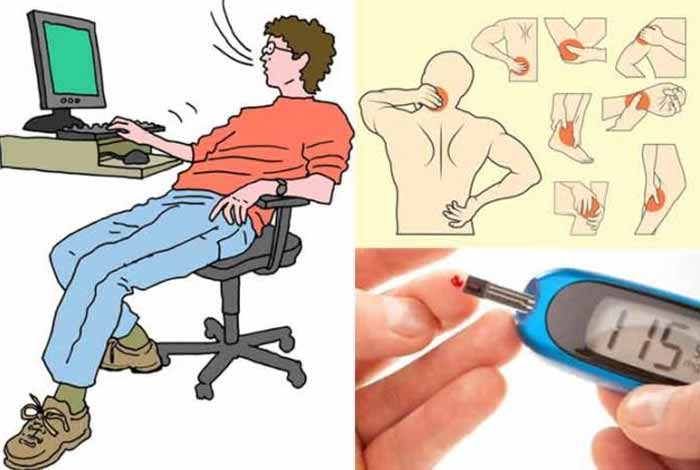
Prevention
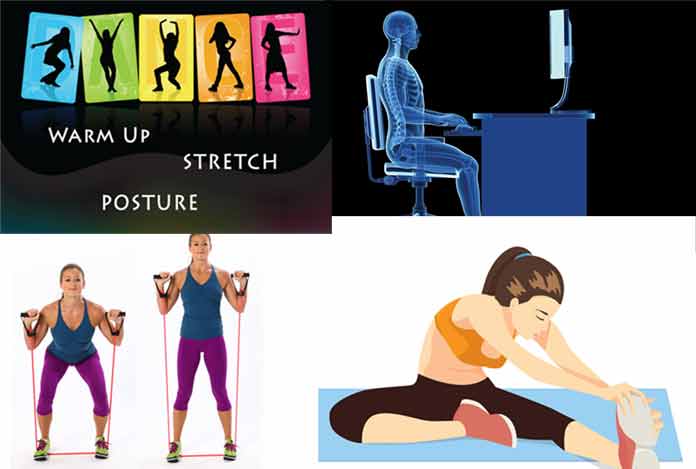
By following some of the steps mentioned below, tendinitis can be prevented. These are:
Ease up: Avoiding activities that cause excessive and prolonged stress on the tendons can help in preventing tendinitis. If pain is observed during exercise, discontinue it and allow it to rest.
Mix it up: If a particular exercise routine is causing persistent pain, it should be discontinued and the tendons should be allowed to rest. Change in exercise regimen can also be beneficial. Cross-training can also be done in which an impact-loading exercise can be coupled with a lower impact exercise.
Improve your technique: If any technique being followed while exercising or performing an activity is flawed, such that it is causing a pain in the muscles or tendons, it should be changed for a more comfortable one. If possible, professional training should be taken before starting any new exercise regime or sports activity.
Stretch: Maximize the range of motion of the joints by stretching after exercise. This will help in minimizing the repetitive trauma that is being faced by the tight tissues. Stretching provides the maximum benefit if it is done after the exercise, when the muscles are all warmed up.
Use proper workplace ergonomics: Excessive stress on the joints and tendons can be prevented by following a proper work ergonomics, in which the chair, desktop and keyboard are all at the optimum height as per the person’s height, arm length and the tasks performed by him.
Prepare your muscles to play: By strengthening the muscles that are more commonly employed in a sport or activity, its ability to withstand stress and load can be increased tremendously.
Diagnosis and Tests of Tendinitis
Following steps are followed in order to diagnose tendinitis
1. Physical Examination and Medical History
In order to make accurate diagnosis, a complete medical history is taken along with a thorough physical examination. The patient is asked to describe his/ her pain and the circumstances in which the pain is experienced. Important diagnostic clues include location and onset of pain, factors that relieve pain and aggravate pain and how the severity varies throughout the day.
2. Selective Tissue Tension Test
Therapists and physicians often prescribe manual selective tissue tension tests in order to identify the tendon that is involved. They palpate specific areas of the tendon in order to isolate the exact area of inflammation or irritation.
