Overview and Statistical Facts of Bursitis
Bones make the framework of the body and help in movement. When bones move, friction occurs between bone and the surrounding soft tissues like muscles, skin, ligaments and tendons. In order to reduce the amount of friction between the bones and soft tissues, nature has provided thin, lubricated cushions at these points that are filled with tiny amounts of fluid in it, called synovial fluid. These structures are called bursae. These structures lie wedged between the bone and the opposing surface like tiny water filled balloons and reduced friction. In an adult body, there are about 160 bursae, which vary in shape and size depending on their location. Some of these structures are present from birth while others develop later in life, depending on the nature of physical activity endured by the person.
When repetitive minor injuries keep on happening around the bursa, it gets inflamed and results in a painful condition known as bursitis. It can be treated at home and the condition usually goes away in a few weeks on its own.
Bursitis can happen to anyone, anytime. People whose jobs or hobby requires repetitive movements of joints are at a higher risk of developing the disorder than other people. Sports person, housemaids and clergy men are at a higher risk of developing the disease. According to the statistics, about 32 out of every 100 people are known to be affected by bursitis.
Types and Symptoms of Bursitis
Although bursa(e) of any region can become inflamed and cause bursitis, there are some regions of the body that are more prone to develop bursitis than others:
Types Of Bursitis
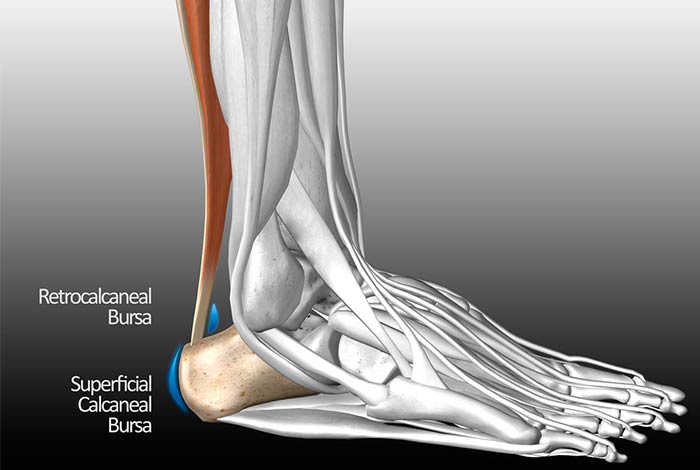
1. Anterior Achilles Tendon bursitis
Also known as Albert’s disease, this type of bursitis occurs when there is extra strain on the Achilles tendon due to disease, injury or by wearing shoes of hard soles. In this condition, the bursa located in front of the attachment of tendons to heel becomes inflamed.
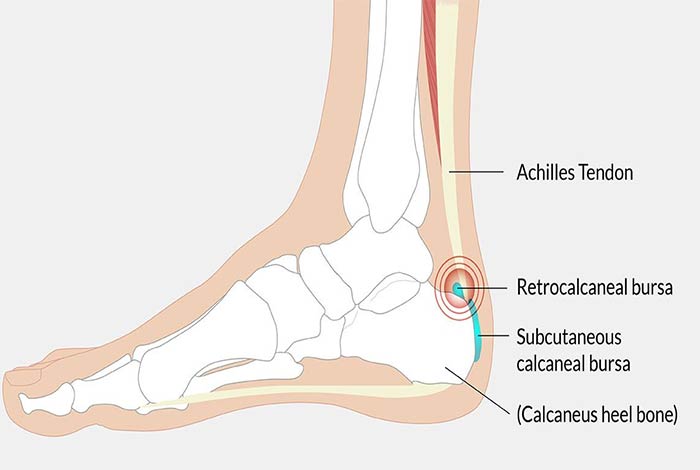
2. Posterior Achilles Tendon Bursitis
When inflammation occurs in the bursa located between Achilles tendon and the skin of the heel, posterior Achilles tendon bursitis occurs which is also known as Haglund’s deformity. It is aggravated by a particular style of walking in which the soft heel tissue is pressed against the hard shoe sole. It is commonly seen in young women.
