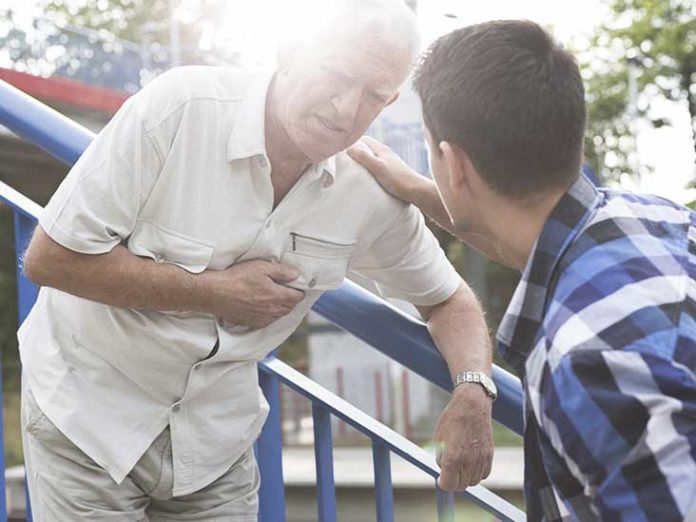

Overview and Facts
Strokes are brain attacks caused by blocking of blood vessels or due to internal bleeding in the brain. Common signs of a stroke include unexpected and severe headaches, weakness, confusion, numbness, problem in walking or talking, and dizziness.
When a stroke occurs, the amount of oxygen and nutrients supplied to brain reduces , which results in the death of brain cells. It is a serious medical condition and requires immediate medical help.
It is one of the leading causes of deaths in the United States (currently coming at the 5th spot). About 800,000 people are hit by stroke every year, which equates to about one person getting hit every 40 seconds. There are about 7 million people in United States that survived a stroke. However, strokes cause about 137,000 deaths every year.
The death rate of women due to strokes is higher as compared to men.
Around 60% of women who suffer an attack of stroke don’t survive, while in men the fatality rate is only 40%.
Types and Symptoms of Stroke
Types of Stroke:
Strokes are broadly classified into following two kinds:
-
Ischemic Stroke
It is the most common kind of stroke which happens due to blocking of arteries, caused by the deposition of a fatty substance known as plaque in them. This is known as atherosclerosis and causes blood clotting.
There are two types of Ischemic stroke, i.e.
-
-
Thrombotic strokes which are caused when an artery that carries blood to the brain is blocked by a blood clot.
-
Embolic strokes which are a result of a blood clot formed at some other part of body and carried via blood vessels to brain, barricading the flow of blood to the brain.
Moreover, there is another ischemic stroke called TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) or a ‘mini-stroke’ which involves temporary blockage of blood flow.
-
-
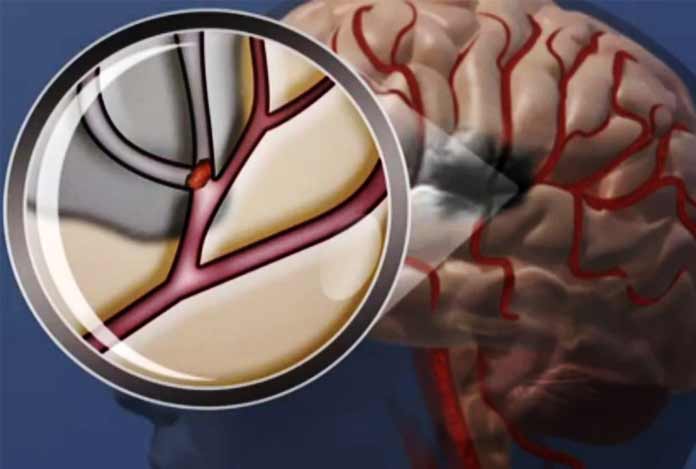
Hemorrhagic Stroke
A stroke caused by bleeding inside brain which causes brain cell damage is referred to as hemorrhagic stroke. They are classified on the basis of the bleeding location, i.e.