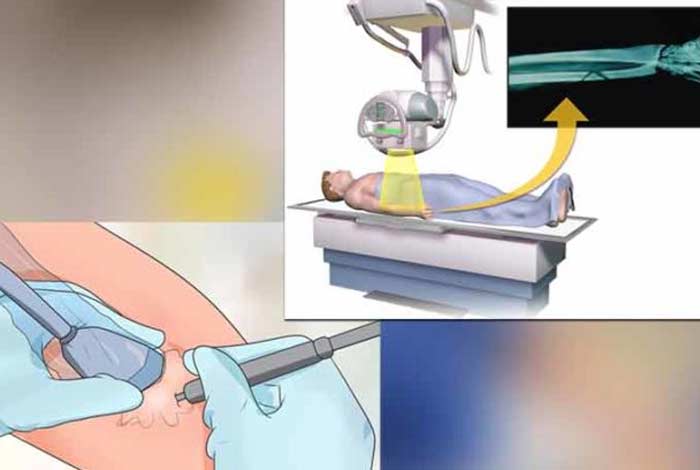
3. X-Ray Scan
X-ray imaging is not very helpful in diagnosing tendinitis as they cannot show tendons on the image obtained. However, they can be used to rule out bone diseases and arthritis that might be thought to cause pain. If there is a tear in the tendon, it can be observed with the help of an X-ray scan. If there is a knee injury, the X-ray scan can show that in quadriceps tendon tear, the patella is seen lower than normal and in patellar tendon tear, the patella is observed higher than normal.
4. MRI
In order to diagnose a partial or total tear, MRI might be suggested by the physician. MRIs can help in detecting any abnormality in the bone as well as in soft tissues like tendons and its coverings.
5. Anesthetic-Injected Test
This is another test that is used for diagnosing tendinitis. Lidocaine hydroxide, a local anesthetic, is injected in the affected area and if a relief in pain is observed, tendinitis is confirmed.
6. Fluid Test
If fluid is observed in the affected area, it is drained and tested for infection.
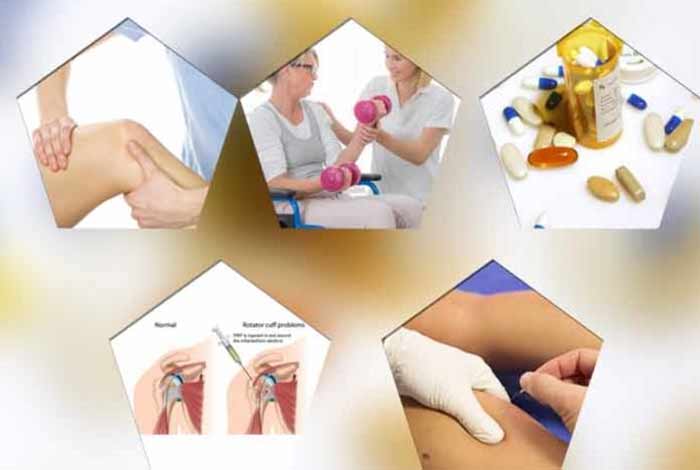
Treatment and Care for Tendinitis
With proper rest, tendinitis can resolve on its own. However, the doctor might prescribe a few medicines to preserve mobility of the tendons for preventing recurrence and disability and to reduce pain and inflammation. If the patient requires specialized treatment, he might be referred to a physiotherapist, an orthopedic surgeon or a rheumatologist. If the condition gets appropriate treatment, the chances of permanent joint damage or disability is minimized.
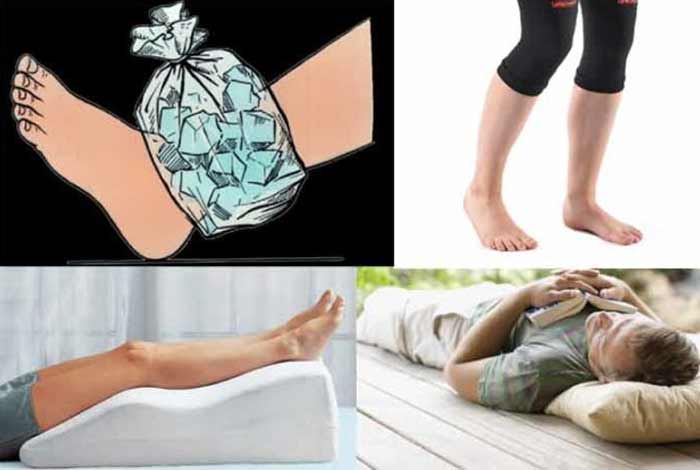
R.I.C.E. therapy is the most commonly prescribed treatment for managing tendinitis. R.I.C.E. stands for rest, ice, compression and elevation. This involves the following steps:
1. Rest
If an injury occurs, it is important to rest the affected area and avoid physical activities that might cause a strain on the tender tendon for the next 24-48 hours. After an injury to the ankle or foot, it is important to lie down in a position that is comfortable in order to reduce pain and swelling.
