is stevia really safer and healthier than artificial sweetenersStevia is a plant-based sweetener, which is obtained from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, belonging to the Asteraceae family. It is a unique product that is valued for something it doesn’t do. Here, in this article, we will explore whether it is as good as it is claimed to be.
There is a lot of difference between the store-bought and naturally grown stevia. Grocery bought stevia does not contain the leaves of its plant, but rather contain refined stevia leaf extracts, known as rebaudioside A (Reb-A).
In fact, there are a number of stevia products that contain very little amounts of it. Reb-A is nearly 200 times sweeter than the normal table sugar. Reb-A sweeteners are known as ‘novel sweeteners’ because it is a blend of several sweeteners like erythritol, Reb-A and dextrose.
Some of the stevia brands also contain natural flavors and the U.S. FDA does not object to the use of the term ‘natural flavors’, provided there is no added colors, synthetics or artificial flavors.[1] Still, ingredients that fall under the category of natural flavor can be highly processed.
The U.S. FDA classifies the green stevia differently[2] and the Center for Science in the Public Interest gives it only one out of two ‘safe’ ratings while comparing substitutes.[3]
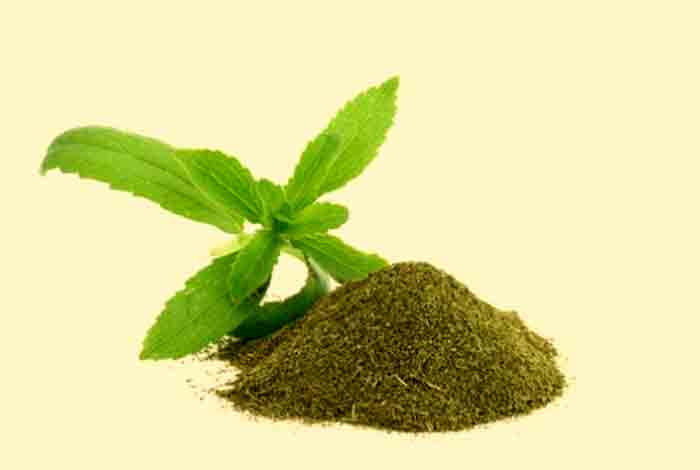
What is Stevia?
It is obtained from the sweet leaves of Stevia rebaudiana plant and the compound responsible for providing sweetness is extracted, dehydrated and purified. The extracted product is 200-300 times sweeter than sugar and has no significant calories.
The packaged version comes in the form of dry powder or liquid. Now, several food manufacturers are also adding stevia in soft drinks, vitamin water, ice creams and yogurts. Manufacturers., these days, are replacing artificial sweeteners with natural sweetener.

Is it Really Safe?
A lot of information is available on the Internet regarding the safety of sugar substitutes. Following are some of the criteria under which, we will discuss the safety of stevia.
1. Natural versus Artificial
Stevia finds itself in the group of sweeteners that is plant based and is not created synthetically in the laboratory. It is one of a few natural sweeteners available commercially. Food products that contain stevia are labeled as ‘no artificial sweeteners.
2. FDA Designation
Stevia is honored by the U.S. FDA too. It is one of the only two sweeteners that have been given the status of Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used as an ingredient.
Apart from stevia, Monk fruit has been given this status. All the other sweeteners like saccharine, sucralose and aspartame come under the category of food additives because they do not meet the specifications laid down by GRAS.
3. International Usage
Stevia has been approved not only by the U.S. FDA but by other organizations dealing with food safety as well, such as Joint Expert European Food Safety Authority and European Food Safety Authority.
Some of the places, where stevia is approved are Asia, Australia, South America, Europe and Japan. What is most astonishing is its approval in Japan, where artificial sweeteners have been banned for nearly 50 years.
4. Health Effects
Low-calorie sweeteners were never so popular, but they have never observed a dip in their popularity as much as they have seen now. They have been held guilty for increasing appetite and leading to conditions like diabetes, obesity, cancer and gut imbalance.
For these reasons, people do not favor low-calorie sweeteners like saccharin, sucralose and aspartame. Stevia, on the other hand, is way better than these low-calorie sweeteners.
a. Cancer
Studies have not indicated that stevia causes cancer or has any role to play in the development of cancer. It is rich in phytochemicals that act as antioxidants.
Conversely, some researchers believe that stevia actually plays a role in preventing cancer. However,[4] there are limited long-term studies on the extracted stevia product being sold in the market.
b. Body Weight
Theoretically, if we replace calories from sugar with a non-caloric sweetener, it would promote weight loss efforts. Although there is some research, which suggests that taking low-calorie sweeteners can increase body weight.
However, studies that are done on stevia do not point towards the same. The satiety, experienced after consuming foods sweetened with sugar, is similar to that experienced after the intake of stevia. No difference in caloric intake was actually observed.
c. Blood Glucose and Insulin Response
Sugar substitutes that do not have calories usually should not affect the blood glucose levels. However, several experts suggest that stevia might have some effect on the insulin level.
On the contrary, some people claim that stevia plays a role in reducing blood glucose level after having a meal and improves insulin response. People with diabetes can also safely take stevia for adding sweetness to their otherwise insipid food.
d. Gut Health
It is a new area of research to determine the effect of low-calorie sweeteners on gut bacteria. They are thought to hold a key to several health issues that arise due to the consumption of low-calorie sweeteners.
This is the area, where there is a lack of ample research. Thus, it is difficult to identify the cause-and-effect in the gut area as it gets affected by so many factors.
As far as stevia is concerned, there is a speculation that maybe it affects gut bacteria. Preliminary studies indicate that there a few factors like person’s existing bacterial count, genetic makeup, diversity, environment and food intake also plays a role.
Conclusion
The biggest concern, at present, is that the effect of consuming low-calorie sweeteners for 50, 60, 70 years is not fully understood. When it comes to consuming stevia, the only thing that can be recommended at the moment is – moderate consumption. We believe that moderate and occasional consumption of it is probably fine. Nevertheless, more research is needed to better understand varied aspects of stevia consumption.