Overview and Statistical Facts of Mumps
When you eat your food, a liquid lubricates the food and enables swallowing. This complex fluid which has a number of functions to perform in the digestion of food is called saliva and is secreted by salivary glands. These are exocrine glands that are located in and around your throat and mouth. There are three salivary glands, parotid, submandibular and sublingual, out of which parotid is the largest.
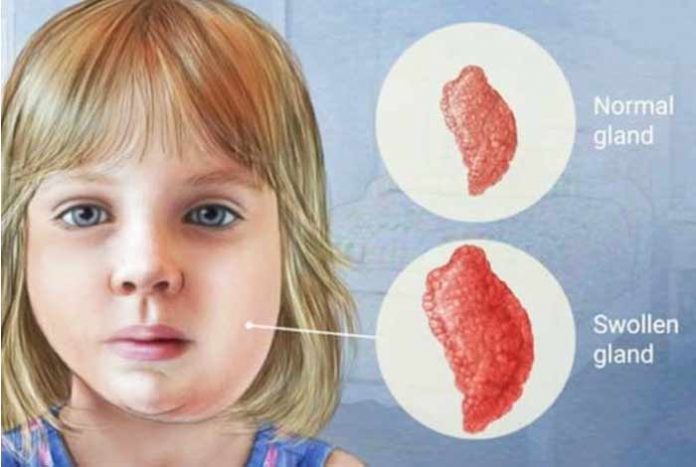
There are two parotid glands, present on both sides of the mouth and in front of both ears. A virus, known as Rubulavirus, is known to affect the salivary glands, particularly parotid gland and cause swelling. This condition is known as mumps or infectious parotitis and is extremely contagious in nature. It results in swollen jaw and puffy cheeks, giving the patient a hamster face appearance. Some people might develop severe symptoms while others can remain asymptomatic. There is also a chance of developing inflammation in other organs as well, which can lead to other diseases like meningitis or orchitis (inflammation of testicles).
Mumps spreads through air when infected person coughs or sneezes or a healthy person comes in contact with his saliva. After an exposure to mumps virus, the symptoms do not appear immediately. There is an incubation period of minimum 16 to 18 days which can extend to 2-4 weeks as well. During this time, the virus multiplies in the body and there are no symptoms. The person who has contracted mumps virus become infectious 7 days before the salivary glands swell to 5 days after the inflammation is reduced.
Asymptomatic people are also contagious and they might spread the virus unknowingly.
The disease generally affects children between the age groups of 5 to 9 years. However, the virus can also affect adults as well in whom the disease is more severe. Some of the complications arising out of mumps are hearing loss, meningitis and orchitis.
During World War I, mumps was one of the leading causes of hospitalization of soldiers. Today, it is considered more of a childhood disease.
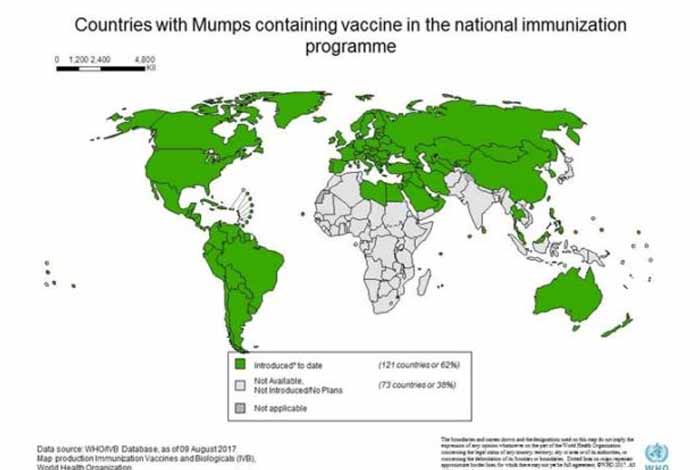
After the immunization programme for mumps was started worldwide, the number of cases has reduced considerably. WHO has put controlling mumps as a topmost priority agenda along with controlling or eliminating measles and rubella.
Types and Symptoms of Mumps
There is only a single type of mumps virus known to mankind that is responsible for causing the disease.
After getting exposed to mumps virus, some people develop mild symptoms while others might have more pronounced symptoms. It usually takes 2-3 weeks for the disease to show symptoms and they include:
- Swollen and painful salivary glands on one or both sides of face (parotitis)
- Headache
- Fever (initially mild but can even be as high as 103o Fahrenheit)
- Reduced appetite
- Fatigue, along with joint and muscular pain
- Inability to chew or swallow something and pain.
The best-known symptom of mumps is swollen salivary gland which makes the cheeks to puff out.
Incubation period:
When a person gets exposed to mumps virus, it enters into the body and starts multiplying within the nose, lymph nodes and throat. The virus also spreads to the brain, liver, thyroid, heart, parotid gland, kidneys, testes or ovaries and heart.
During the initial days of exposure, the patient is not contagious and there are no symptoms of the disease. The symptoms start appearing 16-18 days after the initial contact. This time period between time of contact and appearance of symptoms is called incubation period. It can vary from 12-25 days in mumps patients.
In the initial days of infection, the person is not contagious. However, 3 days before the symptoms start appearing to 9 days after the symptoms subside, the person is highly contagious and can infect other people who come in his close contact.
Complications of Mumps
Serious complications can occur in people with mumps. They are rare in nature and include:
a. Inflammation
Inflammation and swelling is the most commonly observed complication of mumps. Following body parts can get inflamed or swelled up under the influence of mumps virus:
- Testes, causing orchitis
- Pancreas, causing pancreatitis
- Ovaries and breasts, resulting in oophoritis and mastitis respectively
- Brain, causing encephalitis
- Membranes and fluid around brain and spinal cord, leading to meningitis
b. Others
- Hearing Loss
- Miscarriage
Risk Factors of Mumps
Mumps is an infectious disease that can spread through the saliva or mucus of an infected person’s throat, nose and mouth. It can spread while:
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Talking
- Sharing person objects like cups and utensils
- Inanimate objects
Following are the risk factors involved in developing mumps:
- Unvaccinated individuals
- Children between the age groups of 2 to 12 years
- International travel
- Close proximity to the patient or person suspected to have mumps
- Immunodeficient people
- Vaccine failure