2. Ice
By applying ice to the affected area, pain and inflammation can be reduced. It is advised to apply ice for nearly 20 minutes after every 4 hours. Ice should not be applied directly to the skin. Rather, it should be crushed and wrapped in a damp cloth or alternatively, ice packs should be used.
3. Compress
Using an elastic medical bandage, the area can be compressed to reduce swelling and stop any internal bleeding. It should not be too tight so that it cuts off the blood circulation and causes more swelling. If the color changes in the bandaged area or there is a feeling of pins and needles, it indicates that the bandage is too tight.
4. Elevate
Using a pillow, the injured area should be increased the heart level for as long as the person can sustain, in order to decrease swelling and bleeding.
If the person experiences severe pain and immobility, he should visit a doctor as soon as possible and get himself properly checked.
Some of the other commonly available treatment options include
Hot Therapy
After 48 hours of the injury, if the pain is chronic, dry or moist heat therapy can be applied, in the form of hot bath or hot water bottles.
Medicines
A number of medicines can be prescribed for managing the pain and inflammation. Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAIDs) drugs are the drugs that help in relieving pain and inflammation. Some of the drugs that can be given are ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, diclofenac and ketoprofen.
Corticosteroids injections
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal gland that have anti-inflammatory action. Corticosteroids that drugs that mimic the action of cortisol in the body and help in reducing inflammation. These drugs are given only when the patient is not responding to NSAIDs because they have some serious side effects. Regular use of corticosteroid in case of chronic tendinitis can result in tendon tear and rupture.
Physical therapy
In a physical therapy, physiotherapists apply ultrasound, water therapy, laser, hot/cold treatments and soft tissue or joint mobilization. These professionals can design a personalized exercise program, analyze the posture and walking and educate the people about tendinitis.
Occupational therapy
A professional occupational therapist can help the patients by recommending the modifications which he can do in his work habits and daily life in order to prevent re-injury. He can also suggest some assistance devices that can help in making life more easier and pain free for these patients.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
It is a treatment which involves taking a sample of a patient’s blood and spinning it to separate platelets and other healing factors from blood. These healing substances are injected locally at the affected area of chronic tendon inflammation.
It is a rather new therapy which is showing great results in treating chronic tendon conditions.
Topical application of glyceryl trinitarian and nitric oxide
By applying glyceryl trinitarian and nitric oxide over the affected area, a relief in pain can be observed. This is because these drugs increase the blood flow to the affected area by dilating the blood vessels, which aids in fast healing. It is a rather new approach and not much data is available for the physicians.
Ultrasonic Shock Treatment
In case of calcified tendinitis, in which calcium builds up in tendons, ultrasonic waves can be used for breaking these deposits and alleviating pain.
Surgical and other procedures
If the symptoms do not resolve on their own, surgery might be suggested. Some of the procedures that can be performed are as follows:
- Dry needling: In this procedure, small holes are made into the tendon with the help of a fine needle in order to stimulate tendon healing factors.
- Ultrasonic treatment: It is a minimally invasive procedure that employs a small cut to introduce a special device into the affected area in order to remove tendon scar tissue with the help of ultrasonic sound waves.
- Surgery: If a massive damage has been done to the tendons and it has torn away from the bone, surgery might be prescribed to correct this situation.
