Astaxanthin Sources, Benefits, Side Effects & FAQs

Astaxanthin is a red colored lipid-soluble pigment that belongs to carotenoid group. It is a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment that produces red/pink coloration in salmon, trout, lobster, shrimp and other kinds of seafood. Astaxanthin is also called the king of carotenoids and is regarded as one of the most potent naturally occurring antioxidants. Its coloration is caused by conjugated bonds i.e. alternate single and double bonds, in its internal atomic structure.
For its nutrition elements, astaxanthin has industrial application in supplement production. As an antioxidant element, it too supports the immune system in human body. it is also considered as an excellent anti-aging supplement which helps our bodies stay stronger and healthier during the aging process.
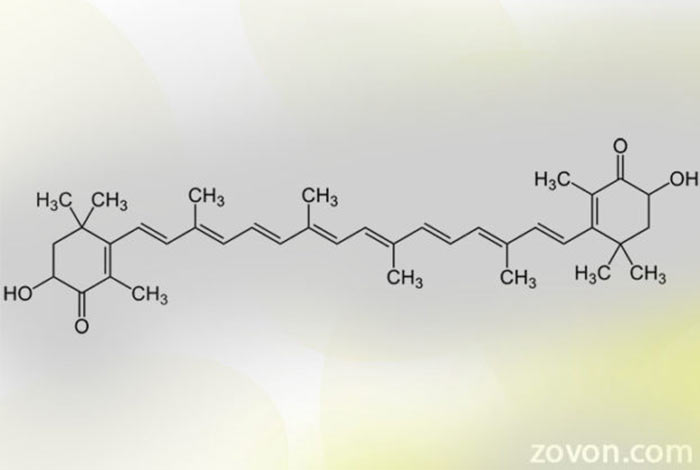
Structure and composition of astaxanthin:
Molecular formula of Astaxanthin is C40H52O4. The important fact about astaxanthin is that it doesn’t get converted into Vitamin A the way other carotenoids do. It only gets absorbed orally as it is soluble in lipids only. It has both natural and synthetic sources. It is a large organic molecule with great antioxidant properties. Astaxanthin is comprised of both alcohol and ketone group and is a derivative from zeaxanthin (alcohol source) and canthaxanthin (ketone source).
Sources of Astaxanthin:
Astaxanthin is one of the most powerful carotenoids and occurs both naturally and synthetically. It is found widely throughout nature as well as it could be synthesized. But, there’s a difference in the functioning groups between the two sources.
Natural sources of Astaxanthin:
- Proteins are the best source of astaxanthin, especially found in seafood. Animal proteins include salmon, red trout, red seabream, Pacific and Antarctic krill, lobster, shrimp, crawfish, crabs, crustacea etc.
- Microalgae, yeast are the green sources of astaxanthin.
- Algae (Haematococcus Pluvialis) is the primary source of astaxanthin in this whole aquatic life cycle. This algae is cultivated at an industrial scale for production of astaxanthin supplement. This algae has two phases in its life cycle one is vegetative phase that is a green phase and the other is resting phase. During this resting phase, it turns red and this is the time when astaxanthin is isolated from it.

Synthetic sources of Astaxanthin:
- It is synthesized from isophorone and hugely used for industrial production. Methanol, ethanol, their mixture and ketone are the organic elements used in the preparation of chemical astaxanthin.
- This is used to produce supplements which have a market price of $200 million approx. (as per June 2012) per year.
Benefits/Uses/Application of Astaxanthin:
Astaxanthin helps in pain relief and inflammation:
- It works for muscle pain and inflammation. It is capable to remove blood barrier in blood vessels which helps in pain relief.
Astaxanthin fights against fatigue:
- It can recover muscle and enhance strength which improves energy level. It is effective against jet lag. It boosts the fatty acids of the body that helps in endurance and prevents muscle and skeletal damage.
Astaxanthin cleans cells:
- It consists of lipophilic and hydrophilic properties that are effective as a filter. Astaxanthin filters every cell of the body.
Astaxanthin protects eye care system:
- It cleanses the retina cells and makes vision clearer.
Astaxanthin works as anti-aging agent and benefits skin:
- As an antioxidant, it supports the collagen formation and helps in peeling off the old skin. It nourishes skin cells and balances the moisture level and smoothness. It cures lines, wrinkles, spots and brightens dull skin. Astaxanthin protects skin cells from UV ray damage.
Astaxanthin is beneficial for energy increasing:
- Athletes used Astaxanthin supplements to increase energy level. Exercise is a routine process for athletes but at the same time, exercise produces free radicals. The greater the body’s ability to neutralize free radicals, the fastest an athlete can recover after a work-out session or practice. Astaxanthin supplements neutralize the free-radicals and restore the energy condition faster.
Astaxanthin prevents Heart diseases and cancer:
- Like all the antioxidants, astaxanthin also protects the heart and other organs from radical disorder as well as cancer.
Astaxanthin works for male-fertility:
- Some researches prove that it is beneficial for male-fertility. In a small-scale study, it has proved that astaxanthin improves sperm count and motility.
Astaxanthin improves digestion:
- Regular intake of astaxanthin improves reflux system and improves the digestion system.
- Astaxanthin is also beneficial against high cholesterol. It lowers the cholesterol limit in blood.
- It is preventive for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and effective for stroke recovery.
Side-effects of Astaxanthin:
An appropriate dose of astaxanthin prescribed by an expert could be beneficial. But overdose and very long-term use without expert’s advice could be adverse. There are as such no known side-effects of astaxanthin except some liver infection. A dose of 4 to 40 grams for 12 weeks could be great for health. Supplements are not reported as harmful. Pregnant, breastfeeding women and children need to ask practitioner before taking it. People who are already on some conventional medication are also advised to consult doctors before astaxanthin consumption.
FAQs: What people normally want to know about Astaxanthin?
1. Is astaxanthin good for all?
It is a red colored pigment found in sea animals such as lobster, trout, krill etc. and is completely safe for humans. Since astaxanthin is an antioxidant, it is beneficial for body immune system. But before consumption of astaxanthin supplements, one must consult with the specialists.
2. What does astaxanthin do?
Astaxanthin is beneficial for athletes for faster energy recovery. It also relieves body pain and inflammation. Its other benefits include protection of optic system, immune system and cardiovascular system. It is also helpful in protection against cancers and male infertility.
3. How does astaxanthin work inside the body?
It does get absorbed by the cells and relieves the body. It sacrifices its own structure to neutralize the free radicals and prevent oxidation.
4. What are the health benefits of astaxanthin?
It prevents cancer, heart diseases, works for the male-fertility system, beneficial for digestion system. It supports the body immunity system and also protects eyes. Its supplements are very helpful for fast energy recovery and muscle relief.
5.What foods are high in astaxanthin?
Animal proteins especially seafood are a great source of astaxanthin. Lobster, shrimp, crawfish, krill, trout, seabream, crab, salmon are essential sources of astaxanthin; Pacific and Arctic krill are great resources. It is also found as microalgae which is the primary source of astaxanthin in nature. These sea-animals consume the algae and then the red/pink coloration is formed among them.
6. How will it take to notice Astaxanthin effects?
It works much faster than other carotenoids. Usually, it takes a couple of weeks to observe the benefits. It does not work overnight like a drug but rather bio-accumulates the body. It has the capacity to filter everybody cell. It cleanses the cells and protects the body system.