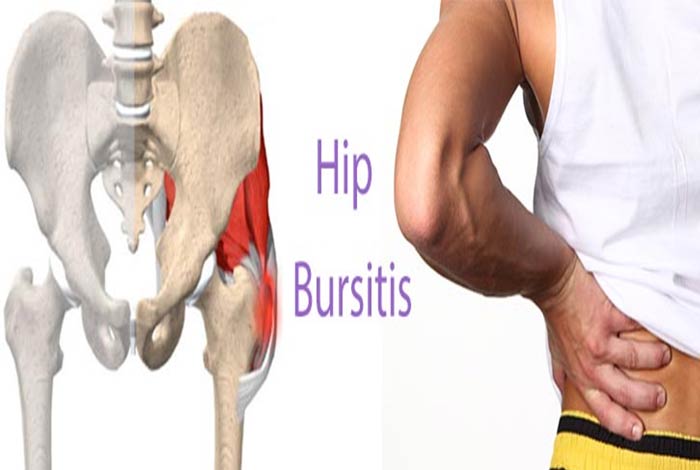
3. Hip Bursitis
Injury, arthritis, overuse, spinal abnormalities and surgery often result in hip bursitis, also known as trochanteric bursitis. It is commonly found in women, middle-aged and older people.
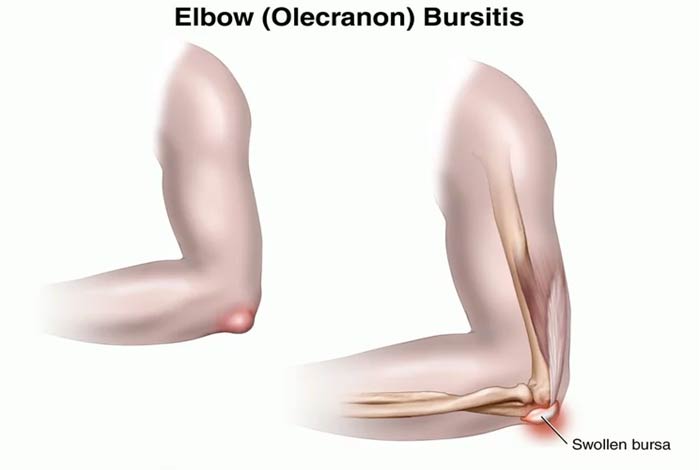
4. Elbow Bursitis
Inflammation of the olecranon bursa which is located between the bones of elbow and skin leads to the development of elbow bursitis. It is triggered due to injury and application of constant pressure on the elbow.
5. Knee Bursitis
Knee bursitis is also known as Pes Anserine bursitis or goosefoot bursitis. The Pes Anserine bursa is located between the three tendons of hamstring muscles and the shin bone on the inner side of the knee. Lacking of stretching before exercising, being overweight, tight hamstring muscles, arthritis and out-turning of knee or lower leg can result in knee bursitis.
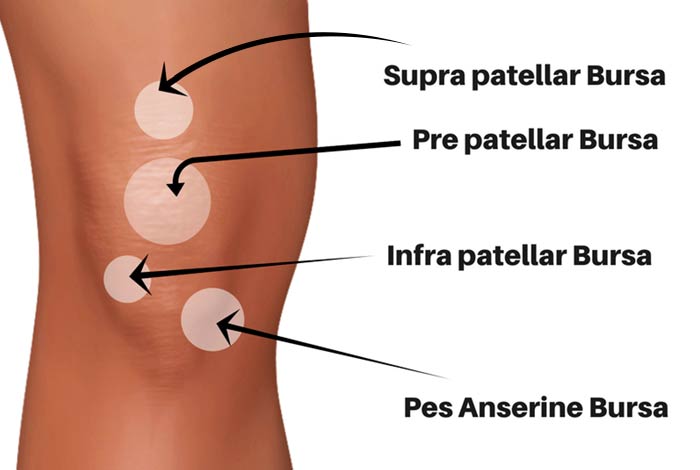
6. Kneecap Bursitis
Commonly seen in people who sit on their knees a lot like clergymen, carpet layers, plumbers and housemaids, there is inflammation in the kneecap, leading to kneecap bursitis or prepatellar bursitis.