-
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage which is caused when the bleeding is in the area between the skull and the brain.
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage when the bleeding is right inside the brain.
-
Symptoms of Stroke:
Symptoms of a Stroke include:
-
Sudden weakness in one side of arm, leg, or face.
-
Short term loss of sensation, strength, vision, coordination, and speech and its understanding, which worsens over time.
-
Vision reduction, majorly in one eye.
-
Loss of body balance, later followed by hiccups, vomiting, nausea, fever or problem with swallowing.
-
Heavy headache followed by loss of consciousness.
Risk Factors of Stroke
There are certain health conditions that might increase the risk of a stroke attack. Some of the health conditions responsible for strokes are:
-
High-Blood Pressure
-
High Blood Cholesterol
-
Carotid or Peripheral Artery Disease
-
Heart Diseases
-
Sickle Cell Diseases
-
Obesity
Moreover, there are various other risk factors that can cause a stroke attack. These include:
-
Age: Stroke risks increase after an age of 55 years and the risk is highest at an age of 65.
-
Gender: Women are likely to have more stroke attacks as compared to men.
-
Genetic Factor: If someone in the family has a history of stroke attack then there are chances that the problem is inherited.
-
Various other factors such as smoking, alcohol or drug abuse and an improper diet can also lead to stroke attacks.
Do I Have Stroke?
You can’t detect a stroke attack before it happens. It happens suddenly and can inflict a lot of damage.
Causes and Prevention of Stroke
Causes of Stroke:
There are various factors that can lead to a stroke attack such as age, genetic factor, or issues with one’s diet. Some habits such as abuse of alcohol or drugs and smoking can also be possible causes of strokes. Having existing health conditions such as heart problems, diabetes, high levels of blood pressure or cholesterol, etc. might also lead to a stroke at some point of time.
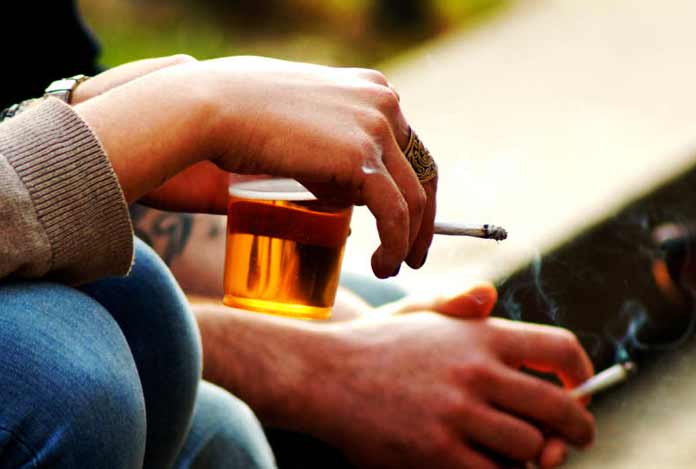

