Introduction
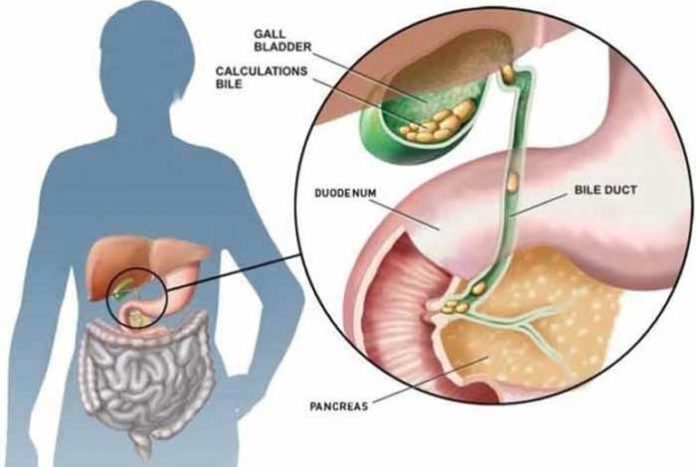
Gallbladder is a small pouch shaped organ located in the abdomen, whose main function is to store bile secreted by the liver and release it at the time of need. Bile is a dark green to yellowish-brown colored fluid that helps in digesting fat. It is composed of bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, bilirubin and others. When there is food in the digestive tract, the body signals the gall bladder to release bile for aiding digestion of fat. Before meals, gallbladder is completely inflated and after meals, it looks like a deflated balloon.
The cholesterol and bile pigments in the bile can sometimes get concentrated and result in the formation of stone like structures, known as gallstones or calculi and the condition is known as cholelithiasis. In approximately 90% of the cases, cholesterol is the major component of gallstones, but they can also be made up of bile pigments. Their size can range from sand grain to golf ball. They can be single or many.
There are four stages of cholelithiasis, namely
1. Lithogenic Stage,a phase in which gallstone formation is favored.
2. Asymptomatic Gallstones , during which the gallstones are dormant and do not produce any symptoms.
3. Symptomatic Gallstones , in which gallstones produce symptoms like biliary colic.
4. Complicated Cholelithiasis, a stage in which complications arise due to blockage of various ducts supplying bile and pancreatic juice to the small intestine. This stage requires immediate medical attention.
Surgery is generally the preferred treatment option in which the gallbladder is completely removed from the system. The surgery done to remove the gallbladder is known as cholecystectomy. A person can lead a normal life without a gallbladder. A person with asymptomatic gallstones does not require any treatment. However, there are chances of gallstones developing symptoms in the future.
Women are more prone to develop gallstones than men. They are more likely to cause complications in elderly and men than in women. Most of the people are unaware that they have gallstones until they become symptomatic. In the U.S.A., approximately 20% people suffer from gallstones but only 1-3% of these people develop symptoms.
Condition and Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones are generally without symptoms. But, they can develop the following symptoms when they block a duct:
- Biliary colic
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Various digestive problems such as gas, bloating, indigestion, etc.
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
- Diarrhea
Biliary colic is the most important symptom of gallstone, in which extreme pain is observed in the upper abdomen, which can sometimes radiate up to upper back, between the shoulder blades. This is the Collin’s sign of biliary colic. Generally, the pain is experienced after consuming a fat rich diet. It is intense and dull and can last for 1-5 hours. After its onset, the pain steadily increases every 10-20 and stops when the gallbladder stops contracting. The pain experienced is constant in nature and no relief is provided by emesis, antacids,faltus, defecation or positional change.
Treatment of Gallstones
The stage of disease dictates the course of treatment. If the treatment is started at the stage when the gallstones are in the seeding stage, its formation can be inhibited and the gallbladder can be saved as well. However, detecting gallstones at such an early stage is extremely difficult. As soon as the gallstones start showing symptoms, surgical removal of gallbladder is the only treatment option. Surgery can be minimally invasive (laparoscopic) or open. The following characteristics of the gallstones are evaluated before proceeding with the minimally invasive surgery:
- Size: Less than 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter
- Good gallbladder function
- Minimal to no calcification
Open surgery has become obsolete in the recent times. It is only performed if there is any complication or, if the hospital or the surgeon is not equipped to perform the surgery.
Treating gallstones through non-surgical measures is not very popular because it does not guarantee permanent solution of the problem. There is a high probability of recurrence of gallstones. It is generally prescribed in the patients who cannot undergo surgery or in those who do not want to have a surgery.
Non-Surgical/Medical Treatment
Treating gallstones with medicines or non-surgical methods is not generally prescribed unless surgery is contra-indicated. In order to proceed with a non-surgical treatment plan, following characteristics of the gallstones should be met:
- Good gallbladder function
- Have gallstones that are less than 1 cm in diameter
- Have non-calcified gallstones
- Have gallstones with high cholesterol content Medical treatment for gallstones include the following therapies, alone or in combination:
- Oral Dissolution Therapy
In this therapy, medicines are prescribed that reduce the content of cholesterol in the bile. This is achieved by decreasing the secretion of cholesterol by the liver and detergent effect of bile salts in bile. When the concentration of cholesterol is decreased in the bile, further formation of gallstones is inhibited. This might even promote dissolution of cholesterol from the stones into bile.
It takes about 6-18 months to fully show its effect. The prerequisite criteria for this therapy to show its effect is that the stones should be small in size, fewer in number and should be composed entirely of cholesterol.
This therapy does not guarantee permanent cure and the recurrence rate is as high 50% within 5 years.
Available as: Tablet and Capsule
Generic Name: ursodiol
Brand Name: Actigall
U.S. FDA Status: Approved
Availability: Prescription
Dosage Form: Capsule
Indicated in Pregnancy: No, unless
Alcohol Content: Absent
Side Effects: Back pain, alopecia, arthritis, bladder pain, dizziness, indigestion, skin rash, vomiting and weakness
Other non-surgical methods for treating gallstones are contact dissolution therapy, lithotropy and percutaneous cholecystostomy.
OTC Drugs for Gallstones
There are no OTC drugs available for Gall Stones. Even the regular painkillers don’t work for this condition. Contact a doctor as soon as possible.
There are no over-the counter drugs available for treating gallstone