Saliva is a liquid that is secreted from the salivary glands located in and our throat and mouth. It helps in lubricating the food we eat so that it becomes easy to swallow. There are three salivary glands, namely parotid, sub mandibular and sub lingual, with parotid being the largest. There are two parotid glands which are present on both sides of the mouth and in front of both ears.
These salivary glands, especially parotid gland, can become infected with by a virus, known as Rubalovirus, that can result in their inflammation and swelling. This condition in which the salivary gland, especially parotid gland, becomes inflamed and swollen is called mumps or parotitis and is extremely contagious in nature.
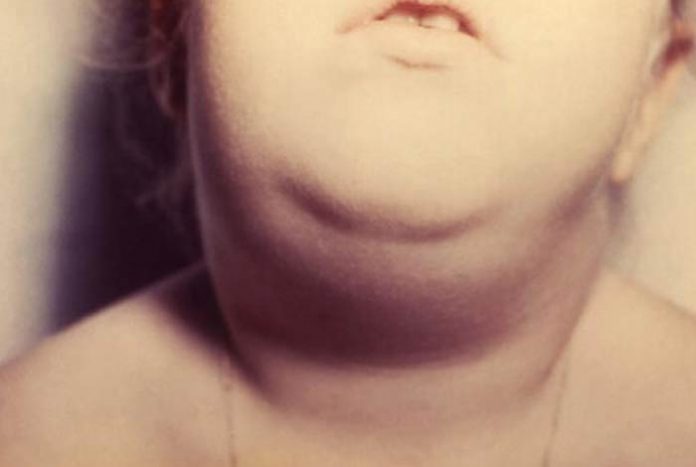
The patient’s jaw becomes swollen and cheeks turn puffy, which gives his or her face a hamster -like appearance. Some people affected by the virus can develop severe symptoms while others can be asymptomatic. The virus causing mumps can cause inflammation in other organs as well and result in serious health issues like meningitis and orchitis (inflammation of testicles).
This disease spreads through the air when a contagious person coughs or sneezes and droplets containing the virus are released in the atmosphere. After being exposed to the virus, the symptoms do not develop immediately. It takes around 16-18 days to 2-4 weeks for the disease to show its symptoms. This period is called incubation period during which the virus takes shelter in the salivary gland and other organs and multiplies. The person becomes contagious 7 days before the salivary gland starts showing symptoms of mumps. Even people who do not develop any symptoms are contagious and might spread the disease to other healthy people unknowingly.
Children in the age group of 5 to 9 years are mostly affected by the disease. However, unvaccinated adults can catch the disease as well.
Symptoms of Mumps
An exposure to mumps virus might result in development of pronounced symptoms in some people and mild in others. After 2-3 weeks of exposure, some of the symptoms that can be commonly seen in patients include:
- Swollen and painful salivary glands on one or both sides of face (parotitis)
- Headache
- Fever (initially mild but can even be as high as 103o Fahrenheit)
- Reduced appetite
- Fatigue, along with joint and muscular pain
- Inability to chew or swallow something and pain.
Puffy cheeks due to swollen salivary glands are the best symptom of mumps. Read symptoms and more…
Treatment
Treatment for mumps is directed at managing the symptoms of mumps as there are no drugs available to cure the disease.
The body fights the disease by producing certain proteins called antibodies specific to the virus that kills it. As mumps is a viral infection, therefore, antibiotics are ineffective. The patient is advised to take proper rest and drink a lot of fluids to speed up the recovery process. The disease gets resolved in 1-2 weeks on its own.
Some of the steps that the patients can take to speed up the recovery process are:
- Taking proper rest
- Drinking enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Caressing swollen area with cool or warm compress.
- Taking painkillers to get relief from the pain
- Eating food that does not require a lot of chewing
Patients can, however, take some analgesics that are available over the counter for managing their pain.
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
These medicines help in relieving pain by inhibiting the synthesis and release of a chemical called prostaglandins which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation. Cyclooxygenase enzyme (COX) is an enzyme which produces prostaglandins. NSAIDs are the drugs that stop the production of prostaglandins by blocking COX enzymes. In this way, the pain, as well as the inflammation, is managed.
Available as: Oral preparations
I. Acetaminophen
US-FDA Status: Approved
Availability: Over-the-counter
Generic name: acetaminophen
Brand name: Tylenol tablet
Side-effects: Bloody or cloudy urine, black or tarry stools, hives, skin rash, sore fatigue
Indicated in pregnancy: Only if absolutely indicated
Alcohol content: Absent
II. Ibuprofen
US-FDA Status: Approved for abdominal migraine
Availability: Over-the-counter
Generic name: ibuprofen
Brand name: Motrin IB tablet
Side-effects: Bloating, belching, acidity, cloudy urine, diarrhea, heartburn, decreased amount of urine
Indicated in pregnancy: Absolutely contraindicated in third trimester as it may affect the fetal cardiovascular system
Alcohol content: Absent
Vaccine Against Mumps
Although no drugs are available for treating mumps, the disease can be prevented by getting an MMR vaccine, which stands for measles, mumps and rubella. The vaccine is extremely safe and effective at preventing the diseases.
However, after getting an MMR vaccine shot, people can develop the following side effects:
- Sore arm from the shot
- Fever
- Mild rash
- Temporary pain and stiffness in joints, especially in teenagers and adult women who were not immunized earlier
Some people have misconceptions about vaccines and do not want their children to get them. Well, getting vaccinated is much safer than getting mumps, measles or rubella. People should be encouraged to get themselves and their kids vaccinated.
MMR Vaccine Dose
Two doses of MMR vaccine are given to children usually in the following age groups:
- First dose: 12 to 15 months of age
- Second Dose: $ to 6 years of age
Those infants who have to travel out of the country when they are between 6 to 11 months old, their parents are advised to get their babies a dose of MMR vaccine before traveling to provide temporary immunity. The child should still get the two doses of MMR vaccine for complete protection that lasts for a long time.
MMR vaccines are needed by adults as well. Many of the adults might be susceptible to the disease without even realizing it. If there is an outbreak of mumps, a third dose of the vaccine might also be required for immunity.
People Who Should Not Get MMR Vaccine
Those people who have the following conditions should not get an MMR vaccine:
- Severe-life threatening allergies
- Pregnancy
- Weak immune system
- Tuberculosis
OTC Medication for Treating Mumps
Following are some of the over-the-counter medicines available in different countries across the globe for managing pain in mumps:
| Name of the Country | OTC Drug(s) Available |
| Argentina | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Australia | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Austria | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Canada | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| China | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Croatia | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Czech Republic | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Denmark | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| France | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Germany | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Greece | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Hungary | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| India | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Ireland | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Italy | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Japan | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Mexico | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Philippines | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Russia | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Singapore | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| South Africa | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| South Korea | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Spain | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| Switzerland | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| The Netherlands | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| UK | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |
| USA | Acetaminophen (oral) Ibuprofen (oral) |