Prevention of Stroke:
Unfortunately, there is no early way to prevent a stroke attack as it happens very suddenly. However, it can indirectly be prevented by getting rid of bad habits such as smoking and drugs, or by treatment of the health conditions that might be responsible for causing it.

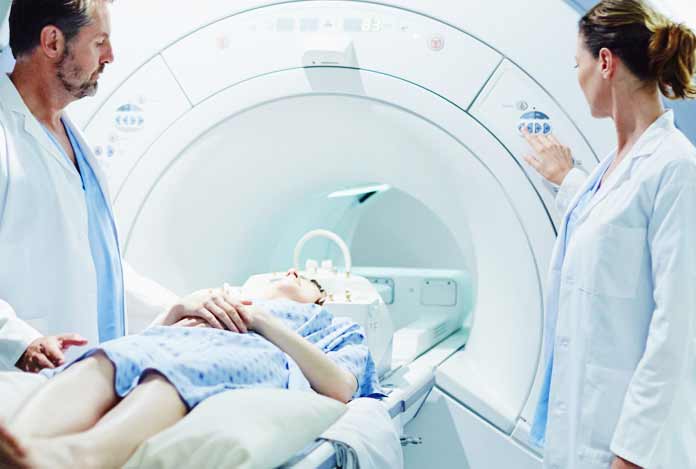
Diagnosis and Tests of Stroke
Diagnosis of a stroke is required for the correct treatment. It helps in the identification of the type of stroke and to find out the bleeding point in the brain. Stroke diagnosis is generally done by a CT scan which follows the study of several X-rays to identify the location of bleeding inside brain. Also, an MRI scan can be performed to diagnose a stroke.
Moreover, various other tests are performed for determining the treatment of stroke or identify some other health conditions. Some of the tests are listed below:
-
ECG or Electrocardiogram which is used to identify any heart problem.
-
Blood tests such as CBC, blood sugar, prothrombin time and INR, etc.
Also, some other tests such as Magnetic Resonance Angiogram (MRA), CT angiogram, carotid angiogram, etc. can be conducted later.
But what to do in case of an emergency stroke? To diagnose an emergency stroke FAST test can be effective, where:
F stands for Face: Check for sagging on the sides of the face.
A stands for Arms: Raise both arms and check whether one of them falls.
S stands for Speech: Try speaking and check whether it sounds slurry or weird.
T stands for Time: Note the initiation time of the problem and call for help.
Treatment and Care of Stroke
There are various methods for the treatment of a stroke and some of these methods are dependent on the type of the stroke. These are:
Thrombolysis for Ischemic Stroke
The most effective and widely used method for the treatment of stroke is thrombolysis. It is also known as thrombolytic therapy and involves the dissolution of blood clots inside the vessels to improve the flow of blood. This prevents damage to the organs and tissues.
Thrombolysis is performed by injecting the clot-busting drugs with the help of a long catheter or intravenous (IV) line. The long catheter is used to directly target the clot location and bust it right there. The catheter is linked with a mechanical device that can function to physically break the clot.
It is effective for the treatment of ischemic strokes. The drug generally used for the treatment is tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), but it needs to be used within 4.5 hours of the stroke attack. Aspirin can also be used for treatment.
In case of Hemorrhagic Stroke
First of all, the treatment of hemorrhagic stroke requires controlling the bleeding inside the brain, which is the main cause of the stroke. One of the major reasons behind this stroke is high blood pressure. Thus, medication is necessary to control high blood pressure and pressure inside brain. This helps in preventing seizures and blood vessels constriction.
Moreover, in case the patient consumes blood thinners or antiplatelet medications such as clopidogrel or warfarin, the patient needs to take drugs that oppose the effect of this kind of medication in order to recover from blood loss.
If the reason behind stroke is aneurysm, surgical methods such as clamping its base or filling it with the help of detachable coils can be used to control the flow of blood.
Sometimes, hemorrhage strokes are caused because of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) i.e. small twisted connection between veins and arteries. If AVM’s are the reason behind stroke, they can be removed by surgical methods for stroke treatment.

OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods for Stroke
OTC Medications for Stroke:
There is no over-the-counter (OTC) medication available for treatment of strokes. Moreover, the medication for treatment of a stroke should only be consumed when recommended by a healthcare expert. Stroke attacks are sudden and intake of any kind of OTC medication isn’t advised as they might worsen the condition.
Instantly asking for help of a medical professional is advised in case there is any symptom of a stroke. FAST diagnosis can help in self-diagnosing the condition and medical help can be requested for instant treatment.
Self-Management of Stroke:
Stroke attacks are unexpected and highly affect the lifestyle of a person even after treatment. Various self-management methods for rehabilitation are required after a stroke attack. Self-management helps in recovery from the side effects of the problem and bring life back to a normal pace.
A person may have to go through physical, occupational and speech therapy which helps in getting back into normal life. If a person who suffered a stroke attack follows the therapy process they can get back on their feet and can go back to their daily routine of life.
Moreover, attending support group sessions and communicating with the people who have been through the same can psychologically help a person in getting over the trauma of a stroke.

Health Tip by Expert
Strokes can be extremely harmful to life. It is advised to instantly ask for help from a nearby hospital in case you observe any symptom of stroke in someone near you. If you observe any kind of symptom in yourself, you must ask someone near you to call a doctor.
Quick diagnosis by FAST is advised to know about the attack as soon as possible. In case of minor stroke or TIA, instant intake of aspirin is advised.