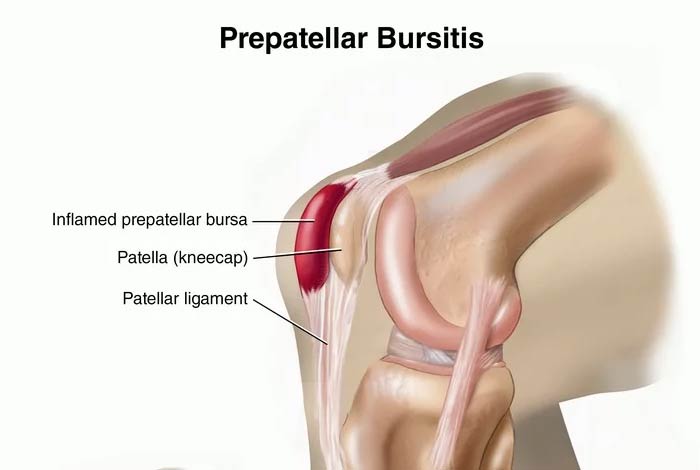
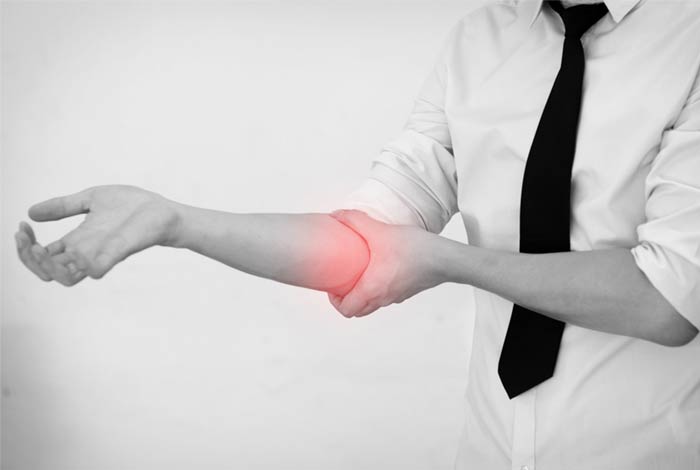
Symptoms of Bursitis
Every individual is prone to develop different symptoms of bursitis. Some of the commonly observed symptoms of bursitis include:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Localized tenderness
- Limited motion of affected area
- Swelling and redness if the bursa is close to the skin surfaces
If a person develops chronic bursitis, following symptoms are observed:
- Repeated attacks of painting
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Deterioration of muscles
- Limited range of motion

Risk Factors of Bursitis
Some people are more at a risk of developing bursitis than other. Some of the factors that increase the probability of developing bursitis are as follows:
1. Age
With age, the probability of developing bursitis increases.
2. Occupation
If a person is involved in a hobby or occupation that involves repetitive motion or pressure on a specific bursa(e), there are chances of it becoming inflamed. Some of these activities include carpet laying, gardening, painting, tile setting and playing a musical instrument.
a. Tennis Elbow
People who play tennis are at a higher risk of developing bursitis as well as tendonitis due to repetitive bending of elbow.
b. Clergyman’s Knee
Repeated kneeling leads to inflammation of bursa in the knee region.
c. Repetitive Stretching
Repetitive stretching can result in bursitis of thighs.
d. Sitting on Hard Surfaces for Long Time
Sitting for long hours on hard surfaces can lead to inflammation of bursae of buttocks and is commonly seen in cyclists and people who have a sitting job.
e. Excessive Running
Runners and sprinters are at a risk of developing hips bursitis.
3. Other Medical Condition
Some of the other medical conditions can also lead to bursitis are rheumatoid arthritis, gout and scleroderma.
4. Wrong Shoes
Wearing wrong shoes can lead to ankle injuries which is common in people who walk too much like athletes and ice skaters.
5. Injury
A hard blow to any joint area can result in bursitis in that area.
6. Infection
People who have a weakened immune system like those suffering from HIV/AIDS or those receiving chemotherapy or radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer and chronic alcoholics are at a higher risk of developing infection in the bursa.

Do I Have Bursitis?
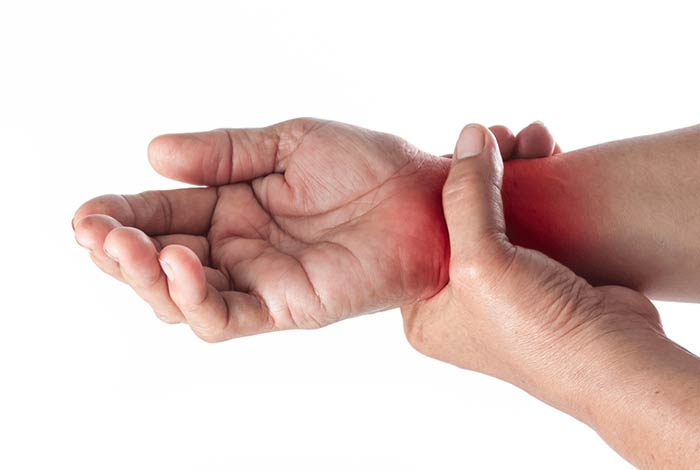
Bursitis occurs when there is an inflammation in the fluid filled sacs (bursa) that cushion the joints. There is a probability you might have bursitis if one of your join becomes:
- painful, which is a dull, achy pain
- warn or tender
- red and swollen
- extremely painful when pressed or moved
Although bursitis can occur in any joints, the most commonly affected joints are those of hips, shoulders, knees and elbows.
