Overview and Facts:
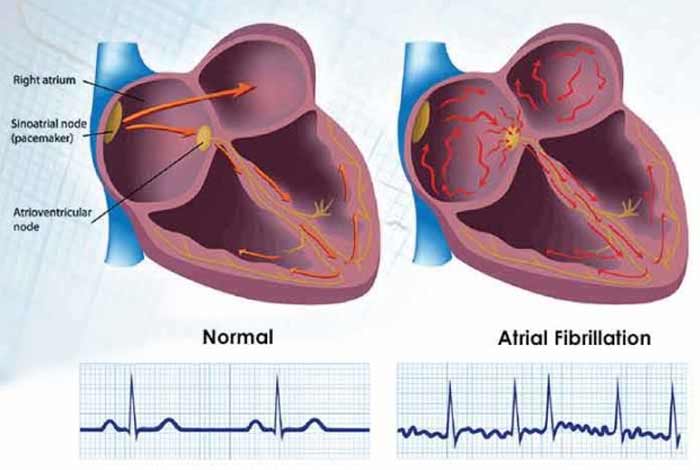
Heart is an essential organ, which is responsible for blood flow in the body. There are four chambers in the heart – two upper chambers, called atria and two lower chambers, known as ventricles.
In atrial fibrillation, the atria of the heart start beating in a discontinuous manner. They start working without being in coordination with the ventricles, which results in irregular beating of heart. Irregular and rapid heart rate poses risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related conditions. Arrhythmia is another term for atrial fibrillation in which the heart beats at a faster rate than normal.
Common symptoms of atrial fibrillation include heart palpitation, breathing shortness and weakness, among others.
Atrial fibrillation is not compulsorily a permanent issue; it can come and go. But, if it remains for a longer duration, then there is a need for its treatment. Although atrial fibrillation is not a life-threatening issue, it is still a serious health problem that require instant treatment.
A major complication associated with atrial fibrillation is blood clotting in the heart that results in restricted blood flow or ischemia. Blood clots may also affect the brain and might lead to stroke.
Some treatment methods available for the issue are medication and other methods to control the heart’s electrical system.
People with certain health problems are at a higher risk of developing the condition of atrial fibrillation. These health conditions include high blood pressure, heart valve diseases, heart muscle diseases, heart surgeries in the past, lung disease for longer duration, highly active thyroid gland, sleep apnea, etc. Mostly, people, aged over 60, are at greater risk of atrial fibrillation in comparison to others.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation:
Atrial Fibrillation has no visible symptoms; thus, people remain unconcerned about the problem. Usually, people learn about their problem of atrial fibrillation only after the physical examination. However, people at times experience some signs before knowing about their problem. These include:
- Palpitation
- Breathing shortness
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Chest Pain
People, who experience these symptoms, must consult a cardiologist immediately. Hospitalization of the person is necessary, if the conditions last for more than 24 hours.
Atrial fibrillation may sometime be occasional (when symptoms come and go back, and last for only a few minutes); persistent (when a heartbeat doesn’t go back to the normal state on its own); long-standing persistent (when the conditions remain for more than 12 months); and permanent (atrial fibrillation is permanent, and cannot be restored to normal state).

Risk Factors of Atrial Fibrillation:
Atrial fibrillation is associated with several risk factors. There are some factors that enhances the risk of developing atrial fibrillation. These include:
- Coronary heart Disease
- High blood pressure
- Rheumatic heart diseases
- Pericarditis
- Heart failure
- Congenital heart diseases
- Obesity
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diabetes
- High amount of alcohol intake
- Sleep apnea
- Genetic factors
Do I have Atrial Fibrillation?
There are several symptoms that are specific to atrial fibrillation like shortness of breath, weakness, lightheadedness, dizziness, palpitation, chest pain and so on.
However, there are several other diseases that exhibit similar symptoms. Diseases like asthma, coronary artery diseases, heart attack, heart valve disease, heart failure have almost similar symptoms. Thus, considering such common symptoms as a sign of confirmation for the existence of a particular disease is not advised.
Instead, consult a doctor or specialist when any of the above symptoms occurs. Self-diagnosis is not a good option in any case as this might aggravate the condition of not properly diagnosed on time.
Causes and Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation:
1. Causes of Atrial Fibrillation:
The most common cause of atrial fibrillation is any kind of abnormalities or damage to the structure of the heart. Some possible causes of atrial fibrillation include heart attacks due to high blood pressure. Existing coronary artery heart diseases and sometimes, congenital heart defects can also become a causative factor. Metabolic imbalance, especially in thyroid gland may result in atrial fibrillation. Abnormality in the heart valves and heart surgery in the past may also affect the heart structure. In some cases, lung infections, viral infections and stimulants are the causative agents. Stress may also be a factor that could lead to atrial fibrillation.

2. Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation:
To reduce the risk of atrial fibrillation, certain measures could be taken. These preventive measures include:
- Take a heart-friendly diet
- Smoking must be avoided
- Regulate body weight
- Increase workout duration
- Avoid or restrict consumption of alcohol or caffeine
- Reduce mental stress and take adequate sleep
Diagnosis and Tests of Atrial Fibrillation:
The initial diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is done on the basis of family medical history, signs and symptoms, and finally, with a physical examination. In fact, there are some techniques that are generally used by doctors for the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation, viz., electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor and event recorder.
Treatment and Care of Atrial Fibrillation:
There are different treatment methods available for treating the symptoms of this condition as well as severe atrial fibrillation conditions. Some common treatment approaches to treat atrial fibrillation are medications, nonsurgical procedures and surgery. These help in slowing down the heart beat and bringing back the normal rhythm of the heart.
- Medications: Medicines help control the heart rate, heart rhythm and clot formation. Different types of medications are heart-rate controlling medicines (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, etc.); heart-rhythm controlling medicines (sodium and potassium channel blockers); and blood thinners (prevents clotting; heparin, aspirin, warfarin, etc.).
- Non-Surgical Procedures: In cases when medicines fail to control the heart rate or rhythm, doctors prefer certain procedures. These procedures are collectively known as cardioversion or ablation. These constitute nonsurgical treatment of atrial fibrillation.
- Surgery: When medication fails, and a person is in severe state, then surgical treatments are used. The most-common surgical methods are left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion and maze procedure.
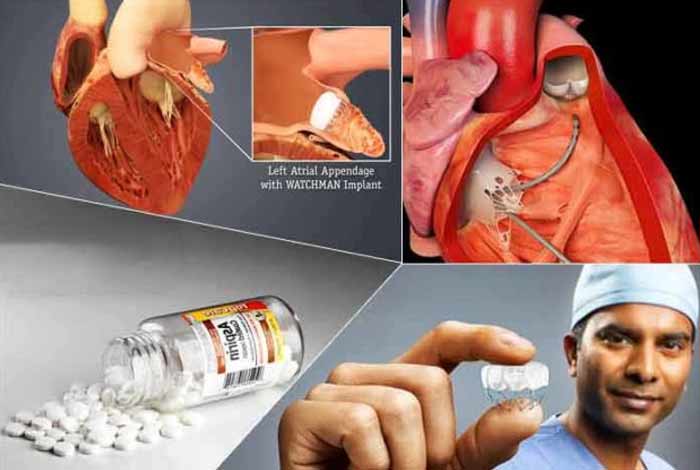
OTC Medications and Self-Management Methods of Atrial Fibrillation:
Atrial fibrillation is treated with some specific medicines that fall under the category of prescription drugs. However, one can reduce the symptoms and prevent factors that contribute to this heart condition. Occasionally, one can consume aspirin that reduces inflammation – a contributing factor to atrial fibrillation. While this can relieve you from the symptoms to some extent, a doctor’s advice is always recommended before consuming any drug.
Some supplements are also known to have antiarrhythmic, detoxification and anti-inflammatory effects. Omega-3 fish oil, vitamins C, D and E, coenzyme Q10, hawthorn berry, Chinese herb wenxin keli among others are a few dietary supplements that can help prevent and reduce the symptoms of this condition.
The best way to treat or cure any disease is to take some measures to prevent the disease. Some of the self-management methods that an atrial fibrillation patient can follow that include measures to prevent stroke and assessing the symptoms to control the heart rhythm. Stress management and routine exercise can also help manage and prevent atrial fibrillation.
Natural Ways to Treat Atrial Fibrillation:
Some natural yet effective ways to prevent atrial fibrillation are listed below:
- Avoid the consumption of food containing caffeine and chocolate.
- Quit smoking
- Take a protein-rich diet that includes lean meat, salmon, walnuts and so forth.
- Sufficient amount of vitamin K is recommended for a healthy heart. Consume foods like asparagus, banana, celery, cauliflower, green beans, avocado, broccoli, kiwi, green tea and olive oil that are rich in vitamin K. The diet portion of vitamin K must be in moderate amount.
- Increase water and fluid consumption, especially coconut water.
- Avoid consumption of alcohol to help reduce the risk for atrial fibrillation.
- For avoiding risk of atrial fibrillation, gluten-rich foods can be eliminated from one’s daily diet.
Health Tip by Expert:
Having a healthy diet is an important way of managing atrial fibrillation. It’s good to discuss with your healthcare provider for diet, especially those, who are on blood thinners.