Do I Have Mumps?
If you observe swollen salivary glands (parotid gland) along with fever, malaise and loss of appetite, there is a probability you might have mumps. However, it is advised to get a proper diagnosis from a doctor as these symptoms can also be observed in case of tonsillitis or during blockage of salivary ducts.
Avoid going to public places and take plenty of rest if mumps is suspected.

Causes and Prevention of Mumps
Mumps is caused due to an infection by a virus belonging to the family Paramyxovirus and is called Rubulavirus. It spreads from one person to another rapidly. The virus enters the body through the respiratory tract and travels to the salivary gland where it starts multiplying, causing swelling and inflammation.
Prevention of Mumps
Immunity against mumps develops either when you get an infection or are vaccinated.
Safe and effective vaccines against mumps have been around since 1960s and have successfully brought down the infection rate.
The vaccine is generally given in the combined form, along with measles and rubella and is known as MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine.
The first dose of the vaccine is given to a child when he is 12 to 15 months old and the second booster dose is given at the age of 4 to 6 years. However, if the second dose is missed, it can be given again when the child is 11-12 years old. There is no age barrier for adults to get vaccinated.
The vaccine generally shows no side-effects but mild fever or rashes can develop in some children. Some people (generally adults) can also observe joint pain for a short duration after vaccination. It should be noted that you will not get mumps from the vaccine itself.
Another vaccine known as MMRV (measles, mumps, rubella and varicella) can be given to children when they are in the age group of 12-15 months to protect them from mumps, measles, German measles and chicken pox. [1]
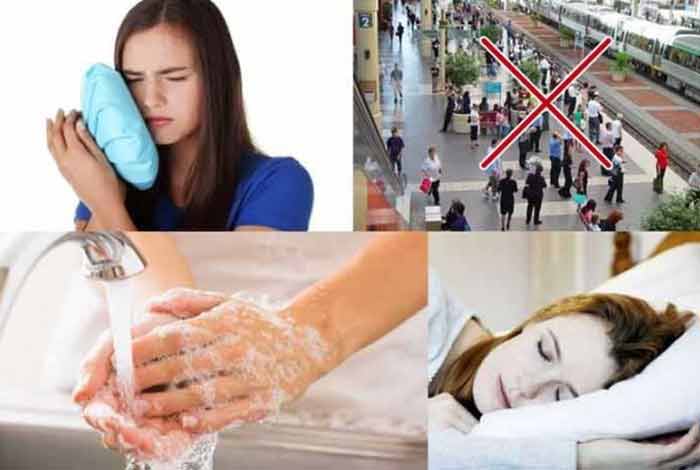
If a person is suffering from mumps, following measures can be undertaken to prevent spread of virus to other people:
- Frequent washing of hands with soap and water
- Cover mouth and nose with tissue while sneezing or coughing
- Absence from school or work