Tendinitis Care
After sustaining an injury to the tendons, R.I.C.E. therapy should be applied as soon as possible. The patient should give proper rest to the tendons in order to allow it to heal. Anti-inflammatory drugs can help in reducing inflammation and pain. The patients can do range of motion exercises in which they are required to move their joints though its full range of motion and back. It can also be performed while the person is giving rest to his tendons. With time, when pain starts to decrease, other exercises can be added to the regimen to strengthen the muscles around the joint. Normal as well as strenuous activities should be resumed gradually over time. Patients are advised to stay away from tobacco smoking as it can delay the healing process.
In most of the cases, tendinitis results from overuse and therefore the best way to prevent it from recurring is to avoid and modify activities that can result in tendon injury.
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods Available for Managing Tendinitis
There are a number of medicines available over the counter for managing the pain and inflammation experienced in tendinitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) drugs help in relieving pain and inflammation and are easily available. Some of the drugs that can be given are ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, diclofenac and aspirin. Different OTC pain relieving topical gels and ointments are also available that can be applied on the affected area for relief.
Self-Management Methods for Managing Tendinitis
Self-management refers to playing a proactive role in treatment of a condition. The ways in which a person can contribute to the healing process of tendon inflammation and irritation is by giving the tendon rest and modifying the activities that cause irritation. The person can also seek help from a doctor and an occupational therapist who can help him by giving suggestions on how to modify your life to modify daily activity. They can also suggest some range of motion exercises in order to improve flexibility and decrease stiffness.
Natural Ways to Cure Tendinitis
The treatment of an inflamed and irritated tendon can be accelerated by making some changes in the diet. These
All types of vegetables, especially green leafy kinds
Vegetables are rich in antioxidants which help in fighting against the oxidative stress put on the body. When the body has some kind of inflammation like in tendinitis, the amount of free radicals escalates. Therefore, it is advised to load up your plate with cooked or raw vegetables like kale, spinach, broccoli and others. Leafy and cruciferous vegetables are extremely helpful in speeding the healijng process because they are rich in antioxidants as well as important minerals and vitamins like vitamin C and K.
High-quality proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of our body and are also involved in repairing the wear and tear that occur in the body. The thumb rule here to avoid protein deficiency is to get at least 4 to 5 ounces of good quality protein with each meal. Lean meat that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, cage free eggs, raw dairy and grass fed beef make some of the best choices for protein. Also these foods are packed with the goodness of zinc, whose work is to aid tissue development and repair.
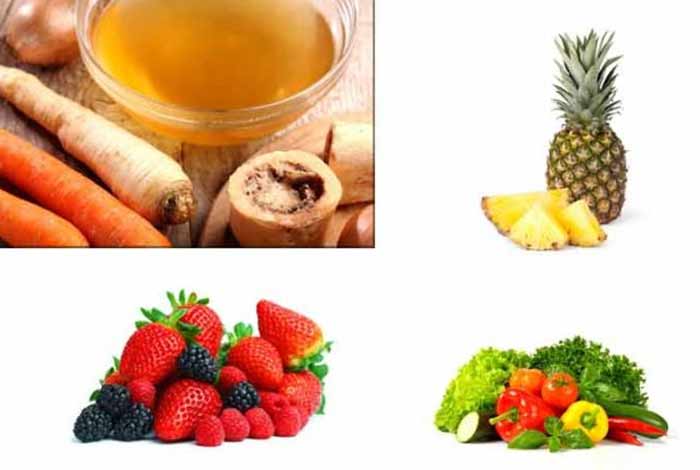
Berries
Berries are loaded with vitamin C that plays an important role in rebuilding collagen, which is an essential component of tendons. Antioxidants are also found abundantly in the berries that can help in fighting against the free radicals that might cause damage to the tissue.
Pineapples
Bromelain is a compound that is abundantly found in pineapples, which help in treating swelling and injuries.
High-potassium and magnesium foods
Foods that are rich in potassium like coconut, avocados and bananas can help in speeding up healing. Magnesium is another micro-nutrient that is commonly found in these foods that is helpful in muscle recovery and improving blood circulation.
Bone broth
Collagen is abundantly found in bone broth that is very effective in healing tendons. It can also be used in case of sprains, ligament injuries and strains.
Health Tip by Experts
Tendinitis can slow down the pace of your life for a while, but it is important to allow your tendons to get proper rest and heal. This brief pause will help you to sprint back to life and chase big goals.