Causes and Prevention of Bursitis
Most common cause of bursitis is injury or repeated use that put excessive pressure on the bursae around a joint. Injury or trauma can also be one of the causes of bursitis. Inflammatory diseases like arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout can also result in bursitis.

Prevention from Bursitis
Although it is not always possible to save oneself from bursitis, precautionary measures can be taken to decrease the risks of developing bursitis. Some of the steps that can be taken to reduce the chances of a bursitis flare up are given below:
1. Use of Kneeling Pad
If the job requires frequent kneeling, some type of padding should be used in order to reduce the pressure on the knees.
2. Proper lifting of Objects
While lifting objects, knees should be bent in order to reduce the stress on the hips, thereby preventing hips bursae.
3. Heavy Loads Should Be Wheeled Away
People should not try to lift and carry heavy loads. Rather, they should be wheeled away. Carrying heavy loads puts excessive pressure on the shoulders and can cause shoulder bursitis.
4. Frequent Breaks
While doing strenuous activities, frequent breaks should be taken to give rest to the joints.
5. Healthy Weight Management
If the person is overweight or obese, the extra weight puts a lot of strain on the joints and therefore can result in bursitis.
6. Regular Exercise
Regular exercise stretches the muscles and helps in protecting the affected joint. However, when the condition is flared up, people should abstain from exercising.
7. Warm up and Stretch Before Strenuous Activity
Before doing any strenuous activity, people should get warm up and stretch in order to protect their joints from getting injured.

Diagnosis and Tests of Bursitis
Diagnosis of bursitis involves taking a complete medical history and performing an extensive physical examination. In most of the cases, bursitis gets diagnosed at this step alone. However, in some case, specific tests might need to be performed. These tests include:
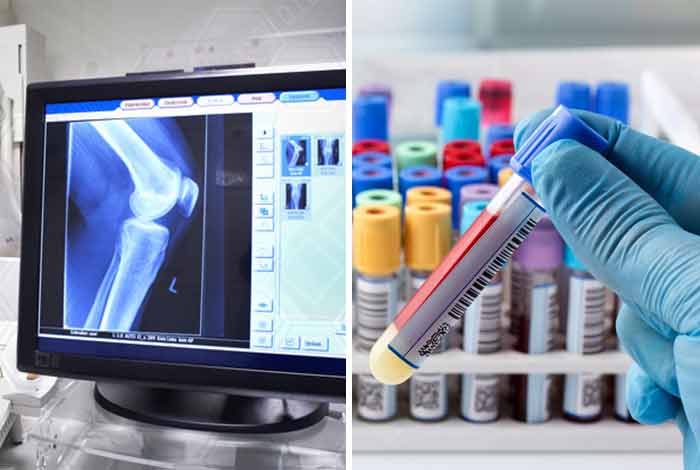
Imaging Tests
X ray images often fail in diagnosing bursitis but they can help in excluding other reasons that might be thought to cause the symptoms. If bursitis cannot be diagnosed easily, MRI or ultrasound can be performed. CT scan or MRI can be done to look out for a torn tendon.
Lab Tests
Blood tests or fluid analysis from bursa might be done in order to determine the exact cause of inflammation and pain of joints. Bursitis caused due to infection might be determined through fluid test.
Treatment and Care of Bursitis
There are a number of ways in which bursitis can be treated, including:
- Avoiding activities that can aggravate the situation
- Giving rest to the affected area
- Icing the affected area immediately after injury
- Protecting the affected area against further injury or damage
- Compressions can be applied in the form of elastic dressing
- Electric stimulation involving ultrasonography and phonophoresis can be done of the affected area
Medicines
Some of the medicines that can be taken in order to treat the condition are iven below:
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used for decreasing inflammation and pain. Although different pain killers are prescribed for different people but generally the treatment begins by prescribing ibuprofen. Topical diclofenac is also available that can be applied topically on the affected area for relief.
Some of the other NSAIDs that are commonly prescribed include naproxen, ketoprofen, celecoxib and indomethacin.