Diagnosis and Tests of Mumps
If there is any indication that a person has mumps, the doctor will perform a physical examination of the patient. He will look out for any swelling under cheeks, position of tonsils and body temperature.
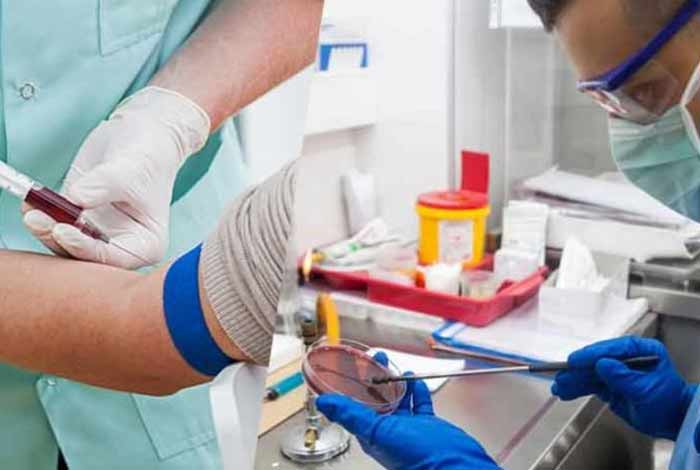
Besides physical examination, doctor can suggest a number of other tests for accurate diagnosis of mumps. These tests include:
Blood Test
Blood tests can be done to check for the presence of antibodies in blood against mumps virus. These antibodies are proteins that are made by our bodies to fight against the virus. If these antibodies are found in the sample, it confirms diagnosis of mumps.
Viral culture
A viral culture can be performed by taking a sample of urine or saliva and examining it for the presence of virus. A sample from CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) can also be used for testing the viral culture.
Treatment and Care of Mumps
Mumps can be treated by allowing the body to fight the disease. No medicines are available to treat the disease. Since the disease is caused by viral infection, antibiotics are not effective. The disease generally goes away in 1-2 weeks on its own. Some of the steps that the patient can take to speed up recovery process.
- Taking proper rest
- Drinking enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Caressing swollen area with cool or warm compress.
- Taking painkillers to get relief from the pain
- Eating foods that do not require a lot of chewing

OTC Medication and Self-Management Methods of Mumps
There are no over-the-counter medications available for treating mumps but the pain and swelling can be controlled with the help of painkillers like paracetamol and ibuprofen. Aspirin should not be given to children below the age of 16 years as it can cause a rare but serious health condition called Reye’s syndrome.
Mumps is an extremely infectious disease and therefore it is important to make sure that it does not spread to people who take care of the patient or to other people who come in close contact with the patient. The patient can make sure that he does not spread the virus to others by following some precautionary measures:
- Covering your mouth with tissue while coughing or sneezing
- Avoiding touching your mouth or nose with bare hands and then touching other inanimate objects
- Getting in close contact with a healthy person
- Going out in public when the symptoms are still there
The patient should take the following steps to manage the disease and speed up healing process:
- Take proper rest
- Avoid public places
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Use hot/cool compress to the swelled region to ease pain and inflammation
- Take healthy diet
- Avoid foods that require a lot of chewing
- Do not take any medicines without consulting with the doctor first.
- Wash your hands properly before eating.

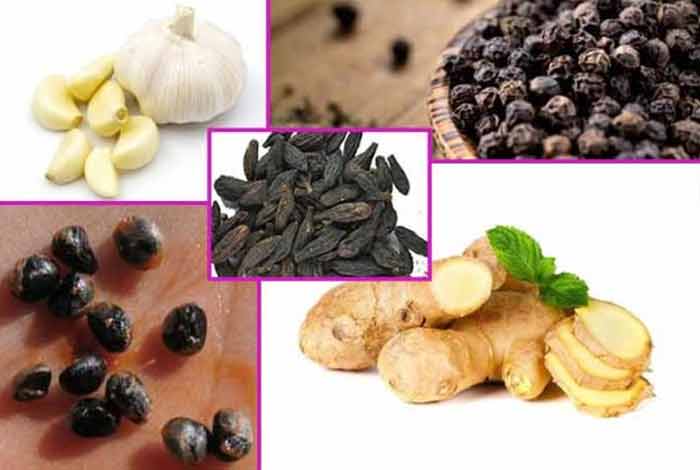
Natural Treatment of Mumps
As there are no medicines available to manage the condition, the patient can try some of the below mentioned home remedies for relief and quick recovery from the disease:
- Chebulic Myrobalan or commonly known as Ink fruit has antibiotic and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be mixed with water to make a paste, which, when applied on the skin can help in getting relief from the pain caused by mumps.
- Sacred Fig or commonly known as peepal leaves are effective for the treatment of mumps. The leaves are first coated with ghee/oil and then warmed-over fire. After this, the leaves are applied to the inflamed area and can help in the treatment of inflammation caused by mumps.
- Ginger can either be consumed directly or can be made into paste by drying and powdering its roots and applied to the inflamed area. It has anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties that can help in treating inflammation caused by mumps infection.
- Black Pepper can also be made into paste and applied on inflamed areas to treat mumps.
- Asparagus seeds can be used along with Fenugreek seeds. These seeds can be mixed with water to form a paste that can help in treating the inflammation caused by mumps.
- Banyan Leaves when coated with ghee/oil and warmed with fire and applied on the swollen portion of the face, can help in treating the pain caused by mumps.
- Carrot juice along with pineapple and grape juice is an effective home remedy to treat mumps naturally
- Garlic is effective in reducing the pain caused by mumps. Just crush a few cloves of garlic and apply it on the swollen part for effective treatment of pain.
Health Tip by Experts
Mumps is a disease that can be prevented through proper vaccination. If you still get the disease, do not worry. Just take rest and consume lots of fluid and believe that this too shall pass.