2. Corticosteroids for Intrabursal Injections
Corticosteroids are known to have anti-inflammatory properties. They also alter the body’s immune system. Corticosteroid injections are directly given in the bursa for immediate action. Hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone and dexamethasone are commonly prescribed for intrabursal injection.
3. Antibiotics
If bursitis is due to infection, antibiotics can be prescribed according to the infecting organism. For this, the fluid of the bursa is tested in the laboratory. In more than 80% of the cases, Staphylococcus aureus is the infecting organism. ABursitisppropriate antibiotics are then prescribed for treating the condition, such as oxacillin, cefazolin, vancomycin, cloxacillin and gentamicin. The duration of antibiotic treatment depends on the organism and the severity of condition.
Surgical Drainage and Excision
Generally, bursitis does not require surgical treatment but in some of the severe cases, surgical intervention might be required. These interventions include:
- Incision and drainage of bursa
- Excision of chronically inflamed bursa
- Removal of underlying bony structures
In case of severe bursitis, the bursa becomes attached leading to a condition known as adhesive bursitis. The adhered bursae are surgically removed.

Care of Bursitis
If a person is prone to developing bursitis, there are a few things he can take care of to avoid his bursae from getting inflamed. Also, if the person already has bursitis, these steps can help in decreasing the symptoms:
Maintain a healthy weight. If the person is overweight or obese, there will be extra weight on his bursa, making it prone to bursitis.
Any cuts or bruises at the site of inflammation should be cleaned properly to avoid infection.
Extra padding and cushion should be applied to the joints for protection against further injuries.Frequent joint movement without taking adequate breaks in between should be avoided.
OTC Medication and Self Management Methods Available for Managing Bursitis
Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are available over-the-counter in most of the pharmacies. Ibuprofen is the most commonly used OTC drug used for treating the symptoms of bursitis. However, medical advise must be taken before taking any drugs.
Self Management of Bursitis
Bursitis can be easily managed at home. Patient can take the following steps to decrease the swelling and pain:
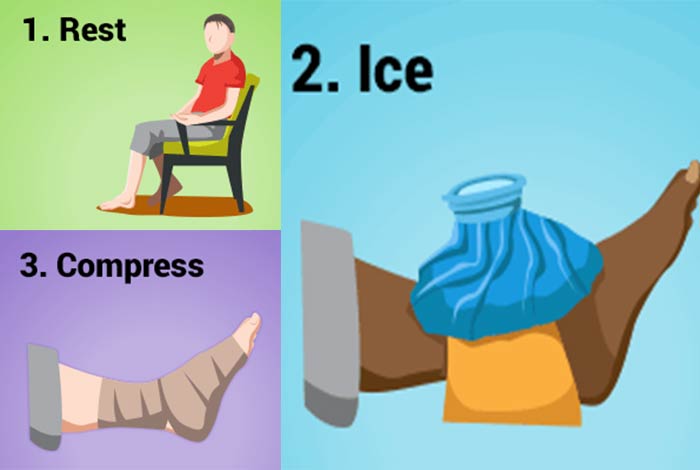
1. Rest
The affected joint should be provided with adequate rest and movement should be avoided, as much as possible. Activities that put pressure on the joint should not be done.
2. Ice
An ice pack wrapped in a tea towel can be placed over the affected area for nearly 10 minutes at a time. This activity can be repeated for a few time throughout the year.
3. Elevate
The affected joint should be kept raised above the heart levels as much as possible.
Painkillers can be taken to manage pain and also to decrease inflammation. Extra cushions might be kept around the affected joint in order to support and protect it.
Natural Ways to Cure Bursitis
Bursitis can be treated with the help of herbs and other commonly available ingredients. Some of these are given below:
1. Castor Oil
Castor oil helps in reducing pain and inflammation in the joints due to the presence of ricin oleic acid. It also helps in improving the mobility of joints.
2. Ginger
Ginger is known to possess natural pain relieving and anti- inflammatory properties. It also helps in promoting proper blood circulation in the affected area that promotes quicker healing.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is extremely helpful in relieving inflammation and can provide instant relief from bursitis.
4. Pineapple
An enzyme bromelain present in pineapples brings down inflammation extremely quickly and relieve the symptoms of bursitis.
5. Orange Juice
Vitamin C is known to have antioxidant properties which helps in speeding up the recovery process.

Health Tip by Experts
Bursitis can sometimes the speed of your life but do not worry. Give it a little rest, if required take some anti inflammatory drugs and you will be ready to chase the goals of your